Indigestion Dyspepsia
advertisement

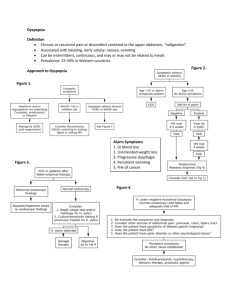
Indigestion / Dyspepsia Please refer to the BNF or SPC for licenced indications, doses, contraindications and other prescribing information. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Definition/Criteria Indigestion/dyspepsia are terms used to describe a number of symptoms often occurring shortly after eating or drinking. It is important to clarify exactly what the patients mean by the term indigestion. Symptoms: upper abdominal or epigastria pain or discomfort. Retrosternal pain. Flatulence/belching. Heartburn. Nausea and, or vomiting. Feeling of fullness in the abdomen. Acid taste in the mouth. Symptoms may be released or worsened by food. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Criteria for INCLUSION Treat Patients who present with characteristic symptoms of indigestion/dyspepsia. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Criteria for EXCLUSION Adverse drug reaction suspected Suspected or previous history of duodenal ulcer/gastric ulcer Pregnant and breast feeding women Patients <18 years Patients with anaemia Patients taking prescribed NSAIDS Patients with alarm symptoms: o Patients over 55 with persistent unexplained recent onset dyspepsia. Patients of any age with the following symptoms: o Unintentional weight loss o Dysphagia o Pain on swallowing o Persistent vomiting or vomiting with blood o Gastrointestinal bleeding/blood in stools/jaundice o Patients who have taken an indigestion/dyspepsia remedy for two weeks with no relief of symptoms ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Action for excluded patients and non-complying patients Refer to GP --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Action for patients who are included for treatment Advice Explain - diet and habitual eating patterns, caffeine, alcohol, certain medicines, stress, smoking, weight and hiatus hernia are all precipitating factors Advise to stop smoking, moderate alcohol intake and lose weight (where appropriate) Reduce caffeine intake Eat small meals slowly and regularly, avoid or reduce foods e.g. spicy, which may aggravate the problem Avoid bending or stooping, wearing tight clothes/belts as these may be aggravating factors Avoid taking NSAIDs or other precipitating medicines where possible Advise that regular use of indigestion remedies may mask the symptoms of gastric cancer Alert patient to the alarm symptoms of gastric cancer ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Treatment choice from the formulary Gaviscon Advance Liquid 500ml The sodium content of some antacids may be important when a highly restricted salt diet is required. Supply: One treatment course in any twelve-month period -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Routine referral to GP* Suspected or previous history of duodenal or gastric ulcer Patient needs to continue NSAIDs or other medicines suspected of causing the symptoms Patients taking prescribed NSAIDs with or without a PPI Symptoms that persist longer than 2 weeks Patients <18 years Pregnant or breastfeeding women Patients requiring repeated courses of treatment Referral to GP within 24 hours* See GP urgently if alarm signs Patients with alarm symptoms: o Patients over 55 with persistent unexplained recent onset dyspepsia. Patients of any age with the following symptoms: o Unintentional weight loss o Dysphagia o Pain on swallowing o Persistent vomiting or vomiting with blood o Gastrointestinal bleeding/blood in stools/jaundice o Patients who have taken an indigestion/dyspepsia remedy for two weeks with no relief of symptoms -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Emergency referral to A&E Pain is sudden and radiates to the back and arms N.B. It is not possible to list all referral criteria and this should be used as a guide. Professional judgement must be used when considering if an emergency referral is required -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------* The pharmacist should complete a referral note for the patient to hand to the surgery detailing why the patient was unable to be treated under the MAS. Version 1.0 29/10/14