Daily Life in the Middle Ages (1000
advertisement

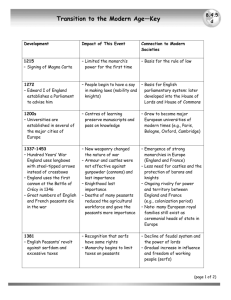
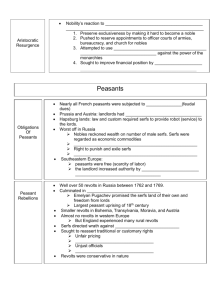
Daily Life in the Middle Ages (1000-1600) I. Rural Areas A. Nobility B. Peasants/Serfs II. Towns/Cities A. Size B. Industry III. Population Drops A. Why? 1. Food 2. Pestilence • • • • • Key Terms Feudalism Vassal/Knight Fief Guild System Black Death Traits of Feudalism (Social/Economic System of Middle Ages) • There was an absence of central authority & “Warlords” dominated. • People sought protection & unique relationship developed between landowners & commoners. • Common in much of Europe—but NOT in Pyrenees (French/Spanish border). Medieval Hierarchy • Monk (clergy) • Knight (noble) • Peasant Nobles (up to 5%) Clergy (5-10%) Peasants (85-90%) Nobility (They did NOT work the land) • Two “Types:” • Lords-usually wealthy landowners • Knights-the Warriors pledged to provide military service to a lord. Fief-Land (and serfs to work it) given to knights in return for military service. • Most were illiterate. Food For Nobles • Dominated by bread/porridge & meat (fish, chickens, pigs & wild game; rarely beef), dairy; beer was common. • Expensive imports: Middle Eastern exotic spices (sugar), wine from France. Peasants/Serfs • Made up 85-90% of the population. • They were tied to the land worked the land for the Lords & knights (50-500 on an estate). • In return they received: – Protection – A portion of the crops they raised (75-90%) • Contracts… Life On Medieval Manor (Nobles Hunt While Peasants Work; Castles vs. Huts) Daily Life in Middle Ages (fast forward 18 seconds) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pypbyC548dw Food & Life For Peasants/Serfs • Diet was VERY monotonous: black bread/porridge & beer were the staples; eggs & dairy (some fish, but not much meat) Famine = threat • Homes: one room, wooden sides, thatched roofs & one (large) bed • Daily routine was dominated by seasons & Christian celebrations Life For Peasants/Serfs • Women were subject to their husband’s authority Children • 30-50% of children died before reaching age 5 • Marriage Age: – Boys = 14 – Girls = 12 Dance of Death Preparing For Winter Baking bread & slaughtering pigs… Entertainment (A Harvest Festival Sponsored by Lord of Manor) Entertainment Cockfighting Taverns Entertainment (Marriage Ceremony) • Up to 1300s couples often waited for a pregnancy to hold a church service • Between 12th & 14th centuries “modern” church services were developed • Marriages were arranged Towns & Cities (Only 5% of population) • London: 10,000 (in 1200s) • Paris: 210,000 (in 1328) • Italy (in 1200s) – Florence: 100,000 – Milan: 90,000-100,000 Guild System (Origins of modern industry) • Guilds: A training/education system to ensure quality in the products produced. – Master: Shop-owner (if they had enough money & connections). – Journeymen: wage plus room & board. – Apprentice: worked for room & board with hope of advancement (seven years). – Unskilled Laborer: received room & board with little or no hope of advancement Master Journeymen Apprentice Unskilled Laborers Guild Workers Dyeing Cloth Population Drops • It is estimated that between 1300-1450 Europe lost 50-65% of its population. • Why? 1. Famine: between 1000-1300 population doubled, but food production didn’t. 2. Disease (Pestilence): Beginning in 1350 the “Black Death” spread & killed many. A Physician In A Plague-Protecting Suit Despair All Over Society Daily Life in the Middle Ages (1000-1600) I. Rural Areas A. Nobility B. Peasants/Serfs II. Towns/Cities A. Size B. Industry III. Population Drops A. Why? 1. Food 2. Pestilence • • • • • Key Terms Feudalism Vassal/Knight Fief Guild System Black Death