Christian Europe 600-1200
advertisement

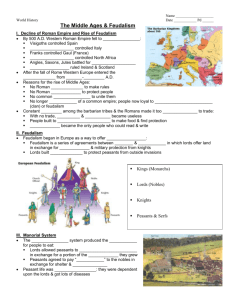
Christian Europe 600-1200 1. Describe the political development of Europe after the fall of Rome. What factors led to the development of feudalism? 2. Who were the Vikings and what effect did they have on Europe? 3. Describe the political and religious significance of the Carolingian Empire and the Holy Roman Empire. 4. What are the root causes of the split between the Western (Latin) and Eastern (Greek) churches? 5. What were the causes and impact of the Crusades? I. Fall of Rome 1. 476 CE Rome falls to Visigoth invaders 2. Centralized government disappears 3. Loss of Greek and Roman learning and common language 4. Transportation, trade and communication halts II. Long Term Effects 1. Constant warfare/invasions 2. Cities abandoned as economic/political centers 3. Population becomes rural: Political, economic, cultural change in W. Europe 4. Feudalism develops III. Stages of Middle Ages 1. (476-750): No unity. Several small kingdoms form: Franks, Visigoths, Saxons – Viking raids begin • William the Conqueror invades England 1066 2. (750-814)- Holy Roman Empire under Charlemagne (747-814) prevents Muslims from invading W. Europe. – Some strength/unity but still quite fragmented 3. (815-1050)- Carolingian Empire falls apart and feudalism becomes dominant social and political system KINGS • Divides and distributes land (feifdoms) • Pledges loyalty • Sends military when requested NOBLES(LORDS) •Pledges loyalty •Serves in noble’s military • Provides shelter, protection and means to produce food (serfs) KNIGHTS •Provides shelter, protection and land •Farms the land •Pays rent and taxes PESANTS/SERFS Social Structure • Nobles- wealthy ruling class that owned all the land: kings, lords, knights • Serfs- largest but poorest part of population. Did most of labor. • Freemen- lived in town; craftsmen who made/sold goods. Not naturally part of feudal system. Manorial System • Large estates that were able to meet all of their own needs • Smaller farmers ceded land to nobles for protection • Made up of fields, small town w/ a mill and workshops, a church, and castle 4. (1050-1300)- Rise of national monarchs brings some stability – Agricultural revolution allows for population increase – Commercial revival: Trade starts up again, cities are repopulated IV. Western Church 1. Headed by pope 2. Crowned Holy Roman Emperor (962) in attempt to combine religious/political power 3. Investiture Controversy: rulers/popes disagreed over appointing bishops 4. Monasticism• • Celibacy, devotion to prayer, isolation Monasteries were centers of learning, inns, refuge for widows V. Byzantine Empire 1. Emperor was head of church: Patriarch 2. Foreign threats: – – Sassanids (Iran) Muslim Arabs take Syria, Egypt, and Tunisia 3. Schism 1054- split w/ Western Church 4. Constantinople: wellsupplied but rural areas suffered 5. Body of Civil Law (Corpus Juris Civilis)- later became basis for W. European civil law VI. Kievan Russia 1. Poor land- wealth depended on trade 2. Major cities: Kiev and Novgorod 3. Vladimir I (980) adopted Orthodox Christianity VII. Crusades (1100-1250) 1. Causes: • • • • Religious zeal- wanted to liberate Holy Land Knights willing to fight for church Desire for land by Euro. Nobility Trade interests 2. Impact: • Ended Europe’s intellectual isolation! Examples?