Historical Thinking Skills and Periodization
advertisement
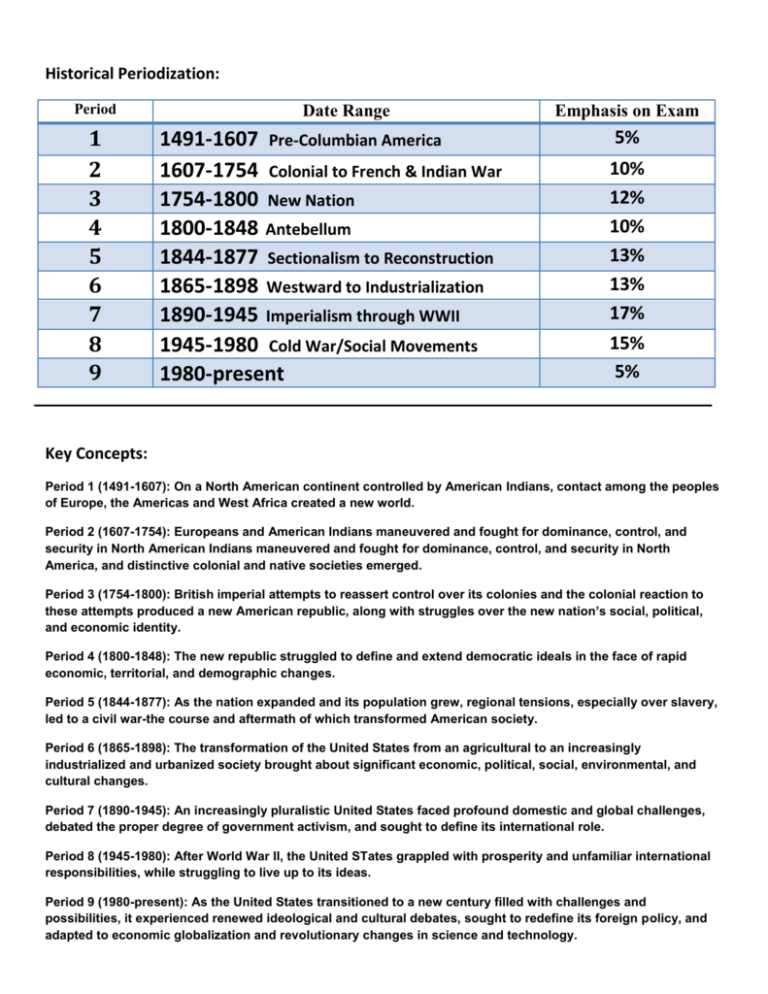
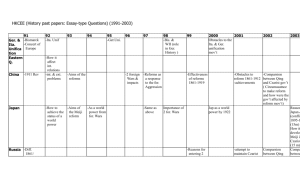
Historical Periodization: Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Date Range 1491-1607 Pre-Columbian America 1607-1754 Colonial to French & Indian War 1754-1800 New Nation 1800-1848 Antebellum 1844-1877 Sectionalism to Reconstruction 1865-1898 Westward to Industrialization 1890-1945 Imperialism through WWII 1945-1980 Cold War/Social Movements 1980-present Emphasis on Exam 5% 10% 12% 10% 13% 13% 17% 15% 5% Key Concepts: Period 1 (1491-1607): On a North American continent controlled by American Indians, contact among the peoples of Europe, the Americas and West Africa created a new world. Period 2 (1607-1754): Europeans and American Indians maneuvered and fought for dominance, control, and security in North American Indians maneuvered and fought for dominance, control, and security in North America, and distinctive colonial and native societies emerged. Period 3 (1754-1800): British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles over the new nation’s social, political, and economic identity. Period 4 (1800-1848): The new republic struggled to define and extend democratic ideals in the face of rapid economic, territorial, and demographic changes. Period 5 (1844-1877): As the nation expanded and its population grew, regional tensions, especially over slavery, led to a civil war-the course and aftermath of which transformed American society. Period 6 (1865-1898): The transformation of the United States from an agricultural to an increasingly industrialized and urbanized society brought about significant economic, political, social, environmental, and cultural changes. Period 7 (1890-1945): An increasingly pluralistic United States faced profound domestic and global challenges, debated the proper degree of government activism, and sought to define its international role. Period 8 (1945-1980): After World War II, the United STates grappled with prosperity and unfamiliar international responsibilities, while struggling to live up to its ideas. Period 9 (1980-present): As the United States transitioned to a new century filled with challenges and possibilities, it experienced renewed ideological and cultural debates, sought to redefine its foreign policy, and adapted to economic globalization and revolutionary changes in science and technology. Historical Thinking Skills: Skill Type Historical Thinking Skill What does it mean? I. Chronological Reasoning 1. Historical Causation 2. Continuity and Change over Time 3. Periodization -Compare/Contrast, Cause/Effect -What stayed? Stayed same? -Ways events can be organized II. Comparison and Contextualization 4. Comparison 5. Contextualization -Compare things across time -Events in larger scales III. Crafting Historical Arguments from Historical Evidence 6. Historical Argumentation 7. Appropriate Use of Relevant Historical Evidence -Analyzing interpretations -Analyzing POV and sides IV. Historical Interpretation & Synthesis 8. Interpretation 9. Synthesis -What does it mean as a whole? -Making inferences from sources Historical Themes: Identity -How and why have debates over American national identity changed over time? -How have gender, class, ethnic, religious identities changed in different eras? Work, Exchange & Technology -How have changes in markets, transportation and tech. affected American society from colonial time to the present day? -Why have different labor systems developed overtime? (Colonial through today)? Peopling -Why have people migrated to, from, and within North America? -How have changes in migration and population patterns affected American life? Politics and Power -How and why have different political and social groups competed for influence over society and gov’t in what would become the US? -How have Americans agreed on or argued over the values that guide the political system as well as who is a part of the political process? America in the World -How have events in North America and the United States related to contemporary developments in the rest of the world? -How have different factors influenced US military, diplomatic and economic involvement in international affairs and foreign conflicts, both in North America and overseas? Environment and Geography -How did interactions with the natural environment shape the institutions and values of various groups living on the North American continent? -How did economic and demographic changes affect the environment and lead to debates over use and control of the environment and natural resources? Ideas, Beliefs and Culture -How and why have moral, philosophical, and cultural values changed in what would become the United States? -How and why have changes in moral, philosophical, and cultural values affected US history?