Chapter 1 Atmosphere Study Guide
advertisement

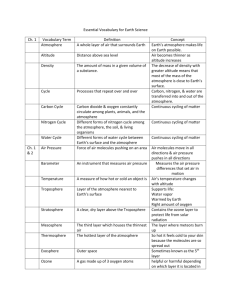
“Chapter 1 Atmosphere Study Guide” Shane McMullen 12-5-13 Oxygen is 21% of Earth’s atmosphere Water in the form of a gas is called Water vapor Oxygen is 21% of the gases in dry air A process that uses oxygen in fire burning The atmosphere is always because the amount of vapor varies from place to place The envelope of gases that surrounds Earth is the atmosphere Because air has mass, it has density and pressure An instrument that is used to measure air pressure is a barometer Two different units used to measure air pressure are inches of mercury and millibars Another word for elevation, or distance above sea level, is altitude Air pressure decreases as altitude increases As air pressure decreases, so does air density Air pressure is greater at sea level than on top of a mountain because air pressure at sea level has the weight of the whole atmosphere pushing on it As altitude increases, air density decreases The amount of oxygen in each breath is less at high altitudes Altitude is greater at point A Air pressure is greater at point B Density of the air is greater at point B A cubic meter of air has less mass at point A The percentage of oxygen in the air at point A is about 21% The distance above sea level is altitude An instrument that measures air pressure is a barometer The amount of mass in a given volume of air is density Layer of Atmosphere: Troposphere: weather occurs here Stratosphere: ozone layer Mesosphere: stops meteoroids Thermosphere: 2 layers ionosphere, exosphere- Northern Lights Temperatures generally rise as altitude increases in the Stratosphere and Thermosphere Harmful substances in the air, water, or soil are known as pollutants Some natural sources of particles in the atmosphere is dust, smoke, and chemicals Photochemical smog is caused by the action of sunlight on chemicals Rain that contains more acid than normal is known as acid rain Air quality in this country has generally improved ove the past 30 years