Chapter 2 Molecules of life
advertisement

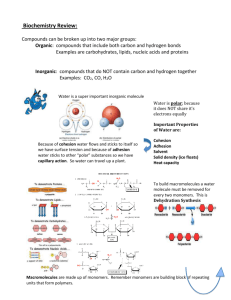
MONDAY 12-1-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • WHAT ATOMS ARE, AND • DIFFERENT PARTS OF AN ATOM ENTRY TASK: • START A NEW PAGE IN YOUR JOURNAL AND TITLE IT: CHAPTER 2 – THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE PLAN OF THE DAY • THE MYSTERY OF THE ICEFISH • BIOCHEMISTRY NOTES Icefish https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WpIe8_pUSu4 WHAT IS AN ATOM? BIOSPHERE ECOSYSTEM COMMUNITY POPULATION ORGANISM ORGAN SYSTEMS ORGANS TISSUES CELL MOLECULE ATOM MATTER: MADE OUT OF ATOMS Matter made out of the same kind of atom is known as an ELEMENT There are 25 elements that are present in living organisms The four main ones are: Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon & Hydrogen Compounds are two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio What is an ATOM? SUBATOMIC PARTICLE CHARGE MASS (in relation to other particles) LOCATION IN ATOM PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON Generally, same number of protons as electrons When the number of Protons changes, the kind of atom changes Generally, the same number of protons as neutrons. If number of neutrons is greater than protons, then the atom is called an isotope TUESDAY 12-2-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • WHY THE WATER MOLECULE IS SO IMPORTANT TO LIFE ENTRY TASK: • READ PAGES 36-37 (CHEMICAL BONDS) AND ANSWER THE QUESTION AT THE END OF THE SECTION Chemical Bonds Ionic bonds → TRANSFER of electrons Covalent bonds → SHARING of electrons PLAN OF THE DAY • BIOCHEMISTRY NOTES • CRASH COURSE WATER • WATER PROPERTIES TABLE COVALENT BONDS The structure of water Why is water such a unique substance? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HVT3Y3_gHGg Crash course water WATER MOLECULE Water structure Water Properties COHESION ADHESION Properties of water Cohesion Adhesion Temperature Moderation Density of Ice Universal Solvent Meaning Implications of Property in Nature In your group, read pages 40-41 Fill out the information on the chart for each of the properties of water Property Meaning Implications of Property in Nature Cohesion Water molecules stick together due to H bonds Small animals may walk on water Adhesion Water molecules stick to other molecules Capillary action. Water pulled to top of trees Temperature Moderation Water makes it so changes in temperature do not happen quickly Animals can gradually change their internal system with changes in water temperature Density of Ice Ice is less dense than water so it floats Ice insulates organisms living beneath Universal Solvent Many compounds dissolve in water Dissolved compounds can be brought to cells (via sap or blood) or move about cell cytoplasm WEDNESDAY 12-3-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • MAIN MACROMOLECULES OF LIFE ENTRY TASK: • EXAMINE THIS FOOD LABEL. HOW DO YOU KNOW IF IT IS HEALTHY OR JUNK FOOD? PLAN OF THE DAY • FINISH WATER PROPERTIES TABLE • START MACROMOLECULES SECTION • HTTPS://WWW.GOOGLE.COM/#Q=CRASH+COURSE+MACROMOLECULES MACROMOLECULES – CARBOHYDRATES NOTES • BE READY TO TAKE NOTES IN YOUR JOURNAL WHEN THE VIDEO IS PAUSED THURSDAY 12-4-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • WHAT IS THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF TWO MACROMOLECULES – LIPIDS (FATS) AND PROTEINS ENTRY TASK: • WHEN YOU HEAR THE WORD PROTEIN, WHAT IS THE FIRST THING THAT COMES TO MIND? PLAN OF THE DAY • FINISH MACROMOLECULES VIDEO AND NOTES ON MACROMOLECULES • WORK ON HANDOUT 2.3 • HTTPS://WWW.GOOGLE.COM/#Q=CRASH+COURSE+MACROMOLECULES SECTION 2.3 HANDOUT • READ THROUGH SECTION 2.3 AND THEN FILL OUT THE INFORMATION ON HANDOUT 2.3 FRIDAY 12-5-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • WHAT ARE ENZYMES AND HOW DO THEY WORK ENTRY TASK: • SUB, NO ET TODAY PLAN OF THE DAY • READ AND TAKE NOTES OF SECTION 2.4 – ENZYMES • ANSWER QUESTIONS 1-3 (A & B) FROM PAGE 53 MONDAY 12-8-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • WHAT ENZYMES ARE AND HOW THEY WORK ENTRY TASK: • WHAT TYPE OF MACROMOLECULE IS AN ENZYME? • WHY ARE ENZYMES IMPORTANT? PLAN OF THE DAY • REVIEWING MACROMOLECULES • ENZYMES - HOW DO THEY WORK MACROMOLECULES (molecules of life or biomolecules) What is the main chemical element present in all macromolecules? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QnQe0xW_JY4 1:50 – 5:10 ORGANIC COMPOUNDS: Carbon based INORGANIC COMPOUNDS: Non-carbon based Molecules of life Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Monomer – smallest unit of polymer Polymer – Long chain of monomers linked together Carbohydrates: Organic compound made up of sugar molecules Monosaccharides – one sugar unit Disaccharides – two sugar units Polysaccharides – long chains of sugar units Lipids Lipids – Water-avoiding molecule (hydrophobic) Two types of lipids: –Fats – Three long fatty acid chains attached to glycerol molecule (saturated or unsaturated) –Steroids – lipid molecule form of four fused rings (testosterone, estrogen & cholesterol) Proteins Proteins are made in cells by linking amino acids together to form polypeptide chains There are only 20 different amino acids Proteins are composed of one or more polypeptide chains The order of amino acids in polypeptide chains, and the three-dimensional shape of a protein molecule determines its function Protein Shape The long Amino acid chain folds to make the protein useable A proteins shape is changed by its surroundings A protein that is outside of its normal environment will be denatured (misshapen) NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic Acid: A large molecule like DNA and RNA made up of smaller molecules called nucleotides. Nucleotides: Small molecules made up of a sugar, a nitrogen base, and phosphate Nucleic acids are what our DNA or genetic material and RNA are made of Without nucleic acids our body would not have directions and could not function. NUCLEOTIDE (building block of nucleic acids) Monomers & Polymers MONOMERE CARBOHYDRATE LIPID PROTEIN NUCLEIC ACID http://www.hudson.edu/custom_users/sheldonc/macromo lchart.pdf POLYMERE Monomers & Polymers MONOMERE POLYMERE MONOSACHARIDE (glucose-fructose) POLYSACHARIDE (starch-glycogen-cellulose) PROTEIN AMINOACIDS POLYPEPTIDE NUCLEIC ACID NUCLEOTIDE DNA & RNA CARBOHYDRATE LIPID http://www.hudson.edu/custom_users/sheldonc/macromo lchart.pdf TUESDAY 12-9-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • WHAT ENZYMES ARE AND HOW THEY WORK ENTRY TASK: • WHAT TYPE OF MACROMOLECULE SERVES AS ENERGY STORAGE? PLAN OF THE DAY • FINISH MONOMERS VS. POLYMERS CHART • ENZYMES - HOW DO THEY WORK • AMYLASE DEMO • NOTES • GETTING READY FOR MACROMOLECULES LAB TOMORROW Chemical Reactions In a chemical reaction the atoms of the reactants are rearranged to form the products of the reaction REACTANTS PRODUCTS ENERGY ENDOTHERMIC EXOTHERMIC Enzymes An enzyme is a type of protein Each enzyme is specific to a kind of chemical reaction Enzymes are able to speed up chemical reactions in living cells by lowering the activation energy of the reaction Enzymes are affected by pH and temperature Enzymes Salivary amylase demo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6VN9n S65sFs Preparation for Lab Tomorrow You will be in the same group that you are now when we move to room 222 tomorrow Go directly to that room (next door down the hall) Get goggles when you get in the room (cabinet right of the entrance door) and find your table (they are numbered) Be ready to listen to directions when the bell rings WEDNESDAY 12-10-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • HOW TO DETERMINE THE COMPOSITION OF AN UNKNOWN SUBSTANCE USING CHEMICAL INDICATORS ENTRY TASK: • GET YOUR GOGGLES ON • GET THE CLEAR CUP BY YOUR STATION HALF FILLED WITH WATER AND PUT ONE PACKING PEANUT IN IT. STIR UNTIL IT DISSOLVES COMPLETELY PLAN OF THE DAY • SAFETY REVIEW • MACROMOLECULES LAB • TURN IN LAB AND ‘THINK FURTHER QUESTIONS’ SAFETY AND CLEANUP • PLEASE MAKE SURE THAT YOU ARE QUIET DURING LAB AND YOU ARE PAYING ATTENTION TO THE INSTRUCTIONS TO ENSURE SUCCESSFUL RESULTS!! THANK YOU!! • REMAIN AT YOUR SEAT UNLESS YOU ARE COLLECTING MATERIAL OR GETTING TEST TUBES TO AND FROM HOT BATH • IF I HAVE TO TALK TO YOU ABOUT GETTING BACK TO YOUR SEAT, YOU WILL LOSE POINTS FOR THE LAB • ANY HORSE PLAYING DURING LAB IS A SERIOUS VIOLATION OF LAB SAFETY CONTRACT – AUTOMATIC DISMISSAL FROM LAB AND TOTAL LOST OF POINTS! • GOGGLES HAVE TO BE WORN AT ALL TIMES DURING LAB • GROUPS THAT LEAVE NON-CLEANED MATERIALS AFTER LAB WILL LOSE POINTS • TIDINESS OF YOUR LAB AREA AND MATERIALS WILL GAIN YOU EXTRA CREDIT POINTS. THINK ABOUT OTHER GROUPS THAT ARE COMING AFTER YOU!! Organic Compounds Lab Think a Little Further Questions Why do we have a well and test tube for water and for the different organic compounds? How is this type of experiment/test different from the one we did for the Sprouting Bean Seeds? Can you think of an application of this type of test to a crime scene investigation? Create an scenario and describe how you could get clues to solve the crime using a test for the presence of an unknown substance. THURSDAY 12-11-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • REVIEW FOR TEST TOMORROW • ENTRY TASK: • THE PURPOSE OF THE EXPERIMENT YESTERDAY WAS TO DETERMINE WHAT IS THE PACKING PEANUT MADE OUT OF • WHAT WAS THE PURPOSE OF HAVING A WELL (AND TEST TUBE) WITH WATER AND ONE WITH THE KNOWN SUBSTANCE? PLAN OF THE DAY • ORGANIC COMPOUNDS LAB WRAP UP • REVIEW FOR TEST TOMORROW 2.3 FRIDAY 12-12-14 LEARNING OBJECTIVE: • CHECK YOUR KNOWLEDGE ON BIOCHEMISTRY • ENTRY TASK: • TAKE YOUR NOTES OUT AND REVIEW FOR 10 MINUTES BEFORE THE TEST PLAN OF THE DAY • CHAPTER 2 TEST • WHEN FINISHED WITH TEST, QUIETLY GET A BOOK AND: • READ SECTION 7.1 AND DO NOTES IN YOUR JOURNAL (PAGES 190-192) • DO QUESTION 1(A, B AND C - PAGE 194) • DUE MONDAY, DECEMBER 15