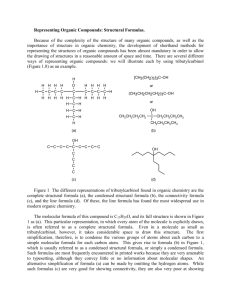
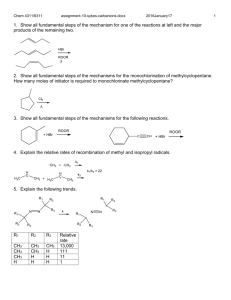
Name: Date: AP Chemistry: Unit 12: Organic Chemistry: Homework
advertisement

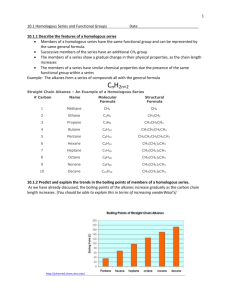
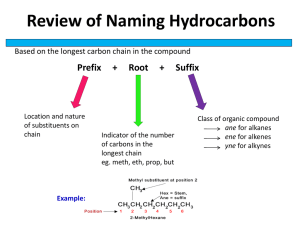
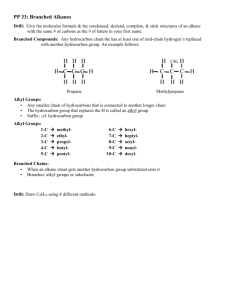
Name: AP Chemistry: Unit 12: Organic Chemistry: Homework Date: 1. Answer the following questions about general hydrocarbon structures. a. What structural feature is associated with each type of hydrocarbon: an alkane; a cycloalkane; an alkene; an alkyne? b. Give the general formula for each. c. Which hydrocarbons are considered saturated? 2. Draw all possible skeletons for a 7-C compound with a. A 6-C chain and 1 double bond b. A 5-C chain and 1 double bond c. A 5-C ring and no double bonds 3. Draw the structure or give the name of each compound: a. 2,3-dimethyloctane b. 1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane CH3 | c. CH3—CH2 —CH—CH —CH2 | | CH3 CH2—CH3 d. e. 4. Each of the following names is wrong. Draw structures based on them, and correct the names: a. 4-methylhexane b. 2-ethylpentane c. 2-methylcyclohexane d. 3,3-methyl-4-ethyloctane 5. Each of the following compounds can exhibit optical activity. Circle the chiral center(s) in each: a. H H b. H | H C H H–C–H C–C–C–H Cl H H H H H H | | | | H–C–C–C–C–C–H | | | | H H H H H–C–H | H 6. Draw structures from the following names, and determine which compounds are optically active: a. 3-bromohexane b. 3-chloro-3-methylpentane c. 1,2-dibromo-2-methylbutane 7. Which of the following structures exhibit geometric isomerism? Draw and name the two isomers in each case: a. CH3 — CH2 —CH= CH —CH3 CH3 CH3 | | b. CH3— C = CH — CH — CH2 — CH3 c. 8. Which compounds exhibit geometric isomerism? Draw and name the two isomers in each case. a. Propene b. 3-hexene c. 1,1-dichloroethene d. 1,2-dichloroethene 9. Draw and name all the constitutional isomers of dichlorobenzene. 10. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) is a common preservative added to cereals and other dry foods. Its systematic name is 1-hydroxy-2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylbenzene (where "tert-butyl" is 1,1dimethylethyl). Draw the structure of BHT. 11. There are two compounds with the name 2-methyl-3-hexene, but only one with the name 2methyl-2-hexene. Explain with structures. 12. Write equations for the following: a. An addition reaction between H2O and 3-hexene (H+ speeds the reaction but is not consumed) b. An elimination reaction between 2-bromopropane and hot potassium ethoxide, CH3 - CH2 - OK (KBr and ethanol are also products) c. A light-induced substitution reaction between Cl2 and ethane to form 1,1-dichloroethane 13. Compounds with nearly identical molar masses often have very different physical properties. Choose the compound will, the higher value for each of the following properties, and explain, your choice. a. Solubility in water: chloroethane or methylethylamine b. Melting point: diethyl ether or 1-butanol c. Boiling point: trimethylamine or propylamine 14. Name the type of organic compound from the following description of its functional group: a. Polar group that has only single bonds and does not include O or N b. Group that is polar and has a triple bond c. Group that has single and double bonds and is acidic in water d. Group that has a double bond and must be at the end of C chain 15. Circle and name the functional groups in the following: a. CH3 – CH = CH – CH2 – OH d. N ≡ C – CH2 – C – CH3 || O || – C – OH b. Cl – CH2 – O e. O || c. N O || – C – O – CH2 – CH3 16. Draw all possible alcohols with the formula C5H12O. 17. Draw all possible amines with the formula C41111 N. 18. Draw the organic product formed when the following compounds undergo a substitution reaction: a. Acetic acid and methylamine b. Butanoic acid and 2-propanol c. Formic acid and 2-methyl-1-propanol 19. Draw condensed formulas for the carboxylic acid and alcohol portions of the following esters: 20. Draw condensed formulas for the carboxylic acid and amine portions of the following amides: 21. Which intermolecular force is primarily responsible for the different types of polyethylene? Explain. 22. Draw an abbreviated structure for the following polymers, with brackets around the repeat unit: 23. Write a balanced equation for the reaction between 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid and 1,2dihydroxyethane to form the polyester Dacron. Draw an abbreviated structure for the polymer, with brackets around the repeat unit. 24. Draw the R group of (a) alanine; (b) histidine; (c) methionine 25. Draw the structure of each of the following tripeptides: a. Aspartic acid-histidine-tryptophan b. Glycine-cysteine-tyrosine with the charges existing in cell fluid 26. Protein shapes are maintained by a variety of forces that arise from interactions between the amino-acid R groups. Name the amino acid that possesses each R group and the force that could arise in each of the following interactions: 27. A synthesis of 2-butanol was performed by treating 2-bromobutane with hot sodium hydroxide solution. The yield was 60%, indicating that a significant portion of the reactant was converted into a second product. Predict what this other product might be. 28. Pyrethrins, such as jasmolin II (below), are a group of natural compounds synthesized by flowers of the genus Chrysanthemum (known as pyrethrum flowers) to act as insecticides. a. Circle and name the functional groups in jasmolin II. b. What is the hybridization of the numbered carbons? c. Which, if any, of the numbered carbons are chiral centers', 29. Write the name of each of the following organic compounds: a. b. c. 30. Write the structures for the following organic molecules: a. methylcyclopentane b. 2-ethyl-2-pentene c. diethylamine 31. Identify each type of reaction.