Course Descriptor Template - Heriot
advertisement
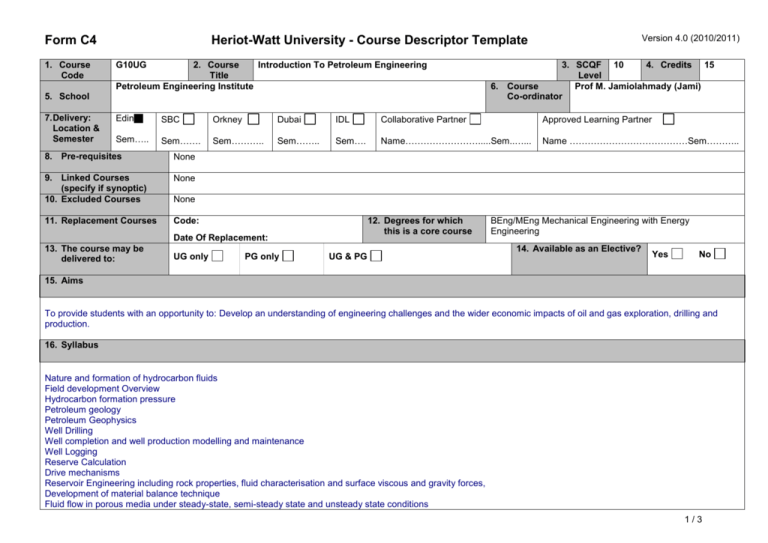
Form C4 1. Course Code G10UG 2. Course Introduction To Petroleum Engineering Title Petroleum Engineering Institute 5. School 7. Delivery: Location & Semester Version 4.0 (2010/2011) Heriot-Watt University - Course Descriptor Template 3. SCQF 10 4. Credits 15 Level 6. Course Prof M. Jamiolahmady (Jami) Co-ordinator Edin SBC Orkney Dubai IDL Collaborative Partner Approved Learning Partner Sem….. Sem……. Sem……….. Sem…….. Sem…. Name…………………….....Sem..…... Name …………………………………Sem……….. 8. Pre-requisites None 9. Linked Courses (specify if synoptic) 10. Excluded Courses None 11. Replacement Courses Code: None 12. Degrees for which this is a core course Date Of Replacement: 13. The course may be delivered to: UG only PG only UG & PG BEng/MEng Mechanical Engineering with Energy Engineering 14. Available as an Elective? Yes No 15. Aims To provide students with an opportunity to: Develop an understanding of engineering challenges and the wider economic impacts of oil and gas exploration, drilling and production. 16. Syllabus Nature and formation of hydrocarbon fluids Field development Overview Hydrocarbon formation pressure Petroleum geology Petroleum Geophysics Well Drilling Well completion and well production modelling and maintenance Well Logging Reserve Calculation Drive mechanisms Reservoir Engineering including rock properties, fluid characterisation and surface viscous and gravity forces, Development of material balance technique Fluid flow in porous media under steady-state, semi-steady state and unsteady state conditions 1/3 Form C4 Version 4.0 (2010/2011) Heriot-Watt University - Course Descriptor Template Gas Reservoirs Petroleum Economy 17. Learning Outcomes (HWU Core Skills: Employability and Professional Career Readiness) Subject Mastery Understanding, Knowledge and Cognitive Skills Scholarship, Enquiry and Research (Research-Informed Learning) On completion of the module, learners will be able to describe Process of formation of hydrocarbon fluids Main phases of field development Main formation pressure regimes and calculate temperature pressure variation within reservoir Geological features that makes a subsurface structure a suitable hydrocarbon reservoir Geophysical methods for hydrocarbon reservoirs characterization Objectives, methods and requirements for drilling of an oil well. Objectives, methods and requirements for completion of a well for oil production and methods and practices for modelling and improvement of the performance of a petroleum production well. Objectives, methods and requirements of well logging used to estimate porosity and fluid saturation Different reserves and calculate oil in place and reserve Principles of different primary, secondary and tertiary drive mechanisms for oil production (i) Main chemical structure of hydrocarbon fluids, (ii) Importance of gravity, viscous and surface forces on fluid distribution and flow within porous media (iii) main rock and fluid properties including porosity, permeability, relative permeability, capillary pressure, wettability, oil formation volume factor, solution gas oil ratio, gas formation factor (iv) Principle of phase behavior (pressure versus temperature and volume diagram) of pure component, binary and multi-component hydrocarbon mixtures (v) calculate average permeability for layered systems Material balance equation and how to use them to calculate reserve and evaluate reservoir performance steady-state, semi-steady state and unsteady state flows including principles of well testing dry/wet/gas-condensate reservoirs and calculate gas properties, initial gas in place and reserves Key economic drivers of energy demand and its impact on the global economic system. Personal Abilities Industrial, Commercial & Professional Practice Autonomy, Accountability & Working with Others Communication, Numeracy & ICT On completion of the module, learners will have developed: An extended awareness of the petroleum industry Their personal skills, including an awareness of both traditional and internet-based information sources; Their skills in problem solving An ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical problems. Understanding of uncertainty and cost of reducing it for improved calculation/operation/management 18. Assessment Methods Method 19. Re-assessment Methods Duration of Exam (if applicable) Weighting (%) Synoptic courses? Method Duration of Exam (if applicable) 2/3 Diet(s) Form C4 Heriot-Watt University - Course Descriptor Template Coursework (in class test) Examination Test 2hr 2hr 25 75 Version 4.0 (2010/2011) None 20. Date and Version Date of Proposal Date of Approval by School Committee Date of Implementation Version Number 3/3