The Endomembrane System
advertisement
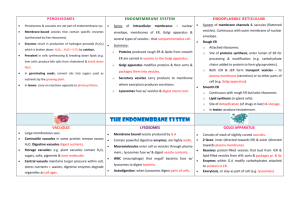
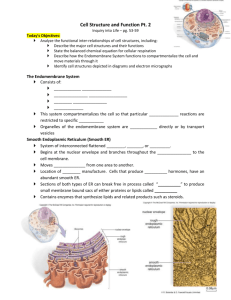
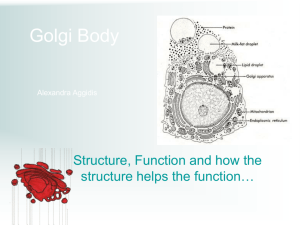
The Endomembrane System The Endomembrane System A series of membranes found in the interior of a eukaryotic cell. It divides the cell into compartments, channels the passage of molecules through the interior of the cell and provides surfaces for the synthesis of lipids and some proteins. The Endomembrane System One of the fundamental distinctions between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. The Endomembrane System 1. Nuclear Envelope 2. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 3. Golgi Apparatus 4. Vesicles (Vacuoles) Nuclear Envelope • Double membrane • Pores permit exit of ribosomal subuints • Separates nucleoplasm from cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum System of membrane channels continuous with outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. Rough ER is: Contiguous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. Studded with ribosomes cytoplasm side. on the Function of Rough ER Protein synthesis and modification. Function of Rough ER 1. Protein synthesis and modification. 2. Membrane Synthesis 3. Distributes Transport Vesicles Destinations of Rough ER Proteins • Exported from the cell • Sent to lysosomes or vacuoles • Embedded in plasma membrane Smooth ER Continuous with rough ER No ribosomes (hence smooth) Function of smooth ER 1. Synthetic processes Phospholipids Steroids Fatty acids 2. Forms transport vesicles 3. Stores Calcium 4. Detoxifies poisons Golgi Apparatus Delivery System Of the Cell Discovered in 1898 Named For Camillo Golgi Golgi Apparatus • Stack of 3-20 slightly curved saccules. • 1 to few (protists) • 20 or more - animal cells • Several hundred – plant cells Golgi Apparatus Receives protein-filled vesicles that bud from the ER. Vesicles fuse with membrane of Golgi apparatus cis face. Golgi Apparatus • Proteins modified as they pass through (form glycoproteins) • Move to outer (trans) face after modification. • Vesicles form & move to different locations in cell. • At plasma membrane, vesicles discharge contents as secretions. Vesicles Enzyme Storehouses Lysosomes – Intracellular digestion centers; bud from endomembrane system Microbodies Peroxisomes – Enzymes catalyze the removal of hydrogen atoms. Glyoxysomes – Found in plants. Enzymes convert fats into carbohydrates Lysosomes Intracellular digestion centers Produced by Golgi Membrane-enclosed vesicles Contains digestive enzymes (function best in acidic environment) Break down organelles Animation: Lysosome Formation Lysosomes Intracellular digestion centers Eliminates cells engulfed by phagocytosis. White blood cells use lysosomes to digest engulfed bacteria. Autodigestion - when lysosomes digest parts of cells. Apoptosis - programmed cell death, a normal part of development Tadpole tail absorption. Degeneration of webbing between fingers Peroxisomes • Abundant in cells that metabolize lipids • Detoxify alcohol in liver and yeast cells • Forms hydrogen peroxide that is broken down to water and oxygen by catalase. RH2 + O2 R + H2O2 H2O + O2 Glyoxysomes (Peroxisomes in plants) In leaves carry out reactions the uses up O2 and releases CO2 that can be used in photosynthesis In germinating seeds - convert oils into sugars used as nutrients by growing plants. Vacuoles • Large membranous sac • Larger than vesicles • Store substances • Vacuoles in protozoans include digestive vacuoles and waterregulating contractile vacuoles. Vacuoles In protozoans include digestive vacuoles and water-regulating contractile vacuoles. Vacuoles Plant cell vacuoles (usually one or two) more prominenet; water-filled and give support to cell. Plant vacuoles store water, sugars, salt, pigments, and toxic substances to protect plant from herbivores.