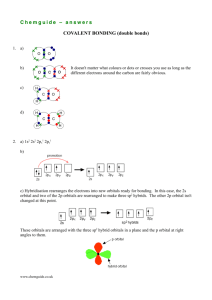
Organic Chemistry Exam 2 - Spring 2013
advertisement
Name :
- - L.A-'.:. Y\- -s'-"--"--=-=------"-______.::7__---------"' we.,y (~
Section_ __
CHEM 226: Elementary Organic Chemistry Exam 2 spring 2013
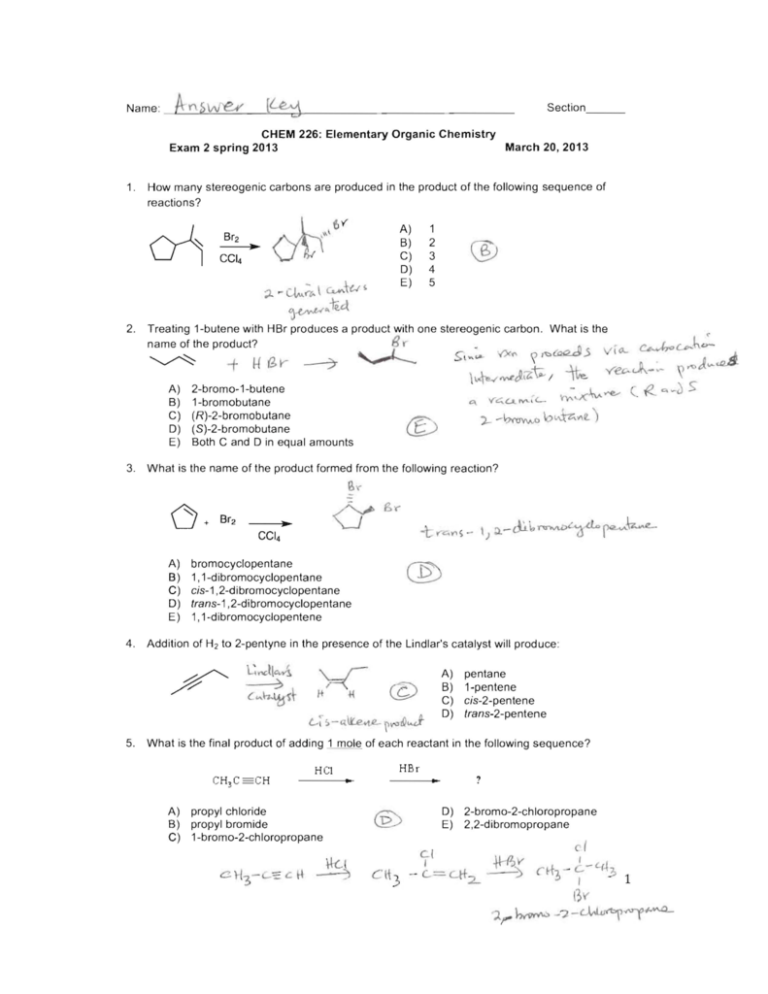
March 20, 2013 1. How many stereogenic carbons are produced in the product of the following sequence of
reactions?
o-l
Br2
CCI 4 ..
, '
~6
;l.
1
2
A)
B)
C)
0)
,,\
~ c.Lu.;&- \ c...."Ju ~ ®
3
4
5
E)
Gj~,,-li4 2. Treating 1-butene with HBr produces a product with one stereogenic carbon . What is the
Br
name of the product?
~
A)
B)
C)
0)
E)
-t
Ii
(2,y-
--7 -
~
S"l "'.....(X~
~
~
-+-
\~~J~~ I
2-bromo-1-butene
1-bromobutane
(R)-2-bromobutane
( S)-2-bromobutane Both C and 0 in equal amounts '<4L.t..~1 <-
""
~(p..h:'"
n J
yec-.~- ,- n ~ (7.. ~
v{"o...
..s
.li.
-lite..
-
~
'fy.. ...;c
\
___ (. r<. C<~~
,-~~Io~",~) 3. What is the name of the product formed from the following reaction?
~\"'"
A)
B)
C)
0)
E)
bromocyclopentane 1, 1-dibromocyclopentane cis-1 ,2-dibromocyclopentane trans-1 ,2-dibromocyclopentane 1, 1-dibromocyclopentene 4. Addition of H2 to 2-pentyne in the presence of the Lindlar's catalyst will produce:
L-~ :. - Q.tt:.e<-1.L ~~& ....J
A)
B)
C)
0) pentane
1-pentene
cis-2-pentene
trans-2-pentene
5. What is the final product of adding 1 mole of each reactant in the following sequence?
He!
A)
B)
C)
.. HBr
?
propyl chloride
propyl bromide
1-bromo-2-chloropropane
0)
E)
c(
2-bromo-2-chloropropane
2,2-dibromopropane
-- ~= Lit 2. .j-l--PJ~
cl
c rho;) - LI - '-(~'p
1
t>V'
?.rh~ -?-~4""'~
5
6.
What type of carbocation will form from the addition of a H+ to 2-methylpropene?
U@ ~
A)
B)
C)
0)
E)
7.
Upon ozonolysis which alkene will give only acetone, (CH 3hC=O?
A)
B)
C)
0)
E)
8.
2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
2,2-dimethyl-2-butene
3-hexene
2-methyl-2-pentene
2-methyl-3-hexene
(C.l-l3)~ c. -=
D
l-\-~
@
C::=:: CH ",­
3
What is the percent s character in an Sp2 hybrid orbital?
A)
B)
C)
0)
E)
9.
H3C+
1°
2°
3°
Allyl
oS
25%
33%
50%
67%
75%
~~
r
\.,...
Sf?~ ~
_ l_ )(~b1.>
:3
--
­
g ~~/->
®
The triple bond in ethyne is made up of
A)
B)
C)
0)
E)
two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals.
a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral
overlap of two p orbitals.
a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral
overlap of two p orbitals.
two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlay of two p orbitals, and a sigma bond formed
by end-on overlap of two sp orbitals.
V
two pi bonds, each formed by end-on overlap of two p orbitals, and a sigma bond formed
by lateral overlap of two sp orbitals.
10. Bending vibrations in the infared region occur at:
A)
B)
C)
0)
E)
6~ri~ 5~~ \'", ~ h"" ~~~{- 'l~ti'"
i.o ~.,..u l \.f .> '" (. ~ I
1
3000 cm2200 cm- 1
1700 cm- 1
1
below 1400 cm1
over 3000 cm-
®
2
Short Answer Questions
11. The Diels-Alder reaction is very important in the synthesis of six-membered rings. Draw the
reagents that can be used to synthesize the product shown by this method?
0
<
t-
+
dienophile
diene
12. How many peaks would you expect in the proton decoupled
bromopentane?
b
b
NMR spectrum of 3­
13 C
O-~ ~
(>,
13. A monochloroalkane shows two parent ion peaks m/ z at 92 and 94 . What is the molecular
formula? 5 CI and 37 CI are the most common isotopes of chlorine)
e
I~ L-h
\-\
-;2••'\-t\
c..l
IS
,::t..... -t~"' .... , -+ 35 -::::
\4" VI ~ -:=, b -- q ~
\'-f .... z.. 5 G
14 . A student lost the labels of two compounds and was required to run experiments to
distinguish and identify them. She took an IR spectrum of both compounds A and B and both
1
showed a broad band in the 3200 to 3500 cm- region of their IR spectrum? She then took
both lH NMR and 13 C NMR spectra, and compound A had four peaks , while compound B had
two peaks in both NMRs . Identify compounds A and B.
/"',
M
HO
::-.....
OH
q
/"',
OH
::-.....
OH
15. What is the molecular geometry of an alkynes like acetylene and a hydrogen cyanide
HC=N
HC=CH
_C.:::::.c - H
>f'
Sp \5
16. How many hydrogens are there in an alkyne with 13 carbons?
p
-C==- N ',
Se
~ f>
':ZLf
3
17. The 1H NMR spectrum of benzene (C6H6) and cyclohexane (C 6H12 ) are shown below. Match
the spectra with the correct molecule.
TMS
12
11
6
10
12
5
11
10
9
6
5
1
18. A compound, C 5H10 0, has an intense IR band at 1725 cm· . Its 1H NMR and 13C NMR are
shown below. Deduce the structure of the compound.
H NMR
triplet
quartet
TMS
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
o
5
4
3
o
2
CNMR
TMS
i i i
~
~
~
,
100
I i i
100
1~
i
1~
o
100
00
i
00
~
~
0
4
For questions 19-25, fill in the missing reagent(s) and the major product(s) for the
following reactions
NaNH2' liquid NH3
19.
•
20 .
\'-----,
Lindlar's
+
\
catalyst
..
~
21.0
22.
23 .
U
BH3
.
THF
((D~
•
H2 0 2 /OH­
. (Y
1­
2.
24 .
03
Zn, H+
..
0
o 0
D
~
--r
ca
IV
uJ
25.
CX
+
qJ
5
Table 12.2
lH Chemical Shifts (Relative to Tetramethylsilane)
Typical
OllH
B (ppm)
Type of 'H
[) (ppm)
Type
C- CH]
0.85- 0 .95
-CH.-F
4.3- 4.4
C-C H .-C
1.20- 1.35
-C H2- Br
3.4-3 .6
-C H -I
3 .1- 3.3
c
I
C- CH- C
1.40- 1. 6 5
CH. =C
4.6- 5.0
CH,-C=C
1.6- 1.9
- CH=C
5.2-5 .7
CH ,- Ar
2. 2- 2 .5
Ar- H
6 .6-8.0
CH, - C= O
2. 1- 2 .6
-C-C- H
2.4-2.7
I
0
CH -N
CH
./
2.1-3.0
"
II
- C- H
9.5- 9.7
0
0­
II
3.5 - 3.8
-C-OH
10-13
-C H -CI
3.6-3 .8
R-O H
0.5-5.5
-C HCI 2
5.8- 5.9
Ar--Q H
Table 12.4
4- 8
Infrared Stretching Frequencies of Some Typical Bonds
Bond type
Frequency range (em-I)
3300
3 500··3 700 (free)
3200- 3500 (hydrogen ·
bonded)
doub le bonds
triple bond s
D-H
carboxy lic acids
2500-3000
N- H
S-H
amines
3200- 3600
thiol s
2 550 - 26 00
C=C
alkenes
1600- 1680
C=N
C= O
imines, oximes
aldehydes, ketones,
esters, acids
1500- 1650
1650- 1780
C~
alkynes
2 100- 22 60
C=N
nitriles
2200- 2400
6