Chemistry Practice Final Exam
advertisement

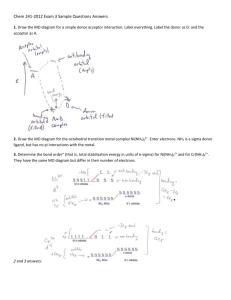
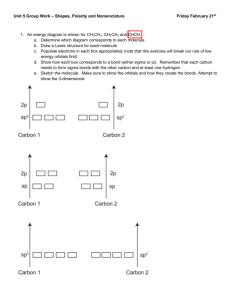
Practice Final Exam If you need, look up at the note on the bottom of the last page. 1. Answer the terms, elements, and numbers that fit in to the following definition. a. _________________________: energy due to position or composition. b. _________________________: an element which has the configuration, [Xe]6s24f55d0. c. _________________________:the number of waves per second that pass a given point in a space. d. _________________________:consists of system and surroungings. e. _________________________:the maximum number of electrons in an atom that has n=4 and ms= +1/2. f. _________________________:6.626 x 10-34・s g. _________________________: the electrons in the outermost principal quantum level of an atom. h. _________________________:the configuration of Cu. i. ________________________:partial pressure of vapor that exists above a liquid or solid. j. _________________________: reactions that absorb energy from the surroundings. k. _________________________: the unit for specific heat capacity (c). l. _________________________: ions containing the same number of electrons. m. _________________________: Psoln = χsolvent Posolvent 2. Calculate the work associated with the expansion of a gas from 24L to 72L at a constant external pressure of 1560. torr. Answer in J. 3. Calculate the energy required to excite the hydrogen electron from level n=1 to level 3. How long the wavelength of light must be absorbed by a hydrogen atom in its ground state to reach the excited state. 4. A 6.8g sugar cube (sucrose C12H22O11) is dissolved in 80oC water. When this solution’s molality is 2.42, what amount of water do you need? Answer in L. the density of 80oC water is 0.975g/mL. 5. Identify the most important types of interparticle forces present in the solids of each of the following substances. a. H2O: _________________________ b. NaCl: _________________________ c. NH3 : _________________________ d. I2: _________________________ 6. List the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity. H, Cl, F, K, O 7. List the following ions in order of increasing size. Se2-, Sr2+, Rb+, Sb5+, Br-, In3+, Sn4+ 8. List the following elements in order of increasing ionization energy. He, F, S, Te, Sr, O, Cl 9. Which central atom has the hybridization dsp3? a. CaCl2 b. HCl c. ClF3 d. IF5 e. CH4 10. Calculate the energy and frequency of red light having a wavelength of 6.80 x 10-5cm. 11. Write the orbital diagrams for Cu. 12. A sample solution contains 91.6g of sodium hydroxide and 750.mL of water. Assume the density of the water is 0.995g/mL. a) What is the molality of sodium hydroxide in this solution? b) What is the percent by mass of sodium hydroxide in this solution? c) What is the mole fraction of sodium hydroxide in this solution? 13. What is the molar mass and molecular formula of a nondissociating compound whose empirical formula is C4H2N, if 3.84g of the compound in 500.g benzene give a freezing point depression of 0.307oC? the molal freezing point depression constant for benzene is 5.12oCkg/mol. 14. Calculate ΔHrxn for 2NOCl(g) → N2(g) + O2(g) + Cl2(g) Given; 1/2N2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) → NO(g) NO(g) + 1/2 Cl2 → NOCl (g) ΔH= 90.3 kJ ΔH= - 38.6kJ 15. Complete the following table. Molecule SF6 PBr3 ClF3 # total valence e-s Lewis Dot Structure Bond angle Total # of e-pairs around the central atom Molecular geometry Hybridization 3D picture of the molecule (indicating hybridization) 16. An aluminum ball at a temperature of 35.8 oC is dropped a beaker of water with a mass of 26.4 g and at a temperature of 80.1 oC and the temperature the aluminum and water reaches 72.8oC. Assume no heat transfer to or out of the beaker. Calculate the mass of the aluminum ball. 17. Calculate ΔHo for the following reaction. 2NaOH(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) → NH3(aq) + H2O(l) + NaCl(aq) 18. At 20oC, the vapor pressure of benzene (C6H6) is 75 torr, and that of toluene (C7H8) is 22 torr. Assume both form an ideal gas solution. What is the mole fraction when a vapor pressure of the solution is 40.torr at 20.oC. <note> Specific heat capacity; water: 4.18J/oC·g, aluminum: 0.089J/oC·g ΔHof(kJ/mol); NaOH(aq): -470, NaOH(s): -427, NaCl(aq): -407, NaCl(s): -411 NH4Cl(aq): -300, NH4Cl(s): -314, NH3(aq): -80, NH3(g): -46, H2O(g): -242, H2O(l): -286