Therapeutics/Pharmacology – Anticonvulsant Drug Classification
advertisement

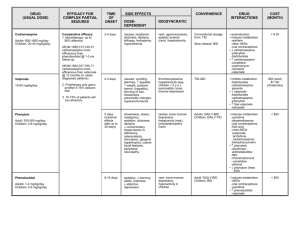
ANTICONVULSANT DRUG CLASSIFICATION BARBITURATES Phenobarbitol Primidone Mephobarbitol HYDANTOIN Phenytoin Mephenytoin Ethotoin Fosphenytoin SUCCINIMIDES Ethosuximide Methsuximide Phensuximide SULFONAMIDES Zonisamide Trimethadione OXAZOLIDINEDIONES Paramethadione Diazepam Lorazepam BENZODIAZEPINES Clonazepam Flebamate Clorazepate dipotassium Carbamazepine Valproic acid Topiramate Tiagabine Levetiracetam Drug Carbamazepine Mechanism Act by reducing polysynaptic response and blocking post synaptic potentiation. Dose Initial oral dose of 200 mg twice daily. Gradually inc to 800-2000 mg daily in divided doses Children <12 yrs: 10-20 mg/kg daily Phenytoin Inhibits spread of seizures at motor cortex and blocks posttetanic potentiation by influencing synaptic transmission. There is an alteration of ion fluxes in depolarization, repolarization, and membrane stability phase and altering calcium uptake in presynaptic terminals LD: 900 mg – 1.5 mg iv 300-700 mg daily Children: 4-7 mg/kg divided every 12 hours. IV dose of 15 mg/kg may be given. MISC Lamotrigine Gabapentin Pregabalin Oxcarbazeping ADRS & SES Jaundice, abd pain, pale stool, darkened urine, unusual bruises and bleeding, fever, sore throat, mouth ulcer. Dizziness, drowsiness, unsteadiness, ataxia, diplopia, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, hyponatremia, aplastic anemia (rare), thrombocytopenia, ameia, pruritic and erythematous rashes, steven-johnsons syndrome, and lupus erythematosus Swollen or tender gums, skin rash, nausea, vomiting, slowwn glands, bleeding, jaundice, fever, sore throat, infection, ataxia, dysarthria, insomnia, maculopapular rashes, lupus erythematosus, gingival Valproic Acid Increases levels of GABA; potentiates a postsynaptic GABA response by inhibiting the enzymatic response ofr the catabolism of GABA; affects the potassium channel, creating a direct membrane-stabilizing effect Orally 1000-3000 mg daily in divided doses Children: 15-60 mg/kg daily in 23 divided doses Should be taken with food Phenobarbital Increases the seizure threshold by decreasing postsynaptic excitation by stimulating postysynatic GABA-A receptor inhibitor responses as a CNS depressant 90-300 mg daily in 3 divided doses or single dose at bedtime Children: 3-6 mg/kg in 2 dicided doses Lamotrigine Similar to phenytoin. Inhibition of voltagedependent sodium currents and reduction of sustained repetitive neuronal activity. 50 mg/day in 2 divided doses (Patients taking valproic acid must be given 25 mg every other day) upto 100 mg/day in (25 mg valproic acid daily) Children: 0.6 mg/kg/day in two divided doses (0.15 mg/kg/day if on valproic acid) upto 1.2 mg/kg/day (0.3 mg/kg/day of valproic acid) hyperplasia, coarsening of facial features, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, granulocytopenia Abd pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia (signs of pancreatitis), tremor, ataxia, diplopia, lethargy, drowsiness, behavioral changes, dipression, inc appetite, alopecia, petechiae, thrombocytopenia, bruising, hematoma, and beeding, inc AST, ALT, LDH. Dec levels of prolactin irregular menses and secondary amenorrhea Sore throat, mouth sores, easy bruising or bleeding, signs of infection, agitation, confusion, lethargy, drowsiness, hypoventilation, apnea, hypotension, bradycardia, nausea, diarrhea, consiptaiton, megaloblastic anemia, osteomalacia, Steven-Johnson syndrome Dizziness, diplopia, ataxia, blurred vision, nausea, dose-reated rash, and vomiting, headache, dyspepsia, diarrhea