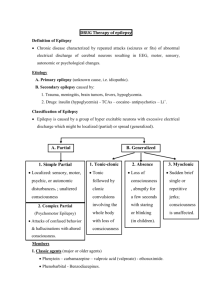
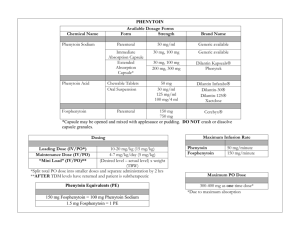
13.11.02 - Drug Chart - Individual.utoronto.ca
advertisement
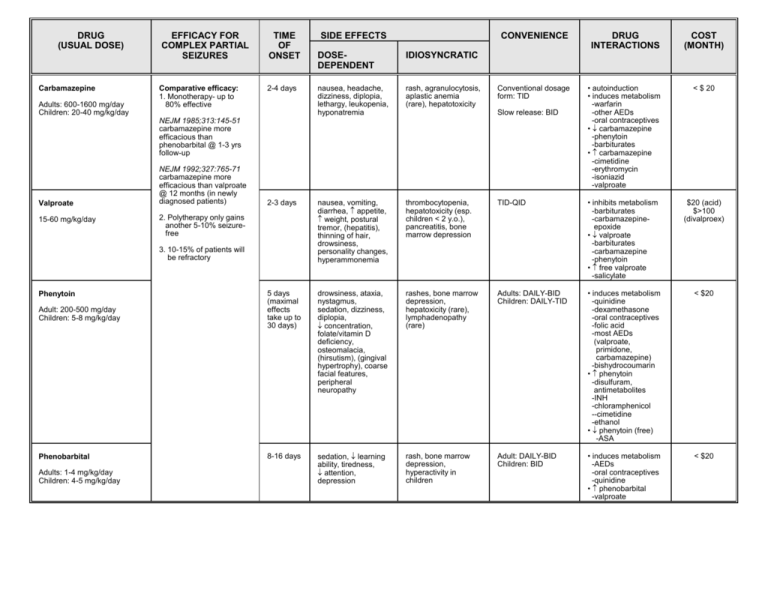
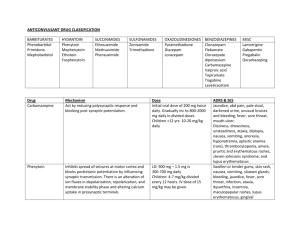
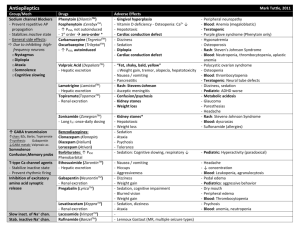
DRUG (USUAL DOSE) Carbamazepine Adults: 600-1600 mg/day Children: 20-40 mg/kg/day EFFICACY FOR COMPLEX PARTIAL SEIZURES Comparative efficacy: 1. Monotherapy- up to 80% effective TIME OF ONSET SIDE EFFECTS CONVENIENCE DRUG INTERACTIONS COST (MONTH) Conventional dosage form: TID • autoinduction • induces metabolism -warfarin -other AEDs -oral contraceptives • carbamazepine -phenytoin -barbiturates • carbamazepine -cimetidine -erythromycin -isoniazid -valproate < $ 20 DOSEDEPENDENT IDIOSYNCRATIC nausea, headache, dizziness, diplopia, lethargy, leukopenia, hyponatremia rash, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia (rare), hepatotoxicity 2-3 days nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, appetite, weight, postural tremor, (hepatitis), thinning of hair, drowsiness, personality changes, hyperammonemia thrombocytopenia, hepatotoxicity (esp. children < 2 y.o.), pancreatitis, bone marrow depression TID-QID • inhibits metabolism -barbiturates -carbamazepineepoxide • valproate -barbiturates -carbamazepine -phenytoin • free valproate -salicylate $20 (acid) $>100 (divalproex) 5 days (maximal effects take up to 30 days) drowsiness, ataxia, nystagmus, sedation, dizziness, diplopia, concentration, folate/vitamin D deficiency, osteomalacia, (hirsutism), (gingival hypertrophy), coarse facial features, peripheral neuropathy rashes, bone marrow depression, hepatoxicity (rare), lymphadenopathy (rare) Adults: DAILY-BID Children: DAILY-TID • induces metabolism -quinidine -dexamethasone -oral contraceptives -folic acid -most AEDs (valproate, primidone, carbamazepine) -bishydrocoumarin • phenytoin -disulfuram, antimetabolites -INH -chloramphenicol --cimetidine -ethanol • phenytoin (free) -ASA < $20 8-16 days sedation, learning ability, tiredness, attention, depression rash, bone marrow depression, hyperactivity in children Adult: DAILY-BID Children: BID • induces metabolism -AEDs -oral contraceptives -quinidine • phenobarbital -valproate < $20 2-4 days Slow release: BID NEJM 1985;313:145-51 carbamazepine more efficacious than phenobarbital @ 1-3 yrs follow-up Valproate 15-60 mg/kg/day NEJM 1992;327:765-71 carbamazepine more efficacious than valproate @ 12 months (in newly diagnosed patients) 2. Polytherapy only gains another 5-10% seizurefree 3. 10-15% of patients will be refractory Phenytoin Adult: 200-500 mg/day Children: 5-8 mg/kg/day Phenobarbital Adults: 1-4 mg/kg/day Children: 4-5 mg/kg/day DRUG (USUAL DOSE) Primidone Adults: 500-1000 mg/day Children: 10-20 mg/kg/day Clonazepam Adults: 1.5 - 10 mg/day (in 2-3 divided doses) Initiate at 1.5 mg/day and increase by 0.5 - 1.0 mg every 3 days. Children: 0.01 - 0.03 mg/kg daily in 2-3 divided doses, increase to a maximum of 0.2 mg/kg daily. EFFICACY FOR COMPLEX PARTIAL SEIZURES TIME OF ONSET SIDE EFFECTS CONVENIENCE DRUG INTERACTIONS COST (MONTH) DOSEDEPENDENT IDIOSYNCRATIC 2-3 days (maximal effects take up to 2 wks) sedation, ataxia, GI, cognitive effects, hyperactivity in children, impotence, folate deficiency, vitamin D deficiency bone marrow depression Adults: BID-TID Children: TID-QID • induces metabolism -AEDs -quinidine -tricyclics -corticosteroids -chlorpromazine -furosemide • primidone -valproate < $20 2-3 days (maximal effects in 2 weeks) sedation, ataxia, behavioural problems in children, bronchial hypersecretions, hypersalivation bone marrow depression (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) BID-TID • Effect of clonazepam on: < $20 • levodopa • digoxin • clonazepam by phenytoin DRUGS (USUAL DOSE) Vigabatrin Adult: 2-4 g/day Children (wt-specific): (e.g. 35kg, 1.5-3 g/day) Gabapentin Adult: 900-2400 mg/day Children (4-12): 15-20 mg/kg/day Lamotrigine Adult: with valproate: 50-100 mg/day with inducers: 200-500 mg/day alone: 50-200 mg/day Children: with valproate: 1-5 mg/kg with inducers: 5-15 mg/kg alone: 2-8 mg/kg Topiramate Adult:* 200-400 mg/day (2 divided doses) Initiate at 50 mg qhs and increase weekly by 50 mg/day (in 2 divided doses) to effect. Children: approved for use in children 2-16 years. Dosage reduction required in renal disease patients. Fosphenytoin (Cerebyx - PD) Adult : LD: 10-20 Phenytoin Equivalents (PE)/kg IV (not to exceed 150mg PE/min) MD: 4-6 mg PE/kg/day EFFICACY FOR COMPLEX PARTIAL SEIZURES (BGH #10) SIDE EFFECTS CONVENIENCE DRUG INTERACTIONS COST/MONTH 50% in seizure frequency in 50% of patients when used as adjunct therapy maximal doses achieved in 1-2 wks somnolence (12%), fatigue (9%), wt gain (5%), headache (4%), ataxia (2%), (microvaculization of white matter of brain of rats), long-term sideeffects, ophthalmalogical abnormalities (optic atrophy, visual field constriction, etc.) DAILY-BID (FC-tablets) • none • ( phenytoin after 3-4 weeks?) $113-226 Sabril® - Marion Merrel Dow 50% in seizure frequency in 26% of patients when used as adjunct therapy maximal doses achieved in 1-2 wks somnolence (5%), dizziness (20%), ataxia (17%), fatigue (15%) Three divided doses daily (capsules) • none • dose-dependent absorption • antacids absorption by 25% $65->194 Neurontin® - Parke-Davis 50% in seizure frequency in 18-69% when used as adjunct therapy. Lancet 1995 345:476-9 maximal doses achieved in 2-4 wks dizziness (15-40%), ataxia (36%), diplopia (14%), nausea (29%) rash (dose-related) DAILY-BID (scored tablet) • lamotrigine -inducers • lamotrigine -valproate • carbamazepineepoxide levels? $22-176 Lamictal® - Borroughs Wellcome 50% in seizure frequency in 44-57% when used as adjunct therapy. Neurology 2001; 56(Suppl 3): A332 Topiramate comparable to carbamazepine and valproate in newly diagnosed patients with partial seizures maximal doses achieved in 2-4 weeks somnolence (18%), dizziness (15 %), ataxia (15 %), headache (17%) paresthesia (15%), psychomotor slowing (6%), speech-related problems, mood changes (irritability, depression), rarely kidney stones (1.5%), weight loss, acute myopia (decreased visual acuity, ocular pain, redness) and secondary angle closure glaucoma. BID (available as 25, 100 and 200 mg tablets) • drugs which topiramate concentrations • phenytoin • carbamazepine • (valproic acid) • effect of topiramate on other drugs • valproate • digoxin $120-190 Topamax® - JanssenOrtho Restricted to use as an alternative to IV phenytoin For status epilepticus Converts to phenytoi n Identical to phenytoin except: increased frequency of paresthesias and pruritis (not usually at the infusion site). Daily infusion (ampoules) Caution when administered with drugs highly bound to albumin. $17.64 per amp (100mg/2ml amp) Lamotrigine comparable to carbamazepine in newly diagnosed patients with partial seizures For short term use only Children: safety has not been established Marijuana TIME OF ONSET Category 2 of Marijuana Medical Access Regulations (July 30th, 2001) Interacting drugs identical to phenytoin