Acids & Bases Worksheet: Reactions, Definitions, Tests
advertisement

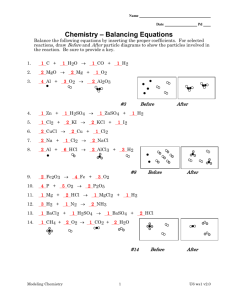
Properties of acids & bases 1. Give the equation for the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl(aq), and: (a) potassium hydroxide solution, KOH(aq). _____________________________________________________________________________________ (b) ammonia, NH3(aq). _____________________________________________________________________________________ (c) copper(II) oxide, CuO(s). _____________________________________________________________________________________ (d) sodium hydrogen carbonate, NaHCO3(s). _____________________________________________________________________________________ (e) calcium carbonate, CaCO3(s). _____________________________________________________________________________________ (f) zinc metal, Zn(s). _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Distinguish between the terms base and alkali. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Describe two different test-tube reactions to illustrate that a solution of sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq) is basic. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Give the equation for the reaction which occurs when solid ammonium chloride, NH4Cl(s) is heated with potassium hydroxide solution, KOH(aq). _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. The image below shows the colour of universal indicator paper at different pH values. (a) Deduce the approximate colour when a strip of the indicator paper is placed in a dilute solution of ammonia. ____________________________________________________________________________________ (b) If nitric acid is added in excess to this solution how would you expect the colour of the indicator paper to change? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 6. State the equation for the reaction between magnesium oxide, MgO(s) and sulfuric acid, H2SO4(aq). _____________________________________________________________________________________ Answers 1. (a) HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + H2O(l) or H+(aq) + OH–(aq) → H2O(l). (b) HCl(aq) + NH3(aq) → NH4Cl(aq) or H+(aq) + NH3(aq) → NH4+(aq) (c) 2HCl(aq) + CuO(s) → CuCl2(aq) + H2O(l) (d) HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(s) → NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) or H+(aq) + HCO3–(aq) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) (e) 2HCl(aq) + CaCO3(s) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) or 2H+(aq) + CO32–(aq) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) (f) 2HCl(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) or 2H+(aq) + Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) 2. A base is a substance than can neutralise an acid. An alkali is a soluble base. 3. (i) Add a dilute acid, such as hydrochloric acid, to the sodium hydroxide solution. Universal indicator paper (or another indicator such as phenolphthalein) or a pH meter can be used to show the pH moves from above 7 to below 7 as the sodium hydroxide solution is first neutralised then the acid is present is excess. (ii) Add the sodium hydroxide solution to solid ammonium chloride and warm. The smell of ammonia being evolved will be noticed. 4. NH4Cl(s) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + NH3(g) + H2O(l) or NH4+(s) + OH–(aq) → NH3(g) + H2O(l) 5. (a) Green/blue as the pH will be about 8-10 depending upon the concentration of the ammonia. (b) Change to red/pink as the pH will drop to about 3 or slightly less depending upon the concentration of the acid. 6. MgO(s) + H2SO4(aq) → MgSO4(s) + H2O(l)