Practice Exam 4- Equine Respiratory System Answer Key
advertisement
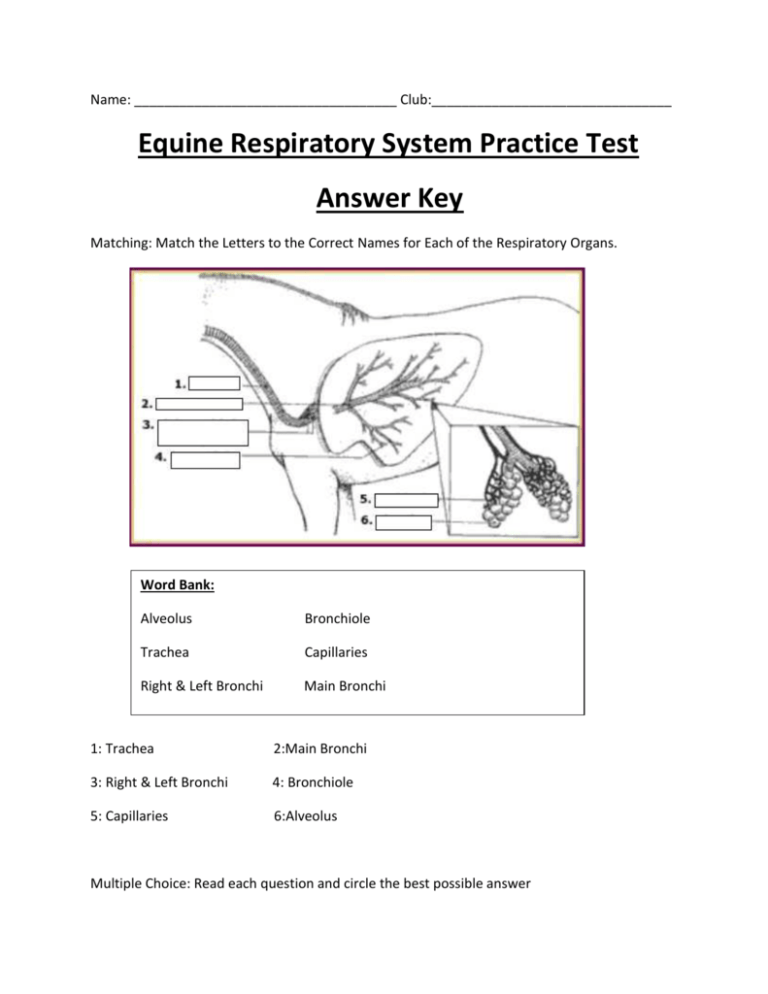
Name: ___________________________________ Club:________________________________ Equine Respiratory System Practice Test Answer Key Matching: Match the Letters to the Correct Names for Each of the Respiratory Organs. Word Bank: Alveolus Bronchiole Trachea Capillaries Right & Left Bronchi Main Bronchi 1: Trachea 2:Main Bronchi 3: Right & Left Bronchi 4: Bronchiole 5: Capillaries 6:Alveolus Multiple Choice: Read each question and circle the best possible answer 7.) What is the normal respiration rate of a horse? a. 8-16 bpm b. 10-20 bpm c. 5-14 bpm d. 30-40 bpm 8.) Which of the following does NOT affect respiration rate? a. Illness b. Gender c. Environmental Temperature d. Exercise 9.) The trachea is formed from partial cartilage rings and it contains tiny hair like structures called cilia inside it. What is the purpose of cilia? a. They help to warm and humidify the air before it reaches the lungs b. They help trap foreign objects and beat them into mucus which is then expelled from the track c. They help move food down the horse’s throat d. They serve no purpose 10.) Which of the following is NOT a function of the equine respiratory system? a. Vocalization b. To transport oxygen molecules and oxygenate the blood c. To help regulate body temperature d. Fight infection 11.) How many lobes does the right lung contain? a. 1 b.2 c.3 d.4 12.) How many lobes does the left lung contain? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 13.) Out of all the functions of the equine respiratory system which is the PRIMARY function? a. Vocalization b. To transport oxygen molecules and oxygenate the blood c. To help regulate body temperature d. There is no primary function, they are all of equal importance Fill in the Blanks: Write a word in the blank that correctly completes each statement. Respiration is the movement of air into and out of the lungs. This movement of air is compelled by contractions of the horse’s chest muscles including the Diaphragm, a sheet of muscle at the bottom of the ribcage, and the Intercostal muscles, muscles in between the ribs. The respiratory system begins at the Nostrils where air is taken in through Inspiration, aka breathing. The air then passes through the Larynx, which helps to direct airflow and prevent foreign particles from entering the tract. It also contains vocal cords that allow the horse to vocalize. After passing through the Larynx (same as previous) air travels down the Trachea to the lungs. This cartilaginous, ringed tube then divides into 2 (#) Bronchi for the right and left lungs. These continue to get smaller turning into Bronchioles and then to Alveolus where blood oxygen exchange occurs. The Alveoli are little air sacs within the lungs. The respiratory system works closely with the Cardiovascular system. Information source: http://www.thebige.com/fair/agriculture/documents/08ag4hhorserespiratorysystem.pdf http://www.equinecentre.unimelb.edu.au/_images/health_resp_preventing_fig1.gif











