Guide
advertisement

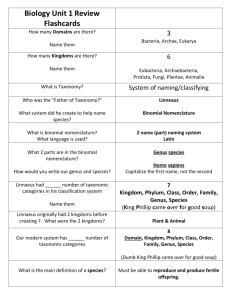
Name ________________________________________________________ Block _____________ Unit 2: Classification & Kingdoms Study Guide 1. What is taxonomy? The discipline where scientists classify organisms and assign universally accepted names to each organism. 2. From the name Ursus americanus, label which is the genus, and which is the species. How did you know which is which? Ursus is the genus and americanus is the species. The genus is always capitalized and the species is lower-case. 3. What is Linnaeus credited for creating/developing? (Two things) Linnaeus developed the binominal nomenclature system of naming (two word naming system) as well as the 7 categories/taxons of classification. 4. List all 7 taxons from largest (most inclusive) to smallest (most specific). Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (Kids playing catch over freeways get squashed) 5. Can you reclassify an organism? What information would you consider if you can? Yes, as more information is available on an organism, it can be reclassified. This information can include structures, genetics (DNA), evolutionary relationships, embryology, and reproductive potential. 6. The earliest forms of life are believed to have belonged to what kingdom? Earliest forms of life are believed to have belonged to the kingdoms Eubacteria and Archaeabacteria. 7. What are some different characteristics we use to classify organisms? Different characteristics can include structures, genetics (DNA), evolutionary relationships, embryology, and reproductive potential. 8. Study your cladogram sheet! 9. What is the definition of species? It is a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring. 10. When looking at the scientific name of organisms, do you look at the genus name or the species name to see if two organisms are more closely related? Why? You look at the genus name because it is the noun and the species is just a descriptor word (adjective) 11. Name all 6 Kingdoms. Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia 12. Define the following words: 13. (1) Autotroph: Makes its own food (remember it AUTOmatically makes food for itself) (2) Heterotroph: Needs to eat/consume/absorb other organisms for food (hetero=other, gets food from others) (3) Prokaryote: Does NOT have nucleus (pro=NO nucleus) (4) Eukaryote: HAS nucleus (eu=true nucleus) 14. Why do we need scientific names? Why can’t we just use common names for organisms? Common names can be misleading because they are misnomers (ex. starfish, jellyfish, neither are actual fish) or common name may vary from region to region (ex: puma & mountain lion refer to the same animal) 15. What are the three domains? Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya 16. What are the kingdoms that comprise each domain? Bacteria – Eubacteria Archaea - Archaebacteria Eukarya – Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia 17. List at least 2 similarities and 2 differences between plants and fungi Similarities: Eukaryotes with cell walls Differences: Plants are autotrophic and have cell walls made of cellulose, Fungi are heterotrophs with cell walls made of chitin 18. Why won’t an antibiotic work on a virus? Antibiotics treat infections or diseases caused by bacteria. Viruses are not living things and are not affected by antibiotics. Study the following: Gold Knowledge Sheet All notes (Classification notes, More classification notes, Kingdoms Notes) Blue Vocab Sheet 6 Kingdoms Mural & Chart Cladogram Worksheet Worm Dichotomous Key Worksheet