Lecture notes - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
advertisement

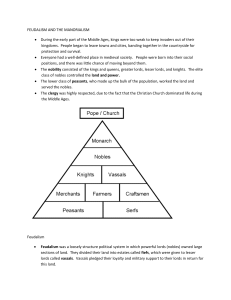
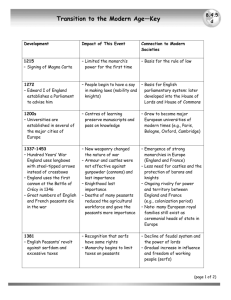
Feudalism – political system - monarch & nobles make alliances (land exchanged for loyalty and military aid*) Why begun? central government becomes weak * *Monarch (king) gives land/fief (and peasants/serfs) Nobles (counts & local officials) give loyalty and military aid Soldiers/knights Get land (called fiefs) and the income lets them buy horses and battle gear* Nobles can pass land/fief on to heir (sons) – land stays in family Pyramid/hierarchy King Lords /nobles Vassal (means each lord serves someone of higher rank) Knights Peasants/serfs (farmers, artisans*) Vassal’s pledge Military aid, # of knights, 40 – 60 days Serve in lord’s court Food/lodging Pay ransom Castle (need picture) Lots of warfare so 1st begun for protection/defense* Wood – stone w/ thick walls, towers (turrets) Hill/mound Moat, drawbridge (major defenses against invaders*) Keep (square building) Open area around keep (bailey) includes: barracks, storerooms, workshops, chapel Nobility: lords, ladies, knights Lord – total control; governs manor and castle* Collected rent from peasants (goods) Settled conflicts between vassals Noblewoman/lady – marries father’s choice Jobs – needlework, making medicines supervise estate* Tournaments (video) Mock battles (jousting, sword fighting) Minstrels (sing, storytelling) Knight training 7 – page (lord’s assistant) 15 – squire (help knight, learns to use weapons) Knight – prove self in battle, trained to fight on horseback* Code of chivalry: defend Christian church, be brave in battle, fight fair, treat noble women w/ gentleness* Manorial system – agricultural system – nobles/lords, serfs/peasants get food, shelter, & protection Nobles/lords give peasants protection, food, shelter Serfs/peasants give lord part of what they produce (satisfy lords material needs) Some days – laborers (repair roads/bridges) Farmers (most) Blacksmith, carpenters, shoemakers, millers, vinters, brewers Women – make candles, cloth, sew Serfs – bound to land, but not slaves (can’t be sold w/o land*) Manor/estate – manor house, fields, woods, village (peasants live) Increased agricultural production*: 1) PLOW – less time 2) new system of planting (3 fields vs 2, fallow field – left unplanted*) Manorial system summary – serfs/peasants get little freedom or opportunity, but they do get protection/security Medieval Church – spiritual, political, social leader in Europe Catholic Pope – authority over all Christians God’s grace earned by sacraments Service in Latin People couldn’t read – learned religion from statues, paintings, stained glass windows (photos) Organization: Pope, bishops, priests (secular – lived “in the world”) Monks, nuns – live monastic life * (life dedicated to God, apart from rest of society*) Monks – cannot own property or marry, must follow monastic rules (simple clothes, plain food, rule of silence) Nuns – convent, prayer and making things with hands Influence of church: Monks copy religious works and classical writings (preserved ancient knowledge & religious info alive when few could read/write*) Schools, hospitals, food for poor, place for travelers teach carpentry, weaving, farming missionaries – results? Mid 1000s most of western Europe is Christian Magna Carta (Great Charter) – limits absolute power of king*, some trace our Constitution to this document King John forced to sign it by his nobles Why nobles upset? King raised taxes & put enemies in jail w/o trial What does it do? Puts limits on power of king (no taxes w/o agreement of a council, freemen guaranteed right to trial by jury) Originally intended to guarantee rights for nobles, but it came to guarantee rights for all Englishmen