Golgi Apparatus: Structure, Function & Cell Wall Synthesis
advertisement

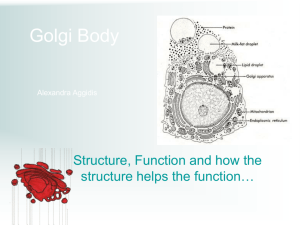
The Golgi Apparatus Defining: Golgi apparatus – a group of flattened stacks of membranes ( Golgi body) Cisternae – individual stacks of membranes ( Latin “ collecting vessels” Cisternae vary in number within the golgi apparatus, depending on what kind of cell they are in Functions: Collection of molecules Packaging of molecules Distribution of molecules The synthesis of cell wall components Parts: Transport vesicles – transport non synthesized materials from ER ( Endoplasmic reticulum) Lumen – storage for materials before going to the cis face Cis face – front, receiving end, located near ER, materials arrive via transport vesicles Parts: Trans face – back, exit, materials are discharged into secretory vesicles Secretory vesicles – carry synthesized materials to their correct location Lysosomes – digestive vesicles, contain high levels of degrading enzymes Collecting, Packaging, & Distribution Transport vesicles bring materials into the cis face, cis face synthesizes and moves materials into the trans face Trans face sends synthesized materials into secretory vesicles which then send them into their proper locations Synthesis: Cell wall components Noncellulose polysaccharides which form part of the cell walls in plants get synthesized After they are synthesized, they get sent to the plasma membrane, they are added to cellulose When added to cellulose, it is assembled on the exterior part of the cell wall