Networking Fundamentals 2
advertisement

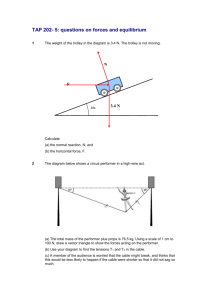
Networking Fundamentals Review Questions Page 101 1. _____ Signals are sent through copper core cable as pulsating electrical energy. 2. Pulsating light waves are commonly sent through _____ cable. 3. Wireless technology commonly transmits _____ waves, _____ waves, and _____ through the atmosphere. 4. What are the two types of electrical signals? 5. Time affects the degree of the slope in a(n) _____ signal. 6. Time affects the duration of the voltage level in a(n) _____ signal. 7. How often an analog or digital cycle repeats in one second is called _____. 8. Frequency is measured in _____ and is represented by the abbreviation _____. 9. How many times does an analog cycle repeat in a 2.3kHz electronic signal? 10. How many times does a digital cycle repeat in a 10MHz electronic signal? 11. What is attenuation? 12. Noise and crosstalk are types of _____. 13. What is latency? 14. A method of transmitting data in the form of a digital signal, using the entire bandwidth of a cable is called _____. 15. A method of transmitting data in the form of several analog signals at the same time is called _____. 16. List the three modes in which communication can occur. 17. What is the difference between half-duplex and full-duplex communication? 18. _____ is opposition to current flow in a DC circuit, and _____ opposition to current flow in an AC circuit. 19. The size of a conductor’s diameter is described by what rating? 20. Which conductor is larger, one that has a 22AWG rating or one that has 24AWG rating? 21. RG-58 is also referred to as _____. 22. List the following characteristics of a 10Base2 network: topology, cable type, connector type, maximum segment length, minimum cable length, and data rate. 23. Explain the 5-4-3 rule and list the 802.3 classifications to which it applies. 24. List the following characteristics of a 10BaseT network: topology, cable type, connector type, maximum segment length, minimum cable length, and data rate. 25. What will happen to an electronic signal in a 10BaseT network if it passes through more than four hubs? 26. What is the term used for a circuit path that is shorter than its intended path? 27. What is the term used for an incomplete circuit path? 28. What is the term used to describe a wire that comes in contact with a metal enclosure that is touching the earth? 29. Name three possible cable problems that might result from improperly wiring twisted cable pairs. Answers: 1. Electronic 2. Fibre-optic cable 3. Pulsating, radio, micro and infrared light, waves 4. Analog and digital 5. Analog 6. Digital 7. Frequency 8. Hertz, Hz 9. 2300 cycles 10. 10 times 10 to the power of 6, cycles 11. All electronic signals degenerate or lose amplitude, over long distances. The loss of signal strength is referred to as attenuation. 12. Interference 13. Latency is the amount of time is takes a signal to travel from its source to its destination. 14. Baseband transmission 15. Broadband transmission 16. Simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex 17. Full duplex: a communication mode in which bi-directional communication occurs simultaneously Half duplex: a communication mode in which bi-directional communication occurs in one direction at a time. \ 18. resistance, impedance 19. AWG rating 20. The smaller the number the larger the diameter of the wire: hence a 22AWG conductor is larger than a 24 AWG rated conductor. 21. Thinnet 22. 10Base2: Topology: bus Cable- type:RG-58 \ Thinnet Connector- type: IEEE 802.3 Maximum segment length:185 m Minimum cable length: .5 m Data rate:10Mbps 23. A 10Base2 network must follow the 5-4-3 rule. This rule states that a 10Base2 network can have a total of 5 segments, 4 repeaters, and 3 segments that are connected to the computers. The rule was developed to limit signal latency. Both the 10Base2 and 10Base5 classifications follow this rule. 24. 10BaseT: Topology: star Cable- type: category 3, 4 or 5 cable Connector- type: IEEE 802.3 Maximum segment length:100 m Minimum cable length: .6 m Data rate:10Mbps 25. The latency of the signal becomes excessive and causes the electronic signal to exceed its TLL setting. The electronic signal is then destroyed. 26. In cabling, when two conductors are improperly connected and result in a shorter circuit path, it is known as “short”. When a “short” occurs in a network cable, data takes a shorter route and does not reach its destination. 27. An incomplete circuit is known as an “open” circuit, because there is an open spot along the length of the conductor. When an “open” occurs in a network system, no data can travel past the point of open. 28. A “ground” occurs when a conductor connects to the earth through a continuous path. When a “ground” occurs in a network cable, all data is prevented from reaching its destination. 29. Reversed pair: a wiring fault in which conductors within a twisted pair cable pair reverse their connection at the opposite end of the cable. Crossed pair: a wiring fault in which two pairs within a twisted pair cable have switched positions at the opposite end of the cable. Split pair: a wiring fault in which one conductor from each of two pairs within a twisted pair cable have switched positions at the opposite end of the cable.