lab 6-1 - SaddleSpace/Haiku
advertisement

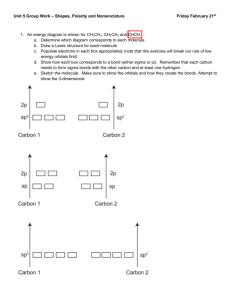
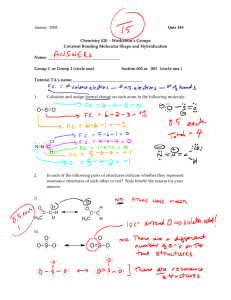
Honors Chemistry Name ________________________ Per ______ Date ________________ Lab 6-1: Molecular Theories and Shapes Background: Using VSEPR, shapes of molecules can be predicted because electron pairs (sigma bonds and nonbonding electron pairs) want to arrange themselves as far apart as possible. Hybridization theory predicts that hybridized atomic orbitals, which can either form sigma bonds or hold nonbonding electrons, will orient themselves so that they also have a maximum separation. Hybridization of a central atom can be determined by counting sigma (single) bonds + nonbonding electron pairs. Bonds + pairs 2 3 4 5 6 hybridization sp sp2 sp3 sp3d sp3d2 Purpose: you will use VSEPR and hybridization theory to explain various molecular geometries and also to determine the shape of several molecules. Materials: computer with access to Internet, brain Procedure: 1) Copy the charts in the data section into your lab book. Leave enough space for drawings were indicated. 2) On the day of the lab, you will access: https://s3.amazonaws.com/files.haikulearning.com/data/SaddleSpace/minisite_2605037/7eb2366468/index. html or find the link on my Haiku website. 3) On the day of the lab, complete Charts 1 & 2 (NOTE: not all of the molecules you need to identify will be on the computer). Also, obtain Lab 6-1, sheet 2 from your instructor. Copy the formulas for the unknown molecules onto your data chart (Chart 3) and complete the rest of the chart using the information you just completed. BE AS PRECISE AS POSSIBLE. 4) Hitting the escape (Esc) key will stop the molecule from rotating. To restart the molecule, use the Reload or Refresh option from the menu bar. 5) NOTE: Ideal bond angles are 90o, 109.5o, 120o, and 180o ONLY 6) Exit all programs and shut down the computer. Complete the conclusion questions. Data: NOTE: A = central atom X = atom bonded to central atom e = nonbonding electron PAIR around central atom Copy the following data charts into your lab notebook. Chart 1 (Use a whole page in your notebook) Molecule Type AX2 AX2-e AX2-2e AX2-3e AX3 AX3-e AX3-2e AX4 AX4-e AX4-2e AX5 AX5-e AX6 Chart 2 Molecule Type AX2 AX2-e AX2-2e AX2-3e AX3 AX3-e AX3-2e AX4 AX4-e AX4-2e AX5 AX5-e AX6 Shape (name) Drawing Ideal Bond Angle(s) Hybridization around central atom Chart 3 (use a whole page in your notebook) See Sheet 2 Formula of Molecule Lewis Structure (Drawing) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) Shape (name) Conclusions: 1) Assuming that all bonding atoms (X) are the same and that all bonds between A and X are polar, which type of molecules (Chart 2) would be polar? 2) Predict the shapes of the following molecules: (HINT: count sigma bonds and nonbonding pairs, then determine the hybridization of the central atom) a) AX3-3e e) AX-4e b) AX-e f) AX-5e c) AX-2e g) AX2-4e d) AX-3e 3) What effect do nonbonding electron pairs around the central atom have on the actual bond angles? 4) Why can atoms in the third row form expanded octets, while elements in the second row cannot? Honors Chemistry Name ________________________ Per ______ Date ________________ Lab 6-1: Sheet 2 1) H2S 2) BeF2 3) SF6 4) SCl4 5) XeF2 6) GeF2 7) CCl4 Honors Chemistry 8) NH3 9) SO3 10) PF5 11) XeCl4 12) ClF5 13) ClF3 Name ________________________ Per ______ Date ________________ Lab 6-1: Sheet 2 1) H2S 2) BeF2 3) SF6 4) SCl4 5) XeF2 6) GeF2 7) CCl4 Honors Chemistry 8) NH3 9) SO3 10) PF5 11) XeCl4 12) ClF5 13) ClF3 Name ________________________ Per ______ Date ________________ Lab 6-1: Sheet 2 1) H2S 2) BeF2 3) SF6 4) SCl4 5) XeF2 6) GeF2 7) CCl4 8) NH3 9) SO3 10) PF5 11) XeCl4 12) ClF5 13) ClF3