ECOSYSTEMS - TangHua2012-2013
advertisement

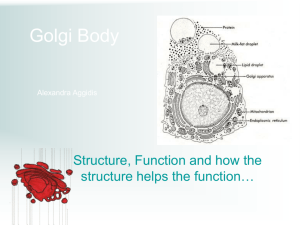
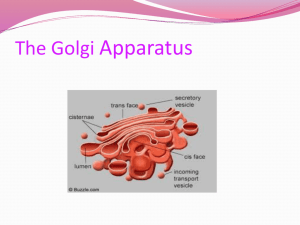
Cell Structure and Function Pt. 2 Inquiry into Life – pg. 53-59 Today’s Objectives: Analyze the functional inter-relationships of cell structures, including: Describe the major cell structures and their functions State the balanced chemical equation for cellular respiration Describe how the Endomembrane System functions to compartmentalize the cell and move materials through it Identify cell structures depicted in diagrams and electron micrographs The Endomembrane System Consists of: ____________ _____________ _______________ _________________ ________ _______________ _____________ This system compartmentalizes the cell so that particular _____________ reactions are restricted to specific ___________ Organelles of the endomembrane system are ____________ directly or by transport vesicles Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) System of interconnected flattened ________, _______, or _________. Begins at the nuclear envelope and branches throughout the _______________ to the cell membrane. Moves ______________ from one area to another. Location of ________ manufacture. Cells that produce __________ hormones, have an abundant smooth ER. Sections of both types of ER can break free in process called “__________” to produce small membrane bound sacs of either proteins or lipids called __________ Contains enzymes that synthesize lipids and related products such as steroids. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) Like Smooth E.R., but with attached _____________ Folds and processes ___________ and packages them in transport vesicles Abundant in cells that produce large amounts of __________ for export from the cell. Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Body) Stack, of a half dozen or more ___________ __________. On one side receives protein-filled vesicles from the ______ Sorts the proteins and packages them in vesicles at the other side. From here the vesicles move to different locations in the ______. Like the ______ _________ of the cell. Many transport vesicles from the ER travel to the Golgi apparatus for _____________ of their contents. The Golgi is a center of manufacturing, warehousing, _________, and ____________. The Golgi apparatus is especially extensive in cells specialized for ____________. Vesicles and Vacuoles Vesicles and vacuoles (larger versions) are _____________ bound ______ with varied functions. Vacuoles ___________ areas for water, nutrients, and salts. Vesicles A small __________ Storage sites in various kinds of molecules. ___________ and _____________ vesicles move their contents within the cell and in and out of the cell. Can be made by the Golgi Apparatus or from an ____________ of the cell membrane Lysosomes Special vacuoles formed by the _______ ________. (double membrane) Contain powerful _____________ ____________ that break down unwanted, foreign substances or worn-out parts of cells Ribosomes Contain __________ and ____________ subunits. Function as sites for ___________ ______________. Found on _____ (proteins for export) or in the ______________ (proteins for use in the cell). Several ribosomes together in a line, all producing the same protein is called a ___________________ Mitochondria (singular – Mitochondrion) Burn glucose to produce ______________ ___________________ Use up oxygen and give off carbon dioxide (this process is called __________ ______________). C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy Composed of two membranes. Considered the ______________ of the cell. Their inner membranes loop back and forth through the inner fluid, __________ of the mitochondria increasing its surface area and producing shelf-like structures called __________ This inner membrane is the site of cellular respiration Cytoskeleton _____________ components of the cytoskeleton provide internal ______________ to maintain the cell’s ________, anchor the _____________, and allows them to _______ when appropriate. Composed of _________________ (actin filaments) and ________________. Like the “bones and muscles” of the cell Cytoskeleton – Microfilaments (Actin Filaments) Primarily functions to maintain cell _____________ and cell movements Extremely thin ___________ fibers usually occurring in bundles. Similar in composition to the protein in the muscle (allows for muscle contraction). Cytoskeleton – Microtubules Maintain the ________ of the cell and act as ________ that organelles can move on. Thin ____________ several times larger than microfilaments. Found in both _____________ and certain organelles. Used to construct material to make up ______, __________ and _______________. Other Organelles Centrioles: short cylinders with a __________ pattern of microtubule triplets Two centrioles lying at right angles form the ____________ which is the microtubule organizing center (__________) Cilia and Flagella: ________ like projections that can move in ____________ fashion (like a whip) or __________ (like an oar) Cells with cilia and/or flagella are capable of ______________ Cilia also line the respiratory system and help remove foreign material from the _______ A cell is a living unit greater than the sum of its parts While the cell has many structures that have specific functions, they must work together. The enzymes of the _____________ and proteins of the _____________ are synthesized at the ______________. The information for these proteins comes from genetic messages sent by ______ in the ___________. All of these processes require energy in the form of ________, most of which is supplied by the ______________. A cell is a living unit greater than the sum of its parts.