Mountain Building Lesson Flyswatter Game Deformation – the

Mountain Building Lesson Flyswatter Game
1.
Deformation – the process by which rocks change shape when under stress
2.
Stress – amount of force per unit area that is placed on an object
3.
Tectonic plate – a block of lithosphere that consists of crust and the outermost part of the mantle
4.
Low temperatures – What temperatures can make materials more brittle?
5.
Higher temperatures – What temperature allows rock to bend?
6.
Break – If stress becomes too great, or is applied quickly the rocks can _____?
7.
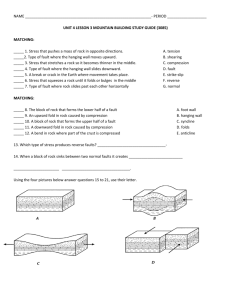
Folds – When rocks bend ________________ form.
8.
Fault – When rocks break ________________ form.
9.
Folds – Bends in the rock
10.
Syncline – a downward fold (use foam to show a syncline)
11.
Anticline – An upward fold (use form to show an anticline)
12.
On the outside of the fold – Where are the youngest rocks in an anticline found?
13.
On the inside of the fold – Where are the youngest rocks in a syncline found?
14.
Fault –Crack that forms when large blocks of rock break and move past each other.
15.
Fault blocks – blocks of rock on either side of the fault
16.
Fault plane – where two fault blocks meet
17.
Hanging wall – the block of rock above the fault plane
18.
Footwall – the block of rock below the fault plane
19.
Shearing – stress that pushes rock in parallel by opposite directions
20.
Strike-slip – The type of fault where the fault blocks move past each other horizontally
21.
San Andreas Fault – an example of a strike-slip fault
22.
Tension – stress that stretches or pulls rock apart
23.
Normal Fault – The type of fault where the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall.
24.
Compression – stress that squeezes or pushes rock together
25.
Reverse Fault - The type of fault where the hanging wall moves upward relative to the footwall.
26.
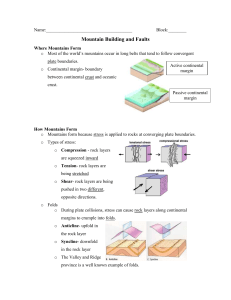
Uplift – a process that can cause land to rise
27.
Folded Mountains – mountains that form when rock layers are squeezed together and pushed upward
28.
Convergent Boundaries – Folded mountains usually form at this type of boundary
29.
Appalachian Mts. – an example of folded mountains
30.
Volcanic Mts. – mountains that form when melted rock erupts onto Earth’s surface
31.
Mt. St. Helens – an example of a volcanic mountain
32.
Fault-Block Mountains – mountains that form when tension makes the lithosphere break into many normal faults
33.
The Teton Mts. – an example of fault-block mountains