Virues and Bacteria
advertisement

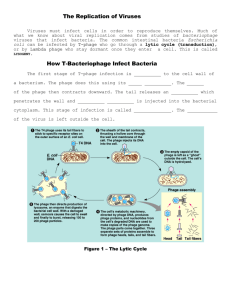
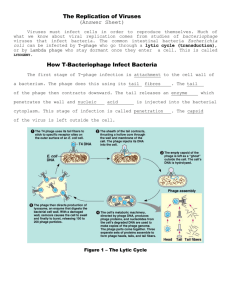
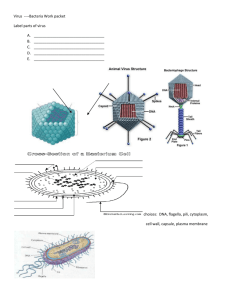
Notes – Bacteria and Viruses Viruses What is a Virus?? Non-living particles that can’t reproduce; contain nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) and is enclosed in a protein coat *Smaller than the smallest bacterium and must have a host; do replicate on their own *Don’t carry out respiration, develop or grow *Found soil, air, water *Can mutate to become more dangerous *Bacteriophages infect bacterial cells *All living organisms can contract viruses *Some are species specific – HIV only affects humans ~~~~~~Bacteriophage that infects Bacteria: 1 Viral Replication Cycles: Lytic Cycle: A virus takes over a host’s genetic material, uses its structures and energy to replicate many viruses and the cell bursts (Lysis) and viruses spread Bacteriophage Attack on a bacterial Cell Step 1 Summary The lytic bacteriophage virus attaches itself to the bacterial cell. ↓ 2 The virus injects the nucleic acid into the cell. ↓ 3 When all the nucleic acid is injected they begin to replicate, and the useless original capsid and tail are detaches from the cell. ↓ 4 The viruses grow using the nutrients of the bacterial cell. ↓ 5 When viruses are mature, they come out of the cell, destroying it, and start to infect other cells. 2 Lysogenic Cycle: The virus’s nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) is integrated into the host cell’s chromosome, the cell is then called a provirus, the virus lay “dormant” as the cell reproduces itself. Below after a virus has injected its nucleic acid: 3 Cancer and Viruses Viruses linked to cancer disrupt mitosis. HPV is the most common (Human Papilloma Virus) causes genital warts and accounts for about 76% of cervical cancers. Bacteria *Archaebacteria – The extremist; Oldest; salt-loving; heat-loving *Eubacteria --Some are photosynthetic (undergo photosynthesis) *Some undergo chemosynthesis – break down surrounding organic compounds for food *Some are heterotrophs – “eat” their own food 4 Bacteria Adaptations Endospore forms around bacteria during harsh conditions, cells grow and reproduce, can produce toxins; Botulism (food poisoning), anthrax (lives in soil). Bacteria can mutate quickly to environmental change and become more dangerous and resistant to antibiotics Helpful bacteriaNitrogen fixation (plant root convert nitrogen gas into usable nitrogen for the plant), return nutrients to soil, produce oxygen, production of cheese, yogurt and pickles. E. coli in the intestines aids in digestion. Used in farming, medicine and food industry. 5