5.2 Notes
Name: _____________________________________ Date: _________________ Period: ______
Chapter 5.2: The Results of Stress
1.
Rock Deformation a.
Caused by the high ___________________ and _________________ of geologic _________________. b.
It is possible for the ____________ to return to its original _________ if the ______________ (stress) is applied and removed slowly. c.
When the ___________ passes the limits of the rock, the rock can be
__________________ permanently and may ___________.
2.
Folding a.
When ____________ responds to stress by becoming permanently
____________________ without breaking. b.
_________________ can be easily observed where the rocks are
______________________ inward and the layers of the rock move into new positions _____________________ breaking. (___________ may appear, but the rock layers remain ________________.) c.
_____________ of folds can vary greatly. i.
Some rock ____________ can be found within a small
____________-size rock while others span of ______________ of miles and must be seen from __________. d.
There are __________ types of rock folding: ___________________,
__________________, & _____________________. i.
An _______________ fold is an _____-curved fold in which the _______________ layer is in the ____________ of the fold.
1.
Mountain ______________ are generally found along
________________. ii.
A _________________ fold is a ____________-curved fold in which the ___________________ layer is in the center.
1.
________________ are generally found along synclines. iii.
A ____________________ fold is a fold in which both sections remain ____________________.
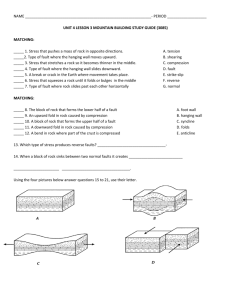
3.
Faulting & Fracturing a.
_______________ do not always respond to __________________ by folding. Under certain conditions rocks will actually ______________ when stress is applied.
Name: _____________________________________ Date: _________________ Period: ______ b.
___________________ & ____________________ of rocks generally occurs _______________ to the Earth’s surface where the rocks are
_________________ and under ___________ pressure. c.
A ___________________ is a break in rock where there is no rock
___________________ on either side of the ______________. d.
A ________________ is a break in rock along which rocks on either side of the break _______________. i.
A fault _____________ is the surface of a fault along which any _________________ occurs. ii.
The __________________ wall is the rock _________ the fault plane. iii.
The _________________ is the rock ______________ the fault plane. e.
There are four types of faults: ________________ Faults,
_________________ Faults, _______________ Faults, and
______________-_________ Faults. i.
A _____________ fault is a fault in which the ______________ wall moves _____________ relative to the footwall.
1.
These faults generally form along __________________ boundaries where the crust is being ____________ apart. ii.
A _______________ fault forms when ___________________ causes the hanging wall to move _____ relative to the footwall. iii.
A _______________ fault is a reverse fault where the fault plane is nearly ____________________. iv.
A strike-slip fault is a ____________ where the rock on either side of the fault plane ______________ horizontally past each other.