Name: Date: Feudalism Chapter 15, section 2 pages 522
advertisement

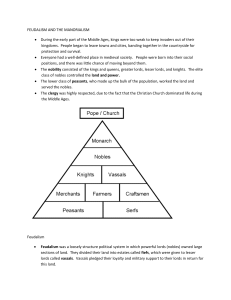
Name:_________________________________ Date:_______________ Feudalism Chapter 15, section 2 pages 522-531 Focusing on the Main idea: I. Feudalism developed in Europe in the Middle Ages. It was based on landowning, loyality, and the power of armored knights on horseback. Knights followed a code of chivalry and lived in castles, while peasants lived in simple houses and worked hard all year long. Increased trade led to the growth of towns and cities sand the rise of guilds and city governments. What is Feudalism? A. Who can be known as the father of feudalism? (who started feudalism?) Charles Martel B. After Charlemagne’s empire collapsed, what happened? Europe lost its strong central government. Landowning nobles became more powerful and collected taxes and enforced laws on their estates. Nobles governed and protected people in return for a service Peasants could not rely on kings, they relied on nobles for protection The shift of power is known as feudalism C. Feudalism- Was based on loyalty and duty among nobles, peasants and knights. D. Vassal- A noble who served a lord of higher rank in return the lord protected the vassal. E. How did a vassal show loyalty? The knights showed loyalty by serving in the army. F. Fief- The land the lord granted to the vassal for military service and loyality G. Knights- They are warrior in armor who fought on horseback. They were vassals. II. What Was the manorial System? A. Serfs- Peasants who could not leave the manor, own property or marry without the lords approval. 1. Most peasants were serfs. 2. Serfs were not considered “enslaved” because lords could not sell the serfs or take away the land given to serfs, providing them the safety they needed to grow crops 3. Serfs worked long hours on the lord’s land and performed services for the lord. 4. They spent three days working for the lord and the rest of the week for themselves. 5. Not easy for serfs to gain their freedom. One way was to run away to the town. If a serf remained in town for more than a year, he or she was considered free. 6. By the end of the Middle Ages, serfs in many kingdoms were also allowed to buy their freedom. III. How did Farming Improve? A. New technology invented1. Heavy wheeled plow with an Iron blade. 2. Horse collar 3. Watermills and grinding grains IV. Life in Feudal Europe A. Knights followed a code of chivalry and lived in castles, while peasants lived in simple houses and worked hard all year long. How Did Nobles Live? A. Knights the Code of Chivalry-guide for good behavior, knights had to obey his lord, be brave, to show respect to women of noble birth, to honor the church, and to help poor people, to be honest and to fight fairly against his enemies. B. Castles-surrounded by a mote a bailey-open space surrounding mote, walls V. What was peasant Life Like? A. The homes of peasants were much simpler. They lived in wood-frame cottages plastered with clay. B. Peasants worked year-round C. Peasants took a break from work and went to church on Catholic feast days. They celebrated more than 50 feast days each year. D. Peasant women worked in the fields and raised children at the same time. VI. Trade and Cities A. When the Roman Empire collapsed: almost all trade in Western Europe came to an end. 1. trade- increased and towns grew larger 2. Bridges and roads-nobles repaired bridges and roads 3. Most people lived- in villages B. Feudalism made life safer and new technology enabled people to produce more goods and food. C. As trade increased towns grew larger and several cities became wealthy from trade. D. Venice- (Italy) built a fleet of trading ships. E. Flanders-center of trade for northern Europe E. People of Italy and Flanders became VII. How Were Cities Governed? A. Towns were often located on land owned by lords. B. Townspeople wanted to make their own laws and were willing to pay for the right to make them. In exchange for paying taxes, people in towns were granted certain basic rights by their lords. C. Some basic rights by townspeople were the right to buy and sell property and the freedom from having to serve in the army. VIII. Crafts and Guilds A. Trade encouraged manufacturing: people made cloth, metal work, shoes and other goods right in their own houses. B. Guilds or business groups formed which created a new middle class in medieval Europe. C IX. What Was City Life Like? A. Narrow, winding streets B. Houses were crowded against one another and the second and third stories were built over the streets. C. Cities were often dirty and smelly