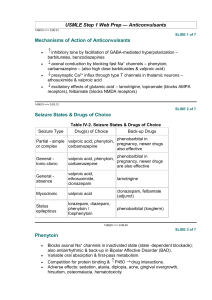
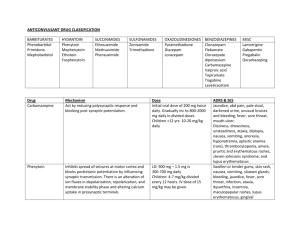
Psychotropic MedicationsMood Stabilizers Valproic Acid (Depakote) Diana Osipova Valproic Acid (Depakote) Generic Name Trade Name Indications Valproic acid is used alone or with other medications to treat certain types of seizures. Valproic acid is also used to treat mania (episodes of frenzied, abnormally excited mood) in people with bipolar disorder (manic-depressive disorder; a disease that causes episodes of depression, episodes of mania, and other abnormal moods). It is also used to prevent migraine headaches but not to relieve headaches that have already begun. Valproic acid is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. It works by increasing the amount of a certain natural substance in the brain. Mechanism of action Works by increasing concentrations of GABA in the brain Common Side Effects ● drowsiness ● dizziness ● headache ● diarrhea ● constipation ● changes in appetite ● weight changes ● back pain ● Adverse Side Effects ● unusual bruising or bleeding ● tiny purple or red spots on the skin ● fever ● rash ● bruising ● hives agitation ● difficulty breathing or swallowing ● mood swings ● swollen glands ● abnormal thinking ● swelling of face, eyes, lips, tongue, or throat ● uncontrollable shaking of a part of the body ● peeling or blistering skin ● problems with walking or coordination confusion ● uncontrollable movements of the eyes ● ● blurred or double vision ● tiredness ● ringing in the ears ● vomiting ● hair loss ● drop in body temperature ● weakness or swelling in the joints Contraindications Hypersensitivity, bleeding disorder, cirrhosis, pancreatitis, Proceed with caution when you have low albumin and renal impairment Benefits and Reasons for taking Valproic Acid Valproic acid is an anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer medication. It is extensively used in the adult population to treat convulsions, migraines, and bipolar disorders. Nursing Implications ■ Assessment and drug effects ■ Monitor for therapeutic effectiveness achieved with serum levels of valproic acid at 50–100 mcg/mL. ■ Monitor patient alertness especially with multiple drug therapy for seizure control. Evaluate plasma levels of the adjunctive anticonvulsants periodically as indicators for possible neurologic toxicity. ■ Monitor patient carefully during dose adjustments and promptly report presence of adverse effects. Increased dosage is associated with frequency of adverse effects. ■ Lab tests: Perform baseline platelet counts, bleeding time, and serum ammonia, then repeat at least q2mo, especially during the first 6 mo of therapy. ■ Multiple drugs for seizure control increase the risk of hyperammonemia, marked by lethargy, anorexia, asterixis, increased seizure frequency, and vomiting. Report such symptoms promptly to physician. If they persist with decreased dosage, the drug will be discontinued. Patient and Family Education ● Do not discontinue therapy abruptly; such action could result in loss of seizure control. Consult physician before you stop or alter dosage regimen. ● Note to diabetic patients: Drug may cause a false-positive test for urine ketones. Notify physician if this occurs; a differential diagnostic blood test may be indicated. ● Notify physician promptly if spontaneous bleeding or bruising occurs (e.g., petechiae, ecchymotic areas, otorrhagia, epistaxis, melena). ● Withhold dose and notify physician for following symptoms: visual disturbances, rash, jaundice, light-colored stools, protracted vomiting, diarrhea. Fatal liver failure has occurred in patients receiving this drug. ● Avoid alcohol and self-medication with other depressants during therapy. ● Consult physician before using any OTC drugs during anticonvulsant therapy. Combination drugs containing aspirin, sedatives, and medications for hay fever or other allergies are particularly UNSAFE. ● Do not drive or engage in potentially hazardous activities until response to drug is known. ● Inform doctor or dentist before any kind of surgery that you are taking valproic acid. ● Carry medical identification card at all times. It needs to indicate medical diagnosis, medication(s), physician's name, address, and telephone number. ● Do not breastfeed while taking this drug Resources U.S. National Library of Medicine. (n.d.). Valproic acid: Medlineplus Drug Information. MedlinePlus. Retrieved February 2, 2023, from https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682412.html Availability. VALPROIC ACID (DIVALPROEX SODIUM, SODIUM VALPROATE). (n.d.). Retrieved February 2, 2023, from http://robholland.com/Nursing/Drug_Guide/data/monographframes/V004.html