Unit 3 Vocabulary - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
advertisement

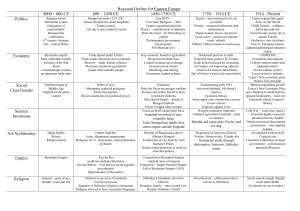
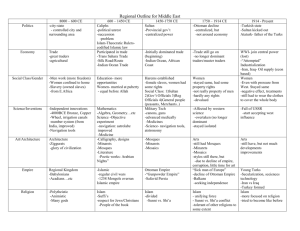
Unit 3 Vocabulary Middle Ages In Europe Byzantine Empire/Manorialism Justinian’s Code of Laws: Emperor Justinian collected all existing Roman laws and organized them into a single code- foundation for Western legal tradition Hagia Sophia: the Cathedral of Holy Wisdom in Constantinople, built by order of the Byzantine emperor Justinian Icon: images of Jesus and Saints (Iconoclasm: the destruction of these images) Middle Ages: the era in European history that followed the fall of the Roman Empire, lasting from about 500 to 1500 ad – also called the medieval period Feudalism: a political system in which nobles are granted the use of lands that legally belong to their king, in exchange for their loyalty, military service, and protection of the people who live on the land Lords: a person who controlled land and could therefore grant estates to vassals Knights: an armored warrior who fought on horseback Serfs: a medieval peasant legally bound to live on a lord’s Manor: a lord’s estate in feudal Europe Manorialism: Economic system of feudal Europe, consisting of the lord’s house and his serfs. Each manor produced its own food, clothing, and shelter Three-Field System: a system of farming developed in medieval Europe, in which farmland was divided into three fields of equal size & each was successively planted with a winter crop, planted with a spring crop, then left unplanted Tithe: a family’s payment of 1/10th of its income to a church St. Augustine: emphasized the role of faith St. Thomas Aquinas: (1225-1274) Catholic thinker who believed in natural laws based on reason and in the right to defy unjust laws Magna Carta: The Great Charter signed in 1215, a document guaranteeing basic political rights in England, drawn up by the nobles and approved by King John- Political ideas limited the power of the nobility, Legal ideas- no one is above the law Great Schism: (1378-1417) Split that occurred in the Catholic Church with 2 Popes, one in Avignon & the other in Rome. The Schism caused many to question the Church’s authority Crusades: (1095-1272) A war requested by the Pope for Christians to recapture the Holy Land from the Muslims. Crusades led to greatly increased trade between Europe and the Middle East Hundred Years War: (1137-1453) War between England and France over succession to the French throne. It strengthened royal power and brought an end to feudalism Black Death: (c. 1350) a disease carried on ships from Asia to Europe that killed millions of people and helped to end serfdom in Europe The Islamic World and Africa Qur’an: the holy book of Islam Islam: Monotheistic religion founded by Mohammed, based on the five pillars Five Pillars: Faith, prayer, charity, fasting, pilgrimage Sunni: the branch of Islam whose members acknowledge the first four caliphs as the rightful successors of Muhammad Shi’a: the branch of Islam whose members acknowledge Ali and his descendants as the rightful successors of Muhammad Sharia: a body of law governing the lives of Muslims Caliph: a supreme political and religious leader in Muslim Gold Salt Trade: Exchange of salt for commodities such as gold and slaves, particularly in West Africa. Atlantic Slave Trade: the buying, transporting, and selling of Africans for work in the Americas Persia/ India Safavids: A Shi’a empire from Persia to central Asia (1500s-1700s) founded by Shah Ismail Mughals: Establishes a Muslim empire in India under Babur, Akbar, and Shah Jahan Tang & Song China/ Mongols/ Ottoman Empire Sultan: A Muslim Sovereign Sikhism: a religion that developed in Northern India, combining both Islamic and Hindu beliefs. Sikhs believe in one God, which can only be known through meditation Chinggis (Genghis) Khan: founder and Great Khan of the Mongol Empire Kublai Kahn: reigning from 1260 to 1294, and the founder of the Yuan Dynasty, a division of the Mongol Empire. Ottoman Empire: Turkic empire established in Asia Minor and eventually extending through the Middle East and the Balkans; conquered Constantinople in 1453 and ended Byzantine Empire