MID-TERM: 8 th GRADE WORLD HISTORY
advertisement

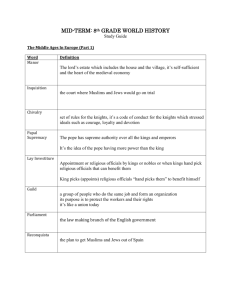
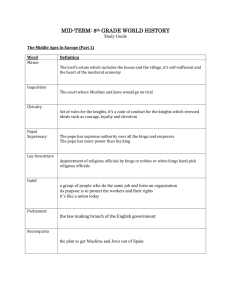
MID-TERM: 8th GRADE WORLD HISTORY Study Guide The Middle Ages In Europe (Part 1) What signaled the beginning of the Middle Ages? The fall or the decline of the Roman Empire Why did Germanic peoples invade the Roman Empire? To settle frontier regions for climate and land What term or words could best summarizes the legacy of the Roman Empire? “Great” law, government, architecture, language, engineering What regions of the world today are still strongly influenced by the achievements of Rome? Europe and the United States What was the feudal system based on? A system of mutual obligations “You do for me and I’ll go for you” Define the feudal contract. A contract between a greater lord and a lesser lord How would you describe a medieval serf? They are bound to the land so they can’t leave the lord’s estate and they can’t be bought or sold as they weren’t slaves Define a medieval manor. A self-sufficient unit How were feudalism and the manor system related? Feudalism was a social order and the manor system was the economic arrangement that supported it. What were the forces holding feudal society together? Mutual obligations and the Church According to the code of chivalry, who did a knight fight for? His earthly or feudal lord, his heavenly Lord and his lady What happened to the status of women during the Middle Ages? Women’s status improved slightly because of the Church Define Chivalry. A code of conduct or rules for knights to follow based on bravery, honor and courtesy Define papal supremacy. Pope has supreme authority over all kings and emperors Define Lay Investiture When the king hand picks or appoints church officials Define Guild An association of people who work as the same jobs and it protects the workers’ rights What was the chief goal of the Crusades? To get the Holy Land from the Muslim Turks What did the Magna Carta guarantee? Your basic legal rights What was the major cause of the Great Schism? Deciding who was the true pope What was the name of the legislative body of medieval England? Parliament What was the central issue of the Hundred Years War? Arguing over who was the king of France What was the most important effect of the Hundred Years War? A development of a national identity of England and France What was the purpose of the Reconquista? To drive the Muslims or non-Christians out of Spain Why did Science make little real progress in Europe during the Middle Ages? They thought that knowledge had to match Church teaching and science doesn’t Describe Gothic cathedral architecture. New style in the Age of Faith, pointed arches, high vaulted ceilings, stained glass windows, and sculpture What did the devastation caused by the bubonic plague contribute to? The end or decline of the Middle Ages The Crusades was a series of three holy wars fought between Christians and Muslims to recapture what city? Christians fighting Muslims for Jerusalem Why did The Middle Ages declined? The end of feudalism or the feudal system, black death, and the corruption in the church Define Inquisition. Court used in Spain to persecute non-Christians and Jews The Byzantine Empire, Russia and Eastern Europe ( Part 2) What was the capital of New Rome, or the Byzantine Empire? Constantinople Describe the city of Constantinople. Big in trade and merchants, Surrounded by a wall and water Due to its central location, it was able to connect Europe and Asia through trade What caused the split between the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church? Worshipping icons or idols rather than praying to God What was the body of civil law that was created for the Byzantine Empire? Justinian’s Code What was one of the most important contribution of the Byzantine Empire? The Greco/Roman or Greek and Christian culture What helped cause the decline of the Byzantine Empire? Justinian’s Plague or the Bubonic Plague Disruption of trade Mongol and Turks attacked Which titles did Ivan III use? Czar Describe the Mongol rule of medieval Russia Mongol use of absolute power After the Great Schism, the Byzantine church became known as what? Eastern Orthodox Church What civilizations most influenced the development of Russia? Byzantine and Mongols The Abbasids were rulers of what empire? Muslim The Seljuks converted to which religion? Islam The Rise of Islam ( Part 3) Islam is an Arabic word meaning what? Submit to God In what ways is Islam is similar to Judaism and Christianity? They are all monotheistic What do Muslims believe about Muhammad? That he’s the last great prophet What is the key difference between the Sunni and Shiites? How the leader or caliph should be chosen What division of Islam believes that only a relative of Muhammad is qualified to be a caliph? Shi’a What was the academic subject developed by al-Khwarizmi and originally called al-jabr ? Algebra Toward what city do Muslims pray? Mecca What are two important teachings that are common to all three faiths? They all believe in one God They all believe in life after death Short Answer Section ( Part 4) 1. Explain how the church shaped medieval life and society? Provide two examples. Page 370 chapter 13 section 4 Introduce the feudal system as a time where there was a weak central government, which gave the church more power. Points to include– The church was a social center in that it acted like a town hall The fear of excommunication as the church was the center of life you’d have no life. Define excommunication Mention and define papal supremacy – the pope held more power than the king or worldly powers Discuss church law or canon law – the church had a court and it provided laws Example of how you could answer this question: In Medieval society, the church was the social center. The church acted like the town hall where people would go for functions or meetings. The church also had its own set of religious laws called Canon Law as well as its own court. It’s these reasons that excommunication becomes the worst punishment of the time because you’re banned from church activities and society. 2. Define feudalism and explain how it helped to create the manor economy. Page 360 chapter 13 section 2 To start this answer you need to define feudalism, the manor system and then explain how they came together to create the manor economy. Part 1 – Feudalism definition– a social structure of medieval Europe that works on a system of mutual obligations Part 2 – Manor system definition – the lord’s estate and property, works on an economic arrangement Part 3 – Connect how they work together – The manor system was a self-sufficient unit where everyone works together and helps one another or “you help me I help you” which is the idea of the feudal contract which is between a greater lord and a lesser lord. Example of how you could answer this question: Feudalism is the social and government structure that helped shape medieval society. Feudalism is based on the idea of mutual obligations meaning “I’ll help you if you help me”. Under this idea people begin working together with a feudal contract. These groups form small villages or towns that develop into manors. Manors run as self-sufficient units because everyone has a specific job that they are responsible to get done. 3. Explain the three issues that to the mistrust and desire to reform the Medieval Church. Page 379 chapter 14 section 1 Three issues that led to the mistrust and desire to change the church… Points that you can include – Simony and its definition Lay investiture and its definition Church leaders getting married instead of only being married to God The church turned its back on the people during the Black Plague Example of how you could answer this question: Three issues that led to the mistrust and desire to reform the church are simony, lay investiture and marriage. Simony is (this is where you’d define the term). Next lay investiture is (this is where you’d define the term). Finally society was unhappy with church officials being married to anyone but God. 4. Define the Reconquista and Spanish Inquisition? Explain how the two are connected. Page 384 chapter 14 section 1 To start this answer you need to define Reconquista and then define the Spanish Inquisition. Then you need to show how they are connected. Example of how you could answer this question: The Reconquista was Spain’s plan to rid the country of non-Christians. The Inquisition was the court system and trial process that let them do this. 5. What were three effects of the Black Death? Page 401 chapter 14 section 4 To start this answer you need to define what the Black Death was and how it came about. Points that you can include End of the Middle Ages Population decline due to so many people dying Lack of trust or faith in the church Church lost power as they turned their backs on the people during this time Leads to the breakdown of cities Trade declined due to fear of Black Death spreading which also caused a decline in money Decline of the feudal system – the manor system breaks apart as people aren’t working together anymore as they’re afraid of getting sick Cities declined as people move to the country to get away from the disease Due to a lack of trade, culture and history (learning) stopped spreading which caused a decline in education Example of how you could answer this question: The Black Death was a plague that was carried by fleas and spread throughout Asia, Africa and Europe. Three effects of the Black Death include…(this is where you’d discuss points that you wanted to include from the list above or ones of your own). 6. What were two main causes of the Crusades? What were two results of the Crusades? Pages 382-384 chapter 14 section 1 To start this answer you need to define what they Crusades are before you name the two main causes of the Crusades and then two results. Definition – series of Holy Wars Causes – to get control of the holy hand Economic gains – more money Political gains – want of power and land Results – trade expands as people are traveling more Spread of knowledge and ideas as the cultures blend Decline in church and religion Loss of the holy land to the Muslims Example of how you could answer this question: The Crusades were a series of holy wars fought between the Christians and Muslims for control of the holy land. Two causes of the Crusades are (this is where you discuss two points from the list above). Two results of the Crusades are (this is where you discuss two points form the list above) 7. Describe three things that Justinian accomplished that improved the Byzantine Empire. Explain why. Page 301-303 chapter 11 section 1 To start this answer you need to say who Justinian is – ruler of the Byzantine Empire Then you need to describe three accomplishments of Justinian Hagia Sophia – famous church that he rebuilt Justinian Code – a set of unified laws He rebuilt the capital He unified the government Example of how you could answer this question: Justinian was the rule of the Byzantine Empire. Under his rule, he (this is where you’d list three of his accomplishments). The (first accomplishment) helped to improve the Byzantine Empire by (this is where you’d explain how it helped the empire or the people) 8. Explain/ Describe the Five Pillars of Islam. Page 267 chapter 10 section 1 To start this answer you need to first explain what the Five Pillars of Islam and then describe each one. The Five Pillars of Islam are the major rules by which all Muslims of the Islamic faith live. The Five Pillars of Islam Declaration of Faith – “I bear witness that there is not god, but God; I bear witness that Muhammad is the prophet of God.” By reciting this, one enters Islamic faith Prayer – Muslims are required to pray five times a day, washing themselves before prayers and facing in the direction of Mecca while praying Giving a Fixed Proportion to Charity – Muslims are required to give away a percentage of their earnings to those less fortunate, regardless of their religion Fasting During the Month of Ramadan – Muslims fast for one lunar month each year, a period called Ramadan. During this time, Muslims reflect on their behavior and strive to purify their thoughts. Pilgrimage to Mecca – If it is physically and financially possible, Muslims are required to travel to Mecca once in their lifetime Example of how you could answer this question: The Five Pillars of Islam are the major rules by which all Muslims of Islamic faith live. The first pillar is (this is where you’d pick on from above and explain it). The second pillar is… Essay Section ( Part 5) Your essay needs an introduction, body and closing paragraph 1. Explain how Feudalism developed in Europe starting with the fall of Rome. The Middle Ages was the time period in Europe just after the fall of Rome. The Middle Ages declined/ended because of three major events. The first event was the Black Death. (The effects of this event can be found in earlier answers) Because of the Black Death people began to lose faith in the church, which becomes our second event. (an explanation to support this can be found in earlier answers). Finally the decline of feudalism… Refer back to your earlier test (chapter 13) where this was an essay question to find more information to answer this question completely. You can also refer to the chart in your notes to help you too. 2. Discuss the main beliefs and concepts connected to the three monotheistic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Explain three similarities and three differences between Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Intro – In the world today there are three major religions, Christianity, Judaism and Islam. Although all three religions have the same origin each one will develop differently. The first religion is Christianity. Christianity like all religions has a holy book called the Bible. Christianity also worship on a holy day, for them it’s Sunday. Finally Christians believe that Jesus was the messiah or spiritual figure who will return again. The second religion is Islam (You’d write this paragraph similar to the one for Christianity only changing how things are different). The third religion is Judaism. (You’d write this paragraph similar to the one for Christianity only changing how things are different). As you see though these three religions are very similar they also have many differences. ****You may use any three similarities and differences that you find in the chart below. You don’t have to use the three in the sample paragraph. Religion Founded by When Sabbath – holy day of worship Holy Text Place of Worship Leader of Worship Judaism Abraham About 2000 B.C. Saturday Christianity Jesus About 33 A.D. Sunday Islam Muhammad About 600 A.D. Friday Torah Synagogue Rabbi Bible Church Priest/pastor Life After Death In World to come the time after the Messiah Heaven or hell Qu’ran Mosque Ulama (group)/ imam (individual) Heaven or hell Judgment is based on how you’ve lived your life Judgment is based on how you’ve lived your life Judgment is based on how you’ve lived your life The Messiah has not come yet Do not believe that Jesus is the Messiah or the Son of God Monotheistic Jesus was the Messiah and the Son of God Believe that Jesus was a prophet and the Muhammad is the last great prophet Monotheistic Monotheistic Follow the 10 Commandments Believe that Jerusalem is the “Holy Land” Not required to make a journey Follow the 10 Commandments Believe that Jerusalem is the “Holy Land” Not required to make a journey Fast for Yom Kippur No fasting Follow the Five Pillars of Islam Believe that Jerusalem is the “Holy Land” Have to travel to Mecca once in their lifetime if they are physically and financially able Fast during the holy month of Ramadan Basic Beliefs and Teachings 3. Evaluate what caused the decline of the Middle Ages. Explain/ describe two reasons. Describe what the Middle Ages were in your introduction and list your two reasons. Your next paragraph is where you can describe your first reason. Your next paragraph is where you can describe your second reason Your closing will wrap up your ideas. ***There are ideas earlier in the study guide to help you with this answer if you chose to do it*** 4. Discuss Eastern and Western Europe during the Middle Ages. Provide four examples of how they developed differently after the fall of the Roman Empire