CHE 2202, Section 101 Spring 2014 Exam IA Name: Honor Pledge
advertisement

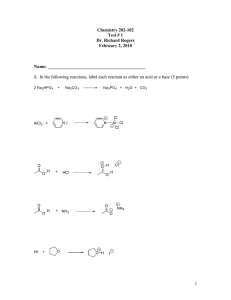
CHE 2202, Section 101 Spring 2014 Exam IA Name: _____________________________________________________________________ Honor Pledge: I pledge on my honor that I have not violated the Appalachian State University Academic Integrity Code. I will not discuss this exam with any students who have not yet taken it. Signature: _________________________________________ Unsigned honor pledges will result in a grade of 0 points. Page 1: _____/ 12 points Page 2: _____/ 14 points Page 3: _____/ 18 points Page 4: _____/ 14 points Page 5: _____/ 22 points Page 6: _____/ 20 points Total: _____/ 100 points 0 1. Use the data below to answer the following questions. Show your work: Mass spec: parent ion at m/z = 100 IR: stretches at 3018, 2980, 2947, 1720 cm-1 a. (9 points) Draw the structure. b. (3 points) There is a major fragment observed at m/z = 85. What is likely lost from the parent ion to produce this fragment? 1 / 12 points 2. (4 points) Which of the following would show two signals in its 1H NMR spectrum? Circle all that apply. 3. (4 points) Rank the 13C NMR chemicals shifts of the carbons in the following compounds from most downfield (=1) to most upfield (=4). 4. (4 points) Circle the correct relationship between the two hydrogens in bold in the following structure. a. homotopic b. enantiotopic c. diastereotopic d. no relationship 5. (2 points) Based on your answer to number 4, would the two hydrogens in bold give the same signal or different signals in the 1H NMR spectrum? Circle the correct choice. Same signal Different signals / 14 points 2 6. (14 points) The following compounds are isomers of each other. Fill in the table below to discuss if and how these structures could be differentiated from each other by 1H NMR and mass spectrometry. Structures Number of signals present Chemical shifts present (provide general ranges) Integration ratio Splitting patterns Parent ion value Fragments Observed from Alpha-Cleavage Fragments Observed from McLafferty Rearrangement 7. (4 points) What is the significance of the base peak in a mass spectrum? Circle the correct answer. a. It gives the m/z value for the unfragmented structure. b. It differentiates the radical cation from the radical. c. It is the tallest peak. d. It is the peak with the largest m/z value. / 18 points 3 8. Consider the following reaction: a.) (2 points) Circle the kinetic product in the reaction scheme above. b.) (6 points) Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the reaction above that illustrates the reaction progress from starting material X to products A and B. Use a solid line ( ) to show the formation of A and a dashed line (-------) to show the formation of B. c.) (3 points) If you are trying to maximize the formation of the kinetic product and minimize the formation of the thermodynamic product, which conditions would be best? Circle your answer. a.) 85 °C, 24 h b.) room temperature, 5 h c.) 0 °C, 1.5 h 9. (3 points) Ethanol, methanol, and cyclohexane are commonly used as solvents for UV-vis spectroscopy because they do not absorb radiation at wavelengths longer than 200 nm. Why not? 4 / 14 points 10. (6 points) Azulene is a blue substance, β-carotene is an orange-red color, and 1,3cyclohexadiene is colorless. Based on the colors of these compounds, draw lines to match each compound to its λmax value. Azulene 259 nm β-Carotene 497 nm 1,3-Cyclohexadiene 696 nm 11. (16 points) Fill in the boxes with the missing starting materials or products for the DielsAlder reaction. pts / 22 pts 5 12. (10 points) Circle the aromatic molecules. For those that are not circled, indicate why these are not aromatic. 13. (4 points) Most diazocompounds are exceedingly, and sometimes disastrously, unstable. However, diazocyclopentadiene is quite stable. Explain, using structures, its stability. 14. (6 points) Draw a structure of an aromatic compound that: a. is made of carbon and hydrogen only, and has 3 rings. b. contains one boron atom in addition to carbons and hydrogens, and has one ring. / 20 points 6