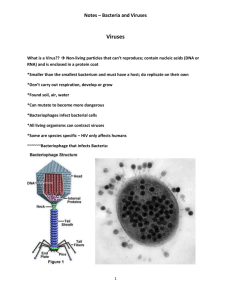
Virus and Bacteria Worksheet: Structure, Types, Diseases
advertisement
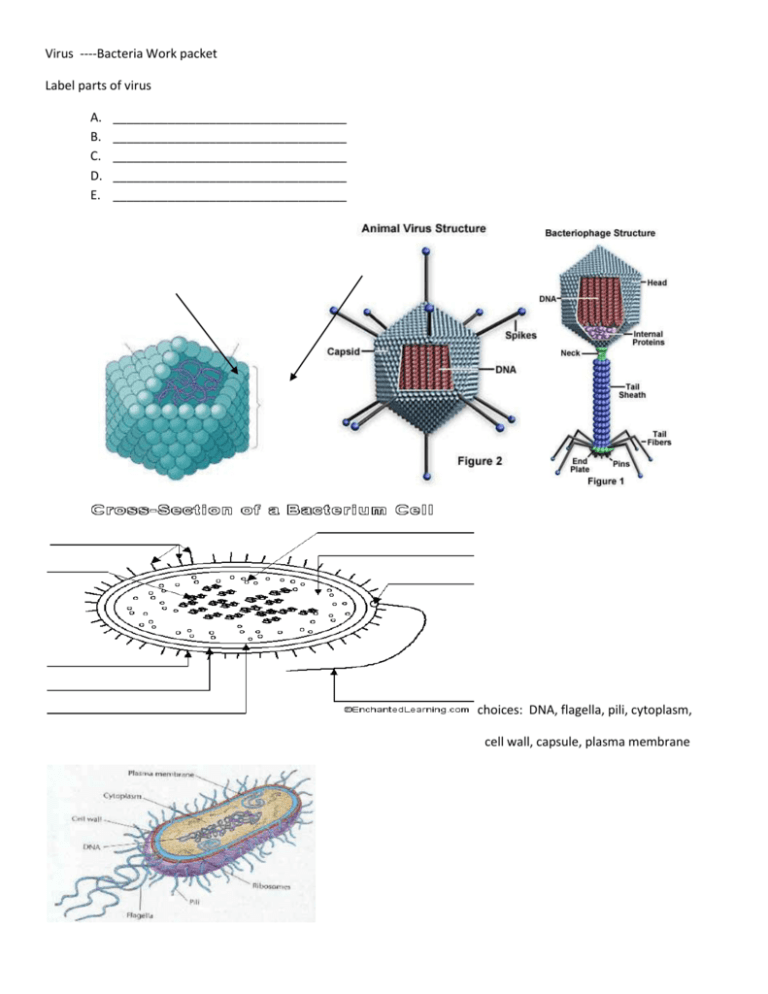
Virus ----Bacteria Work packet Label parts of virus A. B. C. D. E. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ choices: DNA, flagella, pili, cytoplasm, cell wall, capsule, plasma membrane TYPES OF ARCHAEBACTERIA _______________________________________ lives in anaerobic places , makes methane gas. ________________________________________ lives in very salty areas ________________________________________lives in extremely hot and acidic areas Virus Vocabulary ___1. Vaccination a. protein coat surrounding nucleic acid core ___2. Virulent b. have ability to perform reverse transcriptase, RNA- DNA ___3. Capsid c. cell burst due to virus invasion ___4. Envelope d. extra outer surrounding, in some virus, outside the capsid ___5. Host cell e. immunization, process used to equip immune system to fight off viral infections ___6. Retrovirus f. virus – like but no capsid, causes disease in plants ___7. Viroids g. virus ability to make more viruses ___8.prion h. deadly virus __9.lysis i. virus like no nucleic acid, example causes mad cow disease ___10.replication j. cell that the virus attaches Name the shapes of bacteria: 1.__________________ 2.___________________ 3._____________________________ Growth formations of bacteria: 1.__________________________ 2.____________________________ 3._________________________ Type of bacterial reproduction __________________________________________ ______________________________ REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES: _______________ Cycle: (a reproductive cycle that kills the host cell) _______________(Attachment) _______________(Injection) _______________- the nucleic acid copies itself _______________(new nucleic acids and protein coats are put together) _______________(the cell lyses, killing the cell, and releases up to 300 new viruses) _______________Cycle: (an inactive reproductive cycle that does not harm the host cell until activated later) Viruses that reproduce in this way are called _______________ phages. _______________- the nucleic acid of the virus attaches to the DNA of the host cell _______________ - the viral DNA (called the _______________) is copied along with the host cell DNA during mitosis. _______________ - The prophage changes to the lytic cycle and destroys the cell. Bacteria Vocabulary: ___1. Prokaryotic a. asexual reproduction of bacteria ___2. Peptidoglycan b. can cause disease ___3.capsule c. changing Nitrogen gas into a usable ammonia for nitrogen cycle ___4. Pili d. interferes with bacterial cell function. Ex. Penicillin, tetracycline ___5. Decomposer e. cells that have no nucleus or membrane bound organelles ___6. Gram staining f. holds the bacteria together during conjugation ___7. Nitrogen fixing g. protein that helps form the cell wall of eubacteria ___8. MRSA h. poison ___9. Binary fission i. protective coating surrounding bacteria ___10. Conjugation j. way of indentifying bacteria through staining process ___11. Toxin k. sexual reproduction in bacteria ___12. Pathogen L. breaks down dead organisms and recycles nutrients ___13. Antibiotic m. type of bacteria that have become resistant to the effects of antibiotics VIRAL OR BACTERIAL DISEASE V= virus B= Bacterial ___1. AIDS ___2. Rabies ___3. Botulism ___4. Tetanus ___5. Ebola ___6. Chicken pox ___7. Tuberculosis ___8. Common cold ___9. HPV ___10. Whooping cough ___13. Anthrax ___14. Small pox ___15. Mononucleosis ___16. Herpes ___17. Hepatitis ___18. Influenza (flu) ___19. Leprosy ___20. Polio ___11. Rubella ___12.plague