Course Descriptor Template - Heriot
advertisement
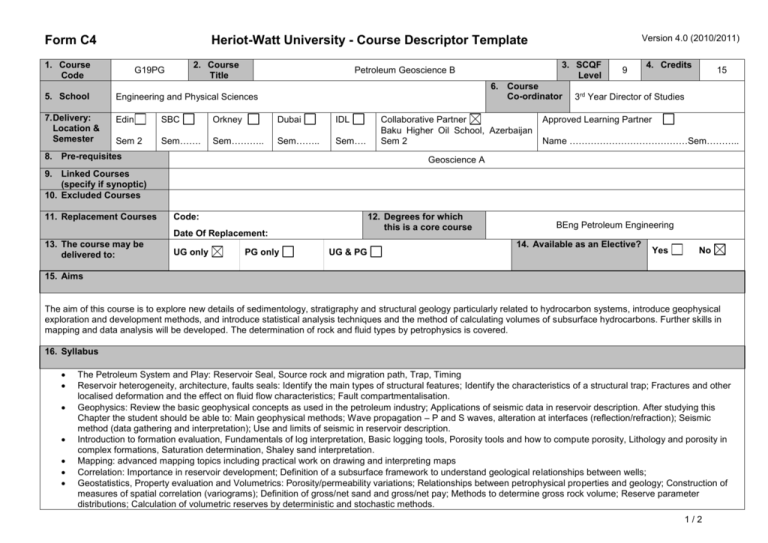
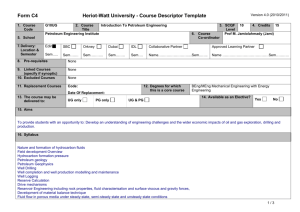
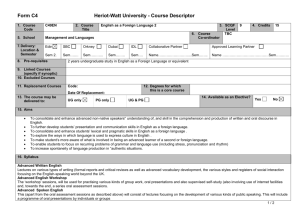
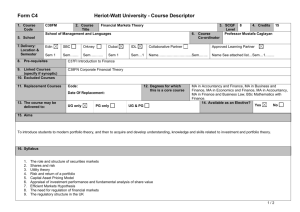
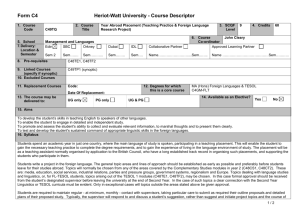
Form C4 Version 4.0 (2010/2011) Heriot-Watt University - Course Descriptor Template 1. Course Code 2. Course Title G19PG 3. SCQF Level Petroleum Geoscience B 6. Course Co-ordinator 5. School Engineering and Physical Sciences 7. Delivery: Location & Semester Edin SBC Orkney Dubai IDL Sem 2 Sem……. Sem……….. Sem…….. Sem…. 8. Pre-requisites Collaborative Partner Baku Higher Oil School, Azerbaijan Sem 2 9 4. Credits 15 3rd Year Director of Studies Approved Learning Partner Name …………………………………Sem……….. Geoscience A 9. Linked Courses (specify if synoptic) 10. Excluded Courses 11. Replacement Courses Code: 12. Degrees for which this is a core course Date Of Replacement: 13. The course may be delivered to: UG only PG only UG & PG BEng Petroleum Engineering 14. Available as an Elective? Yes No 15. Aims The aim of this course is to explore new details of sedimentology, stratigraphy and structural geology particularly related to hydrocarbon systems, introduce geophysical exploration and development methods, and introduce statistical analysis techniques and the method of calculating volumes of subsurface hydrocarbons. Further skills in mapping and data analysis will be developed. The determination of rock and fluid types by petrophysics is covered. 16. Syllabus The Petroleum System and Play: Reservoir Seal, Source rock and migration path, Trap, Timing Reservoir heterogeneity, architecture, faults seals: Identify the main types of structural features; Identify the characteristics of a structural trap; Fractures and other localised deformation and the effect on fluid flow characteristics; Fault compartmentalisation. Geophysics: Review the basic geophysical concepts as used in the petroleum industry; Applications of seismic data in reservoir description. After studying this Chapter the student should be able to: Main geophysical methods; Wave propagation – P and S waves, alteration at interfaces (reflection/refraction); Seismic method (data gathering and interpretation); Use and limits of seismic in reservoir description. Introduction to formation evaluation, Fundamentals of log interpretation, Basic logging tools, Porosity tools and how to compute porosity, Lithology and porosity in complex formations, Saturation determination, Shaley sand interpretation. Mapping: advanced mapping topics including practical work on drawing and interpreting maps Correlation: Importance in reservoir development; Definition of a subsurface framework to understand geological relationships between wells; Geostatistics, Property evaluation and Volumetrics: Porosity/permeability variations; Relationships between petrophysical properties and geology; Construction of measures of spatial correlation (variograms); Definition of gross/net sand and gross/net pay; Methods to determine gross rock volume; Reserve parameter distributions; Calculation of volumetric reserves by deterministic and stochastic methods. 1/2 Form C4 Version 4.0 (2010/2011) Heriot-Watt University - Course Descriptor Template 17. Learning Outcomes (HWU Core Skills: Employability and Professional Career Readiness) Subject Mastery Understanding, Knowledge and Cognitive Skills Personal Abilities Scholarship, Enquiry and Research (Research-Informed Learning) Demonstrate the application of learned skills to analysing geological data to determine location and size of hydrocarbon accumulations. Understand how geological factors affect the position, size, properties and development potential of hydrocarbon accumulations. Choose an appropriate method to solve problems. Use all available resources, including provided notes and directed reading to research and understand core material. Industrial, Commercial & Professional Practice Autonomy, Accountability & Working with Others Communication, Numeracy & ICT Work in groups to research and develop solutions to class problems, and to give group presentations. Develop skills to analyse data, and develop clear methodology to decide not only which technique is appropriate to analyse the data, but which presentation mode is appropriate to present the results (maps, correlations, graphs, diagrams etc). 18. Assessment Methods Method 19. Re-assessment Methods Duration of Exam Weighting (%) Synoptic courses? Method (if applicable) Examination Coursework 2 hours Duration of Exam Diet(s) (if applicable) 75% 25% Examination Coursework as appropriate 2 hours 3 20. Date and Version Date of Proposal 13-8-2012 Date of Approval by School Committee Date of Implementation Version Number 2/2 1.1