BIOLOGY
advertisement

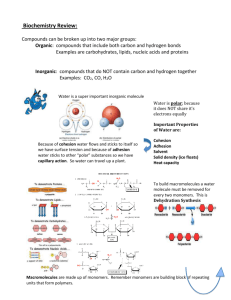
BIOLOGY Semester Exam Study Guide Introduction (Chapter 1) Know the 7 characteristics of living organisms; be able to describe them - Cells (Organization) - Energy (i.e. metabolism) - Homeostasis - Response to stimuli - Regulated growth and development - Reproduction: sexual v. asexual - Adaptation and Evolution What is Decent with Modification? How are living things organized? (i.e. atoms to organisms; groups of organisms) How is life classified (i.e. know the taxonomic hierarchy: DKPCOFGS) - Know characteristics of each Kingdom: - Cell type: prokaryotic v. eukaryotic - Mode of Nutrition: heterotrophic v. autotrophic - Body Type: multicellular v. unicellular - Presence of a cell wall and cell wall composition What is binomial nomenclature? Know the steps of the scientific method - controlled experiment, dependent v. independent variable What is spontaneous generation? Basic Chemistry What is matter? What are atoms? What are the characteristics of their subatomic particles? Know the types of bonding: covalent v. ionic v. hydrogen Know the properties of water: - Polarity - Cohesion v. adhesion Know the difference between acids and bases; characteristics of the pH scale Macromolecules What are the four main macromolecules? What six elements form the backbone of these macromolecules? What is a monomer? What are the monomers of ALL the macromolecules? Do any macromolecules NOT have a monomer? Know the characteristics of carbohydrates (i.e. polysaccharides): - What are monosaccharides (i.e. the 6 carbon sugars)? Examples? - What are disaccharides? Examples? - What are polysaccharides? What are the differences between starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin? Know the characteristics of lipids: - triglycerides (glycerol + fatty acids) - saturated v. mono/poly-unsaturated fats - what are phospholipids? What are the characteristics of proteins (i.e. polypeptides): - What are amino acids? Their characteristics? - What are peptide bonds? How do they form? - What is the importance of protein shape/structure and function? What are the 4 levels of protein structure? - What are six major functions of proteins? - What is protein denaturation? What are the characteristics of Nucleic Acids (polynucleotides): - What are nucleotides? Describe their structure - What are the characteristics of the two main types of nucleic acids? (DNA v. RNA) Cell Structure and Function How were cells discovered? What is the Cell Theory? What are two general types of microscope? How is TOTAL magnification determined using a compound light microscope? Why are cells small? How do the concepts of surface area-to-volume ratio apply. Know the characteristics and differences between the arrangements of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and Plant and Animal cells: - What are organelles? How do they help a cell function? - Be able to describe the structure and function of each organelle Cell Membranes and Transport What is the structure of a cell/plasma membrane? What does it mean when we say that a membrane is selectivelypermeable? What is the Fluid Mosaic Model? Be able to describe the composition/characteristics of the phospholipid bilayer (i.e. hydrophilic and hydrophilic regions). Why is this critical to how cells maintain equilibrium and osmotic balance. What are examples of membrane proteins? What is the function of membrane proteins? What is the function of membrane carbohydrates? What’s a solution? What is the difference between solute and solvent? Be able to explain how particles are transported across a membrane: - Passive v. Active transport - Define passive transport and characteristics of the following types: 1. simple diffusion (what effects diffusion rate) 2. facilitated diffusion (importance of channel and carrier proteins) 3. osmosis (what is tonicity: iso/hyper/hypotonic solutions) - Define active transport and its characteristics: 1. Sodium-Potassium Pump 2. Endocytosis (phago/pinocytosis) v. Exocytosis Miscellaneous Many of the exam questions will require you to analyze charts, graphs, food webs, ecological pyramids, etc. Use your book and the standardized test prep questions at the end of every chapter as a means of helping you study ***ONE FINAL NOTE: This study guide is a means of refreshing your memory about things that you may have forgotten and to direct your attention toward main topics and/or concepts. It is not meant to inform you of every single thing that will be on the exam or to teach you everything that we have learned this past semester. It will be greatly beneficial to know all VOCAB & to study ALL of your notes, labs, concept maps, and other worksheets. HAPPY STUDYING