Endomembrane System
advertisement

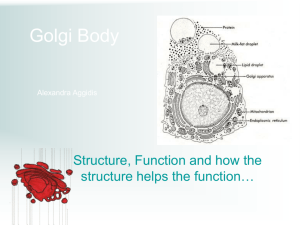
By Mariah Ghant, Saori Ishizuka, and Monica Lin Definition The set of membranes found in eukaryotic cells that carry out a variety of tasks in the cell Tasks include: Synthesis of proteins Protein transport into membranes and organelles out of the cell Metabolism and movement of lipids Detoxification of poisons Major Parts of the Endomembrane Nuclear Envelope Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth and Rough) Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Plasma Membrane Nuclear Envelope Function Structure Encloses the nucleus Double Membrane Separates its contents from the cytoplasm Perforated by pore structures Nuclear side is lined with nuclear lamina Ribosomes on cytoplasmic side Endoplasmic Reticulum Function Rough ER Structure Many proteins and Makes secretory proteins (glycoproteins) Keeps proteins seperated Makes transport vesicles “Membrane Factory” for the cells phospholipids added to its own membrane Has ribosomes continuous with smooth ER Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth ER Function Synthesis of Lipids Metabolism of Carbohydrates Detoxification of Drugs and Poisons Stores calcium ions Lacks ribosomes Structure Membranes system of interconnected tubules Golgi Apparatus Functions Multiple interactions with the product of the ER (proteins): Modifies Stores Sends to multiple destinations 2 poles of Golgi stack: Cis face- receives vesicles containing ER products trans face- dispatches vesicles Structure Consists of flattened membranous sacs (citernae) Lysosomes Functions Used in animal cells to digest macromolecules Autophagy- process of recycling the cell’s own organic material Phagocytosis- process of intracellular digestion in amoebas and small organisms Structure Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes Vacuoles Functions Their functions vary in different cells: Food Vacuoles- fuses with the lysosome during the process of phagocytosis Contractile Vacuolespump excess water out of the cell Central Vacuole- located in mature plant cells; holds important organic compound reserves; main repository of inorganic ions Major role in the growth of plants Structure Membrane-bounded vesicles Container shape Contains pigments that color cells Plasma Membrane Functions Encloses the entire cell Protein secretion occurs here after they’ve been carried by transport vesicles Structure Thin layer of cytosol between central vacuole and plasma membrane Interactions The endomembrane interacts with the nucleus via nuclear envelope The nuclear envelope is connected to the rough ER, which encloses the nucleus 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Review Nuclear envelope is connected to rough ER Membranes and proteins produced by the ER flow in the form of transport vesicles to the Golgi Golgi pinches off transport vesicles and other vesicles that give rise to: lysosomes other types of specialized vesicles vacuoles Lysosome is then available for fusion with another vesicle for digestion Transport vesicle carries proteins to plasma membrane for secretion Plasma membrane expands by fusion of vesicles; proteins are secreted from the cell Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PASnAaulK-Y