resiratory overview-
advertisement

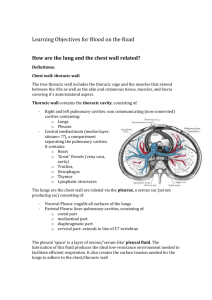
Overview of Respiratory System Dr. Ashraf Hussain Functions • Breathing • Protection of vital organs • Conduit: esophagus, vagus nerves, thoracic duct, phrenic nerve trachea, thoracic aorta, superior vena cava Primary modes of confirming death • Respiration • Heart sound • Pulse “…I know when one is dead, and when one lives. She is dead as earth. Lend me a looking glass. If that her breath will mist or stain the stone, why then she lives” King Lear; Act V, Scene III William Shakespeare Learning Objectives • Demonstrate an understanding of the terminology used to describe the structure and function of the respiratory system and respiratory apparatus. • Describe the gross organization and orientation of the trachea, bronchi and lungs within the chest and their inter-relationships with the pleural cavities, with the heart & pulmonary vessels, and with the other major structures within the mediastinum. • Identify and describe the gross features of the chest wall trachea, bronchi, lungs, pleura and pleural cavities. • Demonstrate an understanding of the mechanics of respiration. Overview of respiratory tract Upper Respiratory System Nasal Cavity Pharynx Lower Respiratory System Larynx Skeleton of Larynx Laryngoscopy Trachea Trachea Tracheostomy Tracheostomy The trachea and main bronchi viewed from the front Bronchi Bronchioles and Alveolus The Lungs Roots of the Lung The Pleura & Pleural Cavities Lines of pleural reflection parietal pleura Bony Thorax (Thoracic Cage) • The thoracic cage is composed of the thoracic vertebrae dorsally, the ribs laterally, and the sternum and costal cartilages anteriorly Ouch. Rib fractures take about six weeks to heal, and there's not much you can do about them. Intercostal spaces Cervical rib Pneumothorax pneumothorax The subdivisions of the mediastinum The diaphragm Movements of The respiration Normal and paradoxical movements of diaphragm Increase in lateral dimension by false ribs Increase in superoinferior dimension by diaphragm Thank you