Virus: disease-causing, nonliving particles composed of an inner
advertisement

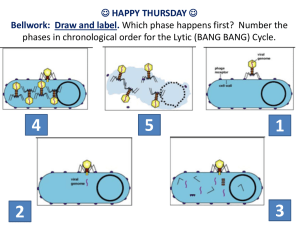
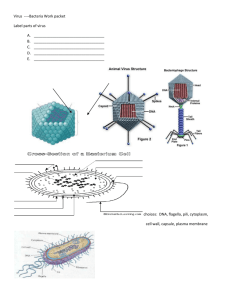
Virus: disease-causing, nonliving particles composed of an inner core of nucleic acids surrounded by a capsid; replicate inside living cells called host cell. C.D.C: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the US agency charged with tracking and investigating public health trends. A part of the US Public Health Services (PHS) under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the CDC is based in Atlanta, Georgia. It publishes key health information, including weekly data on all deaths and diseases reported in the US and travelers' health advisories. The CDC also fields special rapid-response teams to halt epidemic diseases. Host Cell: living cell in which a virus replicates Quarantine: a strict isolation imposed to prevent the spread of disease. Bacteriophage: also called phages, viruses that infect and destroy bacteria Universal Precautions: an approach to infection control to treat all human blood and certain human body fluids as if they were known to be infectious for HIV, HBV and other blood borne pathogens. Use gloves, masks, and gowns if blood or OPIM exposure is anticipated. Use engineering and work practice controls to limit exposure Capsid: outer coat of proteins that surrounds a virus’s inner core of nucleic acid; arrangement of capsid proteins determines the virus’s shape. Lytic cycle: viral replication cycle in which a virus takes over a host cell’s genetic material and uses the host cell’s structures and energy to replicate until the host cell bursts, killing it. Lysogenic cycle: viral replication cycle in which the virus’s nucleic acid is integrated into the host cell’s chromosome; a provirus is formed and replicated each time the host cell reproduces; the host cell is not killed until the lytic cycle is activated. Protocols: a system of rules that explain the correct conduct and procedures to be followed in formal situations; a plan for a scientific experiment or for medical treatment; a document that describes the details of a treaty or formal agreement between countries. World Health Organization: Exponential Growth: growth pattern where a population grows faster as it increase in size; graph of a exponentially growing population resembles a J-shaped curve. Immunity: the directing and coordinating authority for health within the United Nations system. It is responsible for providing leadership on global health matters, shaping the health research agenda, setting norms and standards, articulating evidence-based policy options, providing technical support to countries and monitoring and assessing health trends. Plague: a disease that causes death and that spreads quickly to a large number of people Pandemic: occurring over a wide geographic area and affecting an exceptionally high proportion of the population. Epidemic: occurs when many people in a given area are afflicted with the same disease at about the same time. F.E.M.A: The Federal Emergency Management Agency coordinates the federal government's role in preparing for, preventing, mitigating the effects of, responding to, and recovering from all domestic disasters, whether natural or man-made, including acts of terror.