mountain folded
advertisement
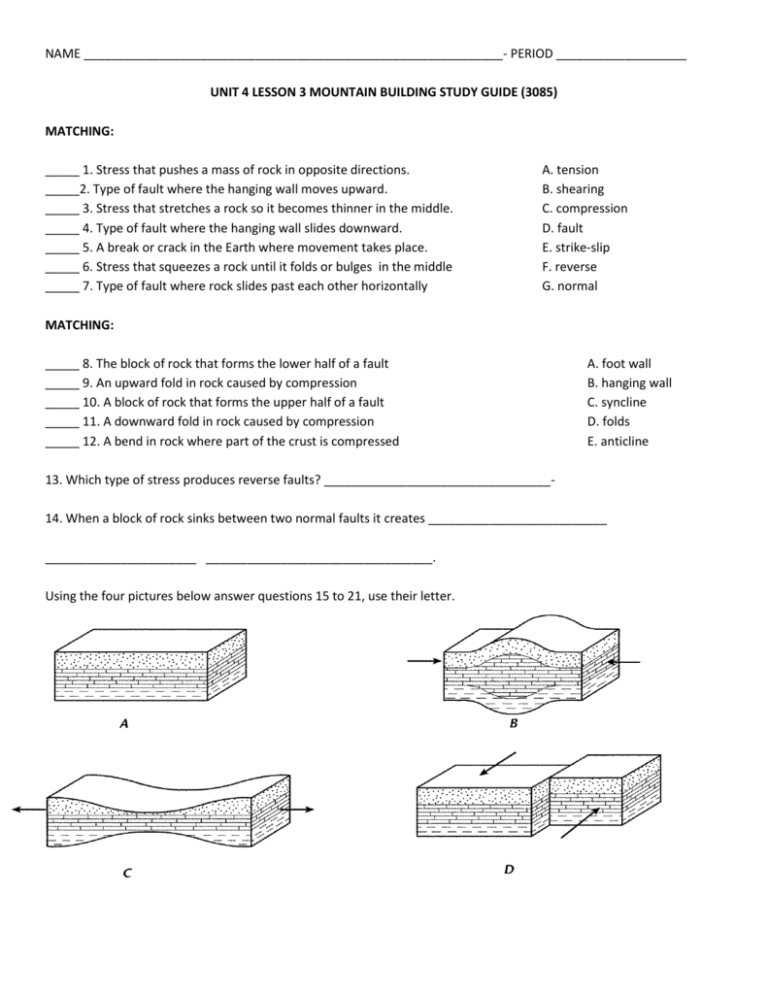
NAME _____________________________________________________________- PERIOD ___________________ UNIT 4 LESSON 3 MOUNTAIN BUILDING STUDY GUIDE (3085) MATCHING: _____ 1. Stress that pushes a mass of rock in opposite directions. _____2. Type of fault where the hanging wall moves upward. _____ 3. Stress that stretches a rock so it becomes thinner in the middle. _____ 4. Type of fault where the hanging wall slides downward. _____ 5. A break or crack in the Earth where movement takes place. _____ 6. Stress that squeezes a rock until it folds or bulges in the middle _____ 7. Type of fault where rock slides past each other horizontally A. tension B. shearing C. compression D. fault E. strike-slip F. reverse G. normal MATCHING: _____ 8. The block of rock that forms the lower half of a fault _____ 9. An upward fold in rock caused by compression _____ 10. A block of rock that forms the upper half of a fault _____ 11. A downward fold in rock caused by compression _____ 12. A bend in rock where part of the crust is compressed A. foot wall B. hanging wall C. syncline D. folds E. anticline 13. Which type of stress produces reverse faults? _________________________________14. When a block of rock sinks between two normal faults it creates __________________________ ______________________ _________________________________. Using the four pictures below answer questions 15 to 21, use their letter. 15. Which of the pictures show no stress involved? ______ 16. Which picture shows compression stress? ___________ 17. Which picture shows tension stress? _______________ 18. Which picture shows shearing stress? ______________ 19. Which type of stress B, C, or D would cause a normal fault to form? ________ 20. Which type of stress B, C, or D would cause a reverse fault to form? ________ 21. Which type of stress B, C, or D would cause a strike-slip fault to form? ________ Using the pictures below answer questions 22 – 25 1 . 22. Which diagram shows a normal fault? ________ What stress caused this fault? __________________ 23. Which diagram shows a reverse fault? ________What stress caused this fault? __________________ 24. Which diagram shows a strike-slip fault? ______What stress caused this fault? ___________________ 25. In diagram B what wall is #1, a hanging wall or a foot wall? ___________________________________ 26. What are the three ways mountains can form? ____________________________________ _________________________________ __________________________ 27. What is the process that changes a rocks shape under stress called? ________________________________________ 28. In a syncline, where are the oldest rocks found? Circle one 29. In an anticline, where are the oldest rocks found? Circle one inside the fold inside the fold outside the fold outside the fold 30. How do folded, volcanic and fault-block mountains differ? 31. How are folded, volcanic and fault-block mountains the same? 32. Imagine you are walking along and see an active volcano in the distance. What can you conclude about the area? 33. When two land masses collide what type of mountain do they form? ________________________________34. When a mountain is made of lava what type of mountain is this? ____________________________________ 35. When a mountain is made from two normal faults, what type of mountain is this? ____________________________________________________________