2nd Semester Study Guide
advertisement

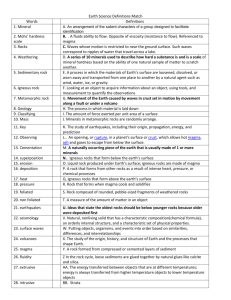
2nd Semester Study Guide Rocks Rock cycle -be able to describe and answer questions about the rock cycle -what process rocks go through from one type to another -law of conservation of matter -James Hutton/uniformitarianism Igneous rocks -difference between lava and magma -3 types of magma -intrusive/extrusive -texture Sedimentary rocks -3 types: clastic or chemical -form in layers (stratification) -form on surface of Earth -how each type forms -how ripple marks and mud cracks form -know what nodules and geodes are Metamorphic rocks -3 roads to metamorphic rocks (heat, pressure, and hot fluids) -foliated and non-foliated -regional metamorphism and contact metamorphism Rocks -answer questions about them -parent rock for metas -foliated for metas -type of rock -grain size for clastic seds -origin (where formed) -intrusive/extrusive for igneous -ocean, riverbeds, swamps for sedimentary Plate Tectonics Continental drift -Alfred Wegner Evidence for supercontinent and drift -4 pieces that support continental drift Other theories -isthmus -island stepping stones -log ferry -etc. Plate tectonics theory 3 types of plate boundaries -what happens at each Seafloor spreading ridge -how it works -locations Rift and rift valley -how it forms -locations Subduction zone -how it forms -locations 13 plates -names and locations -use the map (hint, hint) Seismology -seismograph -seismogram EQ waves -names -way they travel (compressional, oscillating, etc.) -rates they travel -damage they cause Quake locations -three terms involved with locating a quake EQ measurements -intensity and magnitude -different scales Destruction determinators -4 factors 5 after effects of EQs Famous Quakes -China -New Madrid -San Francisco, CA -Chile -Alaska -Loma Prieta, CA -Northridge, CA -Sumatra, Indian Ocean -Haiti -know dates, magnitudes, after effects (tsunamis, aftershocks, etc.), deaths, etc. Types of Deformation -two types -examples of each (chips, taffy, etc.) Types of folds -3 types -what each looks like -domes and basins Types of faults -names -type of movement -identify these using pictures Joints Types of mountain building -3 types -processes -locations Volcanoes -viscosity -violence of eruption -3 factors -volatiles or gasses in magma -2 main ones -types of magma -3 kinds -types of lava -2 kinds -pyroclastic material -4 things -volcano parts -4 main parts -3 types of volcanoes -distinguishing features - nuée ardente and lahars Oceanography Ocean Floor Notes -% of water-land -nicknames of hemispheres -4 oceans -bathymetry -passive continental margins -continental shelf -continental slope -continental rise -submarine canyons -turbidity currents (and turbidites) -active continental margins -subduction zones -trenches -ocean basin -abyssal plain -seamount -guyots -mid-ocean ridge (seafloor spreading ridge) -resources from the ocean Ocean Water and Life Notes -salinity -sources -reasons for increase -reasons for decrease -temperature -thermocline -temps at diff. latitudes -density -why associated with salinity and temp -pycnocline -layering -surface mixed zone -transition zone -deep ocean -types of creatures -plankton -nekton -benthos -zones -classified by amt of light -photic -aphotic -classified by distance from shore -intertidal zone -neritic zone -oceanic zone -classified by water depth -pelagic zone -benthic zone -abyssal zone -where most nutrient-rich water is -food chain -food web Dynamic Ocean Notes -currents -gyres -causes -coriolis effect -wind -affects on climate -upwelling -waves -parts -measurements -refraction -beach erosion -beach drift -longshore current -features -beach deposition -spit -baymouth bar -tombolo -barrier island -stabilizing a beach -groin -breakwater -seawall -beach nourishment -tides -causes -spring -neap -diurnal -semidiurnal -mixed Environmental Science Saving the World -climate change -overpopulation -non-native organisms (invasive species) -deforestation -ways to help -alternate energy -wind -solar -nuclear -hydro -geothermal -biomass -tidal