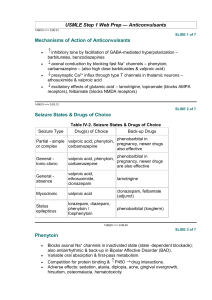
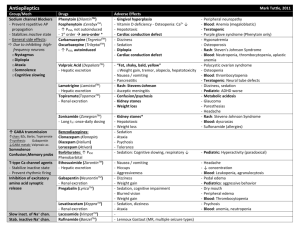
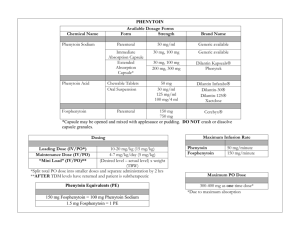
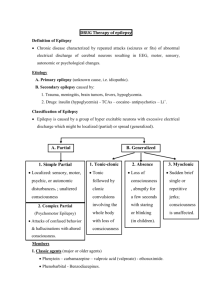
Pharmacology of Epilepsy and Migraines Rachel W. Flurie, PharmD, BCPS VCU School of Pharmacy Which ASD Am I? I am a first generation ASD and am very effective for focal seizures. I induce many CYP450 enzymes. If I reach toxic serum levels the first warning sign may be nystagmus. A. Lacosamide B. Phenytoin C. Carbamazepine D. Valproic acid PHENYTOIN Pharmacokinetics Saturable absorption Divide doses greater than 400 mg into at least two doses Steady state achieved in 7-10 days (half-life 9-42 hours) Loading doses may be used Saturable metabolism Metabolized by CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 A small change in dose may result in a very large disproportionate increase in blood level The dose where saturation occurs cannot be predicted Saturation occurs at lower doses in the elderly Highly protein bound (~90%) and affected by Low albumin Age Renal failure Other drugs PHENYTOIN PHARMACOKINETICS CORRECTED PHENYTOIN CONCENTRATION Patient’s Serum Albumin (gm/dL) 3.5 Measured Total Phenytoin Concentration (mcg/mL) 3.0 2.5 2.0 Adjusted Total Phenytoin Concentration (mcg/mL) 5 6 7 8 10 10 13 14 17 20 15 19 21 25 30 *Adjusted concentration = measured total phenytoin concentration (0.2 x albumin) + 0.1 Note: Can draw free phenytoin levels to avoid albumin interference Therapeutic drug range: Total: 10-20 mcg/mL Free: 1-2 mcg/mL Which ASD Am I? I am a CYP450 enzyme inducer. Similar versions of me have been created since my inception. I commonly cause low serum sodium levels but can also cause a bad rash. A. Zonisamide B. Lamotrigine C. Carbamazepine D. Topiramate CARBAMAZEPINE Pharmacokinetics Auto-induction (induces its own metabolism) Begins after 3 to 5 days, but takes 21 to 28 days to complete Half-life becomes shorter with continued dosing (25-65 hrs vs 12-17 hrs) Occurs with each dosage increase Metabolized to 10,11-diepoxide which is active Suspension is absorbed more quickly than immediate release tablets Variable absorption with generic formulations Therapeutic drug range: 4-12 mcg/mL OXCARBAZEPINE (TRILEPTAL®) Pharmacokinetics Pro-drug; rapidly converted to the monohydrate derivative (MHD) which is active There is no auto-induction MHD excreted unchanged and metabolized by glucuronidation Faster clearance in children Slower clearance in elderly ESLICARBAZEPINE (APTIOM®) Pharmacokinetics Prodrug with the same active metabolite as oxcarbazepine No auto-induction Active drug undergoes glucuronidation Once daily dosing due to longer half-life 66% excreted renally (renal dose adjust) Which ASD Am I? I am a CYP450 inhibitor. I can also be used for migraines. Better monitor liver enzymes because I can cause hepatoxicity. Avoid me in women who are pregnant. A. Topiramate B. Lacosamide C. Levetiracetam D. Valproic acid VALPROIC ACID Pharmacokinetics Absorption is dependent of formulation Syrup and capsule are rapidly absorbed – 3-4 x / day “Sprinkle,” delayed release (Depakote DR) and sustained release (Depakote ER) are slowly absorbed Sprinkle – 2-3 x / day Depakote DR – 2-3 x/ day Depakote ER – once daily Cannot be crushed VALPROIC ACID Pharmacokinetics Highly protein bound (90-95%) which saturates in the therapeutic range Nonlinear PK As dose or concentration increases, clearance rate increases Therapeutic drug range: Total: 50-100 mcg/mL Free: 5-25 mcg/mL Multiple metabolites (10+) 4-ene-VPA metabolite may cause hepatotoxicity VALPROIC ACID Practice Question Patient MH comes to your office with a new diagnosis of migraines. She’s tried acetaminophen OTC without relief and is experiencing the beginnings of a migraine today that she says is mild. PMH: 20 weeks pregnant, asthma Medications: prenatal MVI, albuterol HFA as needed What is the most appropriate agent to recommend for abortive therapy? A. Acetaminophen-aspirin-caffeine B. Ibuprofen C. Ergotamine tartrate D. Topiramate Practice Question A patient with new onset focal seizures was started on levetiracetam in the hospital. Today they are complaining of mood swings and experienced a breakthrough seizure 1 week ago. PMH: Depression, obesity Meds: sertraline Which of the following is the most appropriate therapy to switch the patient to? A. Carbamazepine B. Brivaracetam C. Valproic acid D. Eslicarbazepine