8th Grade Study Guide
advertisement
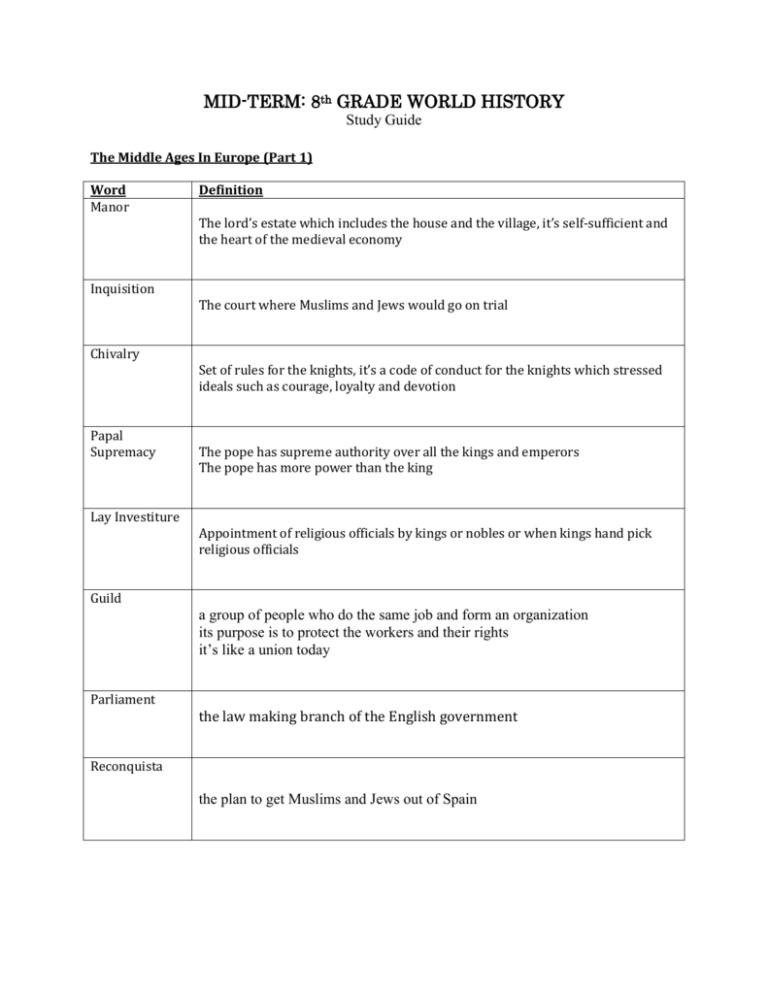
MID-TERM: 8th GRADE WORLD HISTORY Study Guide The Middle Ages In Europe (Part 1) Word Manor Definition The lord’s estate which includes the house and the village, it’s self-sufficient and the heart of the medieval economy Inquisition Chivalry Papal Supremacy Lay Investiture The court where Muslims and Jews would go on trial Set of rules for the knights, it’s a code of conduct for the knights which stressed ideals such as courage, loyalty and devotion The pope has supreme authority over all the kings and emperors The pope has more power than the king Appointment of religious officials by kings or nobles or when kings hand pick religious officials Guild a group of people who do the same job and form an organization its purpose is to protect the workers and their rights it’s like a union today Parliament the law making branch of the English government Reconquista the plan to get Muslims and Jews out of Spain 1. What signaled the beginning of the Middle Ages? The fall or collapse of the Roman Empire 2. What is the feudal system based on? Mutual obligations 3. Who was the feudal contract between? A greater lord and his less powerful noble 4. How would you describe a medieval serf? They were bound to the land but were not slaves as they could not be bought or sold 5. How were feudalism and the manor system related? Feudalism was a social order, and the manor system was the economic arrangement that supported it 6. What was the most powerful institution of the Middle Ages? The Church 7. According to the code of chivalry, who were the three people a knight fought for? His lady, His feudal lord His heavenly Lord 8. What was the chief goal of the Crusades? To recover (or take back) Jerusalem( or the Holy Land) from the Muslim (Turks) 9. What did the Magna Carta grant to the nobles? Basic legal rights 10. What was the major cause of the Great Schism? Arguments about which man holding the position of pope was the true pope 11. What was the central issue of the Hundred Years War? The throne of France 12. Why did Science make little real progress in Europe during the Middle Ages? Most scholars thought that all knowledge must fit with church teachings 13. Describe Gothic cathedral architecture. Stained glass – usually more decorative such as the Rose Glass Light and open High ceilings Fancy and decorative Rib vaults – arched or pointed Flying buttresses are actually used to hold up the walls More open / less wall space Sculpture and statues 14. What did the devastation caused by the bubonic plague lead to? The disruption and collapse of medieval society 15. What city were they looking to recapture during the Crusades? Jerusalem 16. What caused the decline of the Middle Ages? A middle class formed bringing an end to feudalism The Crusades and the Black Death Education was valued again and the corruption of the Catholic Church The Byzantine Empire, Russia and Eastern Europe ( Part 2) Word Justinian’s Code Definition a single set of unified laws based on old Roman laws Czar means emperor, Russian version of Caesar 17. What was the capital of New Rome, or the Byzantine Empire? Constantinople 18. What caused the split between the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church? The use of icons 19. What helped cause the decline of the Byzantine empire? The Mongols and Turks invaded and conquered Constantinople The disruption and the control of Byzantine trade Bubonic Plague 20. Describe the Mongol rule of medieval Russia The Mongols allowed Russians to follow their usual customs as long as they didn’t rebel and they paid tribute or taxes 21. After the Great Schism, what was the new name given to the Byzantine church? Eastern Orthodox Church The Rise of Islam ( Part 3) Word Definition Islam one who has submitted to the will of God, monotheistic religion based on the teachings of Muhammad Sunni The best Muslim male should be the next ruler, who is the best “fit” for the job and not necessarily someone who is a descendant of Muhammad Shiite Or Shi’a - branch of Islam whose members believe that the blood line or descendants or Muhammad should rule 22. What are two important teachings that are common to all three faiths? One God Life After Death 23. Why was the Hijrah important It enabled Muhammad to be accepted as a leader leader, gain followers and gain power Short Answer Section (Part 4) 1. Explain how the church shaped medieval life and society? Provide two examples. Remember to introduce the feudal system as a time where there was a weak central government, which gave the church more power Points that you can include as examples: The church was seen as the social center or “town hall” since their entire social life revolved around the church which was usually in the center of the village Excommunication as the worst punishment of their life as you’re kicked out of the church Canon law – the church had its own laws and its own court Papal Supremacy where the church had power over the kings and the constant fighting back and forth over who was more powerful. Church tax – they took the people’s money especially the poor peasants They built these large gothic cathedrals where they were putting time and money into God as these took a lot of time and money to build 2. Define feudalism and explain how it helped to create the manor economy. The Development of Feudalism Rome fell in A.D. 476 as a result of invasion by the Germanic tribes Central government broke down and trade was disrupted Cities were abandoned and population centers shifted to rural areas Ties of personal loyalty and family bound Germanic peoples together The lack of centralized government created the need for a new social order. Christianity remained a major unifying force throughout most of western Europe. Common needs for economic self-sufficiency The manor became the main economic unit. The feudal system developed with a and local protection led to a new pattern based on land ownership Church leaders helped to integrate community life. king at the top and Mutual duties linking local lords, vassals, and peasants Explanation of the Chart 1. The fall of Rome 2. As a result of the fall of Rome, there is no longer any central government so there is no leadership which causes the cities to fall apart of decline 3. Due to invasions the people bail from the cities to the safety of the rural areas 4. In the rural areas, the people need some protection and a new government structure is formed 5. Groups formed and joined up with a wealthy landlord 6. The manor system grew out of this as a “give and take” type of society where you give me in service and I’ll give you land Remember to define feudalism, and then explain how it enabled the creation of the manor system Points to include: Feudalism is the government or social structure in the medieval society that works on a system of mutual obligations Feudalism began because people were looking for protection. People lost government and needed protection and began to form groups. These groups joined with up with wealthy land owners and began a give and take partnership (feudal contract) The lord needed protection and so he needs knight to fight for him (feudal contract) Thus creating the Manor system which is based on “I got your back you’ve got mine” 3. Explain the three issues that to the mistrust and desire to reform the Medieval Church. Wealthy church tax of 10% was difficult for the poor who had no money Lay investiture – the king pick church people which can lead to corruption The buying and selling of forgiveness or indulgences for the your sins Papal supremacy or the idea of the pope having more power than the king Religious officials had questionable morals - gambling, drinking marrying The Plague – the church wouldn’t help the people in fear of getting sick so the people lost faith in the church Simony the buying and selling of church jobs or positions 4. Define the Reconquista and Spanish Inquisition? Explain how the two are connected. The Reconquista was the organized effort or plan to rid Spain of all the non-Christians (the Jews and Muslims). The Spanish Inquisition was the court that let them put non-Christians on trial to get rid of them. 5. What were three effects of the Black Death? Remember to tell what the Black Death was and how it came about before you talk about the effects Points to include: Population declines due to a lot of people dying People lost faith in the church since they wouldn’t help them Trade declined so prices increased in an attempt to make up the loss of money People left the cities to flee the plague and moved to the country which will lead to the end of the manor system Decline in the education with all the people now living in the country Church lost power due to people losing faith in the church Long Response ( Part 5) 1. Explain how Feudalism developed in Europe starting with the fall of Rome. Feudalism was the social and government structure that developed after the fall of Rome. After Rome fell a series of events occurred that led to the rise of the new social order Once Rome fell No central government No leadership and cities fell apart Invasion led people to move from the cities to the rural country People needed protections and a new government Groups forced to work together Developed their own roles and a partnership from which the feudal society and manor system grew Concluding paragraph can be based on the last bullet 2. Discuss the main beliefs and concepts connected to the three monotheistic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Explain three similarities and three differences between Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In the world today there are three major religions, Christianity, Judaism and Islam. Although all three religions has the same origin each one will develop differently Mention the three similarities one at a time and then make it a difference for how it religion uses/names it Concluding paragraph example: As you can see though these three religions are very similar they also have many differences 3.Explain/ Describe the Five Pillars of Islam. Remember to start this answer by defining what the Five Pillars of Islam are and then describe each one. The Five Pillars of Islam are the major rules by which all Muslims of the Islamic faith live The Five Pillars of Islam Declaration of Faith – “There is no god but God and Muhammad is His Prophet”. By reciting this one enters the Islamic faith. Prayer – Muslims are required to pray five times a day, washing themselves before prayers and facing in the direction of Mecca while praying Giving Alms or Charity – Muslims are required to give away a percentage of their earnings to those less fortunate, regardless of their religion Fasting During the Month of Ramadan – Muslims fast for one lunar month each year, a period called Ramadan. During this time, Muslims reflect on their behavior and strive to purify their thoughts. They are required to fast during this time from sun-rise to sun-set Pilgrimage or Journey to Mecca – If it is physically or financially possible, Muslins are required to travel to Mecca once in their lifetime