KEY Evolution, Bacteria/Virus Vocabulary PRACTICE
advertisement

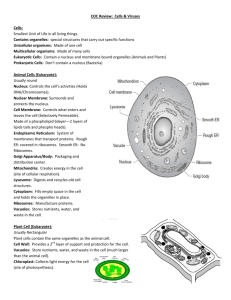
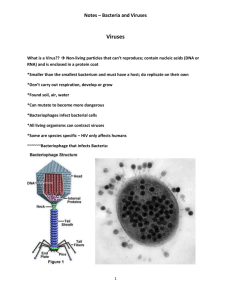
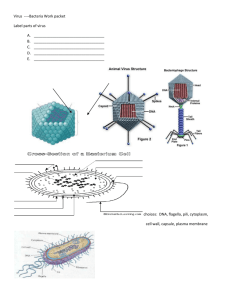
KEY Evolution, Bacteria/Virus Vocabulary PRACTICE Word bank: lytic cycle, binary fission, virus, Charles Darwin, natural selection, adaptation, evolution, species, speciation, camouflage, mimicry, mutation, host, antibiotics, nitrogen fixation, prokaryote, selective breeding. 1. ___mimicry_________This adaptation gives an animal protection from predators by its resemblance to a different animal. Ex: The monarch butterfly and the viceroy butterfly. 2. __Darwin__________English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection. 3. __prokaryote_________A living thing that consists of a single cell and does not have a nucleus. Ex: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria. 4. __adaptation__________A characteristic that improves an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment. Examples: long neck of giraffe, different beaks on finches 5._selective breeding__________The human practice of breeding animals or plants to have certain desired characteristics. 6.__evolution__________ A process in which inherited characteristics in a population change over time so that new species sometimes appear. 7._mutation___________ Any change in genetic information of an organism-a change in the DNA or genes. 8.__natural selection__________ The process that lets individuals that are better adapted to their habitat survive and reproduce more successfully than others. Examples: “Survival of the Fittest” 9.__antibiotics__________ Medicine used to kill bacteria. 10._species__________ Organisms that are closely related and can mate to produce fertile offspring. 11._speciation__________ The formation of a new species when a single population evolves into 2 populations that cannot interbreed. This may occur due to geographic isolation or other changes in the environment. 12.__camouflage_________This type of adaptation allows individuals to blend-in to their environment thus providing safety from predators. Ex: moths in the pre-industrial and postindustrial forest. 13.__binary fission________ Asexual reproduction- single celled organisms split into two cells of the same size. 14._host_________ An organism from which a parasite or virus takes food and shelter, often killing the organism. (These are needed for a virus to reproduce.) 15.__virus________ A microscopic particle that gets inside a host cell and destroys it. 16.__nitrogen fixation________ The process where bacteria take in nitrogen and change it to a form that plants can use. 17._lytic cycle_________ The process where viruses attack living cells and turn them into virus-making factories. The cell explodes (dies) and new viruses are released to attack more cells. True or False 1. ____True___________Viruses are not living however they still have genetic material such as DNA. 2. ____False___________Antibiotics help kill bacteria not virus that attack the body. 3. ____False___________Viruses are not cells so they cannot be prokaryotes. 4. List below one way bacteria is helpful and one way bacteria is harmful. Bacteria may cause disease but they help us in many ways…. Decomposers, help us make food and digest our food, nitrogen fixation 5.Study the shapes below: Which are viruses, protist or bacteria--- explain how you can tell other than size. a. _Protist_____ b. ___bacteria__ c. __virus_____ d. ___protist_________ e__virus__________ has nucleus ___ has no nucleus_______space ship shape___ has nucleus ______ _crystal_____ 6. Create a Venn diagram comparing and contrasting bacteria and viruses. You will need at least 12 total items. Bacteria: always one cell, no nucleus, no membrane bound organelles, circular DNA, decomposers Virus: not a cell, protein coat, lytic cycle, requires a host cell to reproduce, does not do basic metabolic activities (eat, grow, excrete) Protist: Largest of these 3, eukaryote, nucleus, organelles, one or more cells, DNA in nucleus All: have DNA, have some members that cause disease