Deformation of Earth's Crust: Plate Tectonics & Geology
advertisement

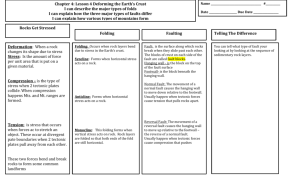
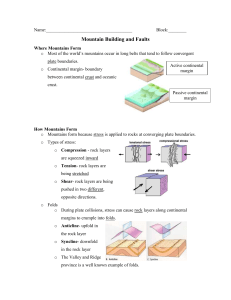
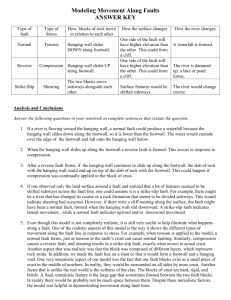
Science *Stack Test Corrections for collection Do Now: 12-2 HW: STUDY TODAY’S NOTES – QUIZ THURSDAY WORK ON PLATE TECTONIC PROJECT 1. LIST THE THREE TYPES OF PLATE BOUNDARIES AND SHOW THEIR MOVEMENT WITH ARROWS. Today ~ Power Point w/notes: Deformation of the Earth’s Crust Deforming the Earth’s Crust Types of Stress • Deformation: When the shape of a rock changes due to stress 1. Compression = squeezing or pushing together (convergent boundaries) 2. Tension = forces stretch an object (divergent boundaries) 3. Shearing = slicing motion back and forth (transform boundaries) Types of Folding • Folding: rock layers bending because of stress 1. Anticline = upward bend 2. Syncline = downward bend 3. Monocline = bend with horizontal ends Types of Faulting • Fault: the surface along which rocks break and slide past each other • Hanging wall: the layers of rock ABOVE the fault line (…above the diagonal) • Footwall: the layers of rock BELOW the fault line (…below the diagonal) FOOTWALL HANGING WALL Hanging Wall and Footwall How can I remember which is which??? Types of Faults • Normal Faults = the hanging wall slides down the foot wall • Reverse Fault = the hanging wall slides up the foot wall • Strike slip Fault = the rocks on either side of the fault line slide past each other “It’s Normal to Hang Down.” Folded Mountains • COMPRESSION…mountains formed at continental/continental convergent boundaries. • Ex. Appalachian Mountains Appalachian Mtns. COMPRESSION Fault Block Mountains • TENSION…causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down compared to the rocks around it. • Ex. Tetons (Wyoming) TENSION Volcanic Mountains • Formed at Ocean/Continental and Ocean/Ocean Convergent boundaries. • Ex. Ring of Fire Ring of Fire Mount Saint Helens You’ve seen this before!... NORMAL FAULT ANTICLINE SYNCLINE