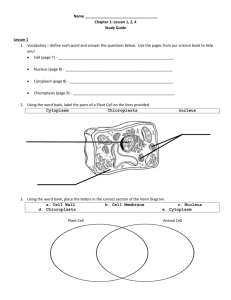
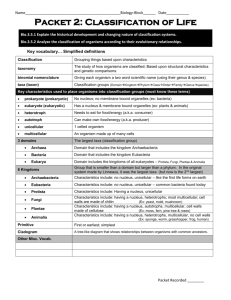
Name _______KEY_____________________________ Date Pd
advertisement

Name _______KEY_____________________________ Date ______________ Pd __________ Test Review: Taxonomy KEY DefineFirst use your Journal and Notes section of your binder to find answers. If you can’t find the definition/ answer check your textbook. 1. Taxonomy- branch of science dealing with classifying organisms 2. Classify- to group something by characteristics 3. Binomial Nomenclature- 2 name naming system for genus and species of an organism, developed by Carolus Linneaus 4. Domain- broadest level of classification, there are 3 Domains 5. Kingdom- 2nd broadest level of classification, there are 6 Kingdoms 6. Species- most specific classification level of an organism, also means “kind” 7. Prokaryote- cell without a nucleus, genetic information free floating 8. Eukaryote- cell with a nucleus, genetic information inside nucleus 9. Heterotroph- organism that eats other organisms for energy 10. Autotroph- organism that can make its own food 11. Multicellular- made of many cells 12. Unicellular- made of one cell Short Answer 13. What do all living organisms have in common? They are composed of cells 14. What is a cell? The cell is the basic unit of life. The basic unit of structure and function in all life. 15. All living organisms are composed of how many cells? All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 16. Scientists classify organisms based on their _____structure___________, _____function _______, and ____relationships__________. Name _______KEY_____________________________ Date ______________ Pd __________ 17. What 4 characteristics classify all organisms into one of the six Kingdoms? Unicellular or Multicellular- one or many cells Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic- presence of nucleus in cells Autotrophic or Heterotrophic- how nutrients are obtained Method of Reproduction- sexual or asexual 18. In Taxonomy, scientists give organisms a specific scientific name for each species, what is the benefit of having a common naming system? Scientists can communicate about experiments and theories about organisms and know that they are discussing the same organism. 19. What is the correct format for writing the genus and species name according to Binomial nomenclature? First word capitalized (genus) Second word lowercase (species) Both words underlined or italicized Ex: Homo sapien Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells 21. List some trait unique to each cell type No nucleus No or very few organelles (cell parts) Small and simpler Inflexible cell wall around cell True Nucleus Has many organelles (cell parts) Larger and more complex Flexible Cell membrane around cell 22. Describe their nucleus and genetic material Do not have a nucleus Genetic material free inside cell Genetic material is circular (kind of looks like scribble scrabble) but is free floating, there is no nucleus around it Has a true nucleus Genetic material enclosed inside nucleus Genetic material is arranged on X shaped chromosomes inside the nucleus 23. Describe organelles None 20. Draw an example of each type of cell, be able to recognize Many membrane bound organelles Name _______KEY_____________________________ Date ______________ Pd __________ 24. What are some similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Both are cells Both are living Both are microscopic Both contain genetic material Both are bound by an outer covering Both have cytoplasm Both have a metabolism for getting energy Both reproduce 25. List the levels of classification from broadest to most specific. Memorize. Use your Mnemonic! Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species 26. What are the 3 Domains? All living organisms are organized into three Domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya 27. What are the 6 Kingdoms? Archaebacteria, Eubacteria ,____ Protista, Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia ___ 28. In the Domain Archaea, what are the possible Kingdoms? Archaebacteria 29. In the Domain Bacteria, what are the possible Kingdoms? Eubacteria 30. In the Domain Eukarya, what are the possible Kingdoms? Protista, Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia 31. In which domain do all the Kingdoms have a nucleus? Eukarya Name that Kingdom 32. Multicellular, Autotrophic, Eukaryotic 33. Unicellular, Prokaryotic, can be beneficial or harmful 34. Multicellular, Heterotrophic, Eukaryotic, very diverse 35. Unicellular, Prokaryotic, ancient 36. Single-celled, cells have a nucleus, autotrophic or heterotrophic 37. Multicellular, Heterotrophic, can be beneficial or harmful ______Plantae__________ ______Eubacteria_________ ______Animalia________ ______Archeabacteria___ ______Protista__________ ______Fungi____________