Sykes CH11 Problems Radical Reactions
advertisement

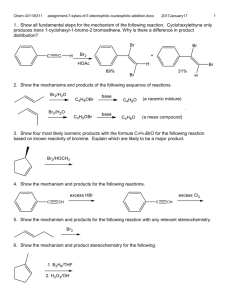
Chem 4311/6311 assignment-10-sykes-carbanions.docx 2016January17 1. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanism for one of the reactions at left and the major products of the remaining two. 2. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanisms for the monochlorination of methylcyclopentane. How many moles of initiator is required to monochlorinate methylcyclopentane? 3. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanisms for the following reactions. 4. Explain the relative rates of recombination of methyl and isopropyl radicals. 5. Explain the following trends. R1 R2 R3 CH3 CH3 CH3 H CH3 CH3 H H CH3 H H H Relative rate 13,000 111 11 1 1 Chem 4311/6311 assignment-10-sykes-carbanions.docx 2016January17 6. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanism for the following reactions for all products. 7. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanism for the following reaction. 8. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanism for the following reaction. 9. Calculate the relative amount of mono-halogenated isomers for each reaction indicated. Bomination: CH =. 2(1600) 2(1600)+8(80)+6(1) 2(80) = 0.832, C2 or C5 CH2 2(1600)+8(80)+6(1) = 0.0416 4(80) 6(1) C4 and C6 CH2 2(1600)+8(80)+6(1) = 0.0832, CH3 = 2(1600)+8(80)+6(1) = 0.00156, chlorination rate CH = 2(6.7) 2(6.7)+8(4.4)+6(1) 4(4.4) = 0.245 , C2 or C5 CH2 = 2(4.4) 2(6.7)+8(4.4)+6(1) = 0.161, 6(1) C4 and C6 CH2 = 2(6.7)+8(4.4)+6(1) = 0.322 CH3 = 2(6.7)+8(4.4)+6(1) = 0.110 or 0.368 : 1 : 0.16532 10. Explain why the following reactions cannot be the propagation steps for methane radical chlorination. 2 Chem 4311/6311 assignment-10-sykes-carbanions.docx 2016January17 3 11. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanism for the following reaction. Include formation of benzene. Compared to 1,5-cyclooctadiene how much initiator is used? No carboxylic acid is formed. 12. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanisms for the following reactions. 13. (t-BuO)2 is often used as a radical initiator. Show the non-radical products it eventually forms if there is nothing reactive present. Hint: review the possible fates (reactions) of radicals. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanism for the second reaction. . Initiation: electron transfer, fragmentation to phenyl radical, oxidation by Cu 2+, phenyl cation addition to benzoic acid or phenyl radical adds to peroxide 14. Isooctane is often used as a solvent for radical reactions, especially when oxygen radicals are formed. Explain. Hint: consider the suitability of heptane versus isooctane. Kinetics is the determining factors. If the reactions with isooctane are slower than with reagents then the isooctane is kinetically inert even though the isooctane radicals may be relatively stable. Primary radicals lack stabilization, the others are sterically hindered. 15. Show all fundamental steps of the mechanisms for the following reactions. 16. . Show all fundamental steps of the mechanism for the following reaction. Chem 4311/6311 assignment-10-sykes-carbanions.docx 2016January17 4