Chapter 4 Review
advertisement

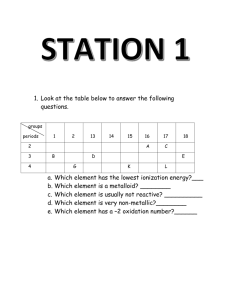
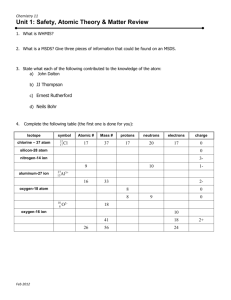
Chapter 4/25 Review History of the Atom: Name Democritus Name: _____________________ What did he do? Dalton Chadwick Bohr Thomson Rutherford Parts of the Atom: Particle Symbol Location Charge Relative Mass Electron Proton Neutron 1. Differentiate between an ATOM, ION, and ISOTOPE 2. The number of _________________determines what the element is. 3. Atomic number equals __________________________ 4. Mass number equals ____________________________ 5. Charge equals _________________________________ 6. One atomic mass unit is defined as _________________of a ________atom. 7. The number of ________________in an atom can’t be changed without changing the element. 8. Should changing the number of neutrons affect the chemical properties of that element? 9. The primary factor determining an atom’s stability is its ratio of ___________to___________. 10. A + ion is called _________________. A – ion is called ___________________ 11. Which statements in Dalton’s original atomic theory are now considered incorrect? 12. Who was Lavoisier? Why was he called the “Father of Chemistry? What law is attributed to him? 13. What element is Priestly famous for discovering? 14. Fill in the table below: Element Symbol (Z) At # # of p # of n (A)mass # of e charge # Carbon atom 12 +1 K 10 22 0 30 34 28 Bromide ion 81 Calcium ion 21 21. The symbol for a silver isotope with a mass number of 107 is written like Write the following isotopes using the format shown for silver above: Neon-22 Iron-57 Calcium-46 Zinc-64 107Ag 47 Oxygen-17 22. Given the relative abundance of the following naturally occurring isotopes of oxygen, calculate the average atomic mass of oxygen. O-16 99.76% O-17 .037% O-18 .204% 23. Sulfur has four naturally occurring isotopes. S-32 comprises 95.00%, S-33 comprises 0.76%, S-34 exists at 4.22% and S-36 is 0.014%. What is the average atomic mass of sulfur? 25. Chlorine, which has an atomic mass of 35.453 amu, has two naturally occurring isotopes Cl-35 and Cl-37 Which isotope occurs in greater abundance? How can you tell? 29. Based on the Bohr Model, what element is pictured below? How are electrons drawn in the Bohr Model? How many electrons can each shell hold? Are there any limitations to the Bohr Model? Chapter 25 Review: 30. What has to happen to an atom to turn it into an ion? 31. What happens to an atom if you change its number of protons? 32. Why do radioactive elements give off radiation? 33. How do the isotopes C-14 and C-12 differ from each other? 34. 24 He What is the top number? bottom number? 35. How could you stop an alpha particle? 36. How could you stop a beta particle? 37. How could you stop gamma rays? 38. Write the symbols for the following: Alpha Beta Gamma Neutron Proton Positron 39. What determines whether an atom is stable or not? 40. Define half-life 41. Define fission ________________________________________________________________________________________ 42. Define fusion ________________________________________________________________________________________ 43. 210 84 Po _______ 24 He 44. 58 B 48 Be _______ 47. 49 Be 24 He _____ 01n 48. ______ 24 He 178 O 11 p 0 45. _______ 234 91 Pa 1 e 46. Write the equation for the alpha decay of U-238: 49. C-14 half-life = 5700 yrs. If a well preserved piece of cloth originally contained 80g of C-14 and now contains 2.5 g how old is it? 50. An isotope of barium has a half life of 215 years. A sample has a starting mass of 346mg beginning in 2009. In what year will the amount remaining be 5.4 mg ?