Cell Review Key - Mercer Island School District
advertisement
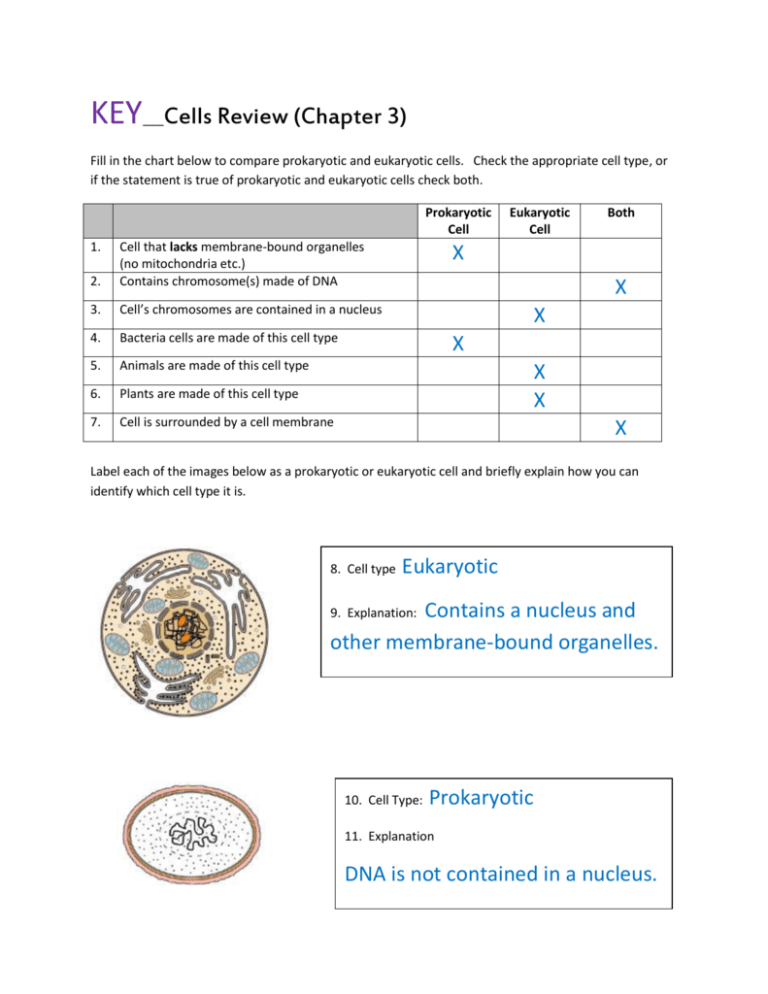
KEY ___ Cells Review (Chapter 3) Fill in the chart below to compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Check the appropriate cell type, or if the statement is true of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells check both. Prokaryotic Cell 1. 2. Cell that lacks membrane-bound organelles (no mitochondria etc.) Contains chromosome(s) made of DNA 3. Cell’s chromosomes are contained in a nucleus 4. Bacteria cells are made of this cell type 5. Animals are made of this cell type 6. Plants are made of this cell type 7. Cell is surrounded by a cell membrane Eukaryotic Cell Both X X X X X X X Label each of the images below as a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell and briefly explain how you can identify which cell type it is. 8. Cell type Eukaryotic Contains a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. 9. Explanation: 10. Cell Type: Prokaryotic 11. Explanation DNA is not contained in a nucleus. For each statement below, place a check in the correct box to indicate whether the statement describes the plasma membrane (cell membrane), cell wall or both. Plasma Membrane 12. A thin, flexible layer that surrounds all cells X X 15. In plant cells, it is composed of a fibrous material called cellulose 16. Composed mainly of lipid, with proteins embedded in it Both X 13. A firm structure that supports and gives shape to a cell 14. External barrier that controls what can enter and exit Cell Wall X X For each of the following questions, identify the missing cell part or give its function. Cell parts may be used more than once. 17. Structure/Function Structure where proteins are produced (site of protein synthesis) 18. Clear fluid inside the cell 19. The powerhouse of the cell- that produces ATP from cellular respiration Cell Part Ribosome Cytoplasm Mitochondria 20. Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from the sun Chloroplast 21. Small bumps on the rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes 22. The control center of the cell- that stores DNA/Chromosomes 23. 24. 25. An organelle that is surrounded by two membranes, with the inner membrane folded to create more surface area. A folded network of membrane bound compartments that help to fold and transport proteins Nucleus Mitochondrion ER Proteins within the cell that provide support and a transportation network. Cytoskeleton 26. A set of stacked membrane-bound sacs that work with the rough ER to transport proteins to their proper destination. Golgi Apparatus 27. The site of photosynthesis 28. Organelle where sugars are broken down to provide usable energy (ATP) for the cell in a process called cellular respiration. An organelle that contains digestive enzymes to break down worn-out cell parts and foreign substances. 29. Chloroplast Mitochondrion Lysosome 30. Compare and contrast vesicles and vacuoles. Vacuoles are more permanent storage chambers while vesicles are temporary transport compartments. 31. The nucleus is often described as the control center of the cell. What material does it contain that store the important information needed to produce all the proteins needed within a cell? DNA/ Chromosomes 32. Compare and contrast cilia and flagella. Both are for movement (of cell or a fluid across the surface). Cilia are shorter and more numerous. For questions 34-57, label the parts of a plant and animal cell. Label plant cell diagram on lettered blanks on the next page. Many of the organelles are present in both types of cells. PLANT CELL D A C B E F L K J I H G 34. A Chloroplast 40. G 35. B Cytoplasm 36. C Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 41. H Golgi Apparatus (or Body) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 42. I Plasma (or Cell) 37. D Cell Wall 43. J Central Vacuole 38. E Nucleolus 44. K Mitochondrion 39. F Nucleus 45. L Free Ribosome Membrane ANIMAL CELL Cell Membrane Lysosome Free Ribosome Mitochondrion Golgi Apparatus Rough ER DNA/Chromosomes Vesicle Nucleolus Smooth ER Cytoplasm Nucleus 58. Name 3 differences between plant cells and animal cells. Plant cells have a rigid cell wall Plant cells usually have chloroplasts Plant cells often have a central vacuole











