Module A.1 Review
advertisement

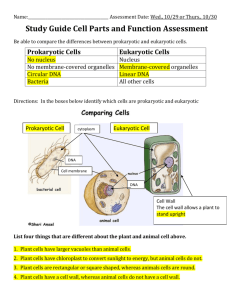
Name_________________________ Keystone Biology Module A.1 Review 1. What are the 7 characteristics of living things? 1. Order 2. Growth and development 3. Homeostasis 4. Metabolism 5. Response to a stimulus 6. Reproduction 7. Evolutionary adaptation 2. Define each of the 7 characteristics from question 1. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. Give an example of a living thing portraying each of the 7 characteristics of life. Order=cells Growth and development=zygote to a human baby Homeostasis=maintaining body temperature Metabolism=digesting food Response to a stimulus=plants growing towards sunlight Reproduction=bacteria dividing Evolutionary adaptation=echolocation in dolphins 4. What are the levels of organization of a multicellular organism? Atom, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism 5. Give an example of how the structure of each level would fit the function of that level for a human (may want to use ideas from your poster for this one). 1 ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 6. What are 4 parts that EVERY cell has? Cytoplasm, cell (plasma) membrane, genetic material (DNA) and ribosomes 7. What are the two major groups of cells on earth? Prokaryotic and eukaryotic 8. What is the primary difference between these two types of cells? Prokaryotic cells lack membrane bound organelles and a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles and a nucleus. Also, eukaryotic cells are much larger and have linear chromosomes; whereas, prokaryotic cells are much smaller and have circular chromosomes. 9. Why are all cells microscopic? Cell are microscopic because it allows them to remain efficient in exchanging nutrients and waste with their environment. If they were too large they would not be able to bring in enough nutrients to keep up with their needs. 10. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Why are prokaryotic cells much smaller than eukaryotic cells? ________________________________________________________________________ 11. What allows eukaryotic cells to be much larger than prokaryotic cells? 2 Eukaryotic cells can be much larger because they have each job compartmentalized into different organelles. This makes them more efficient. 12. Identify the function of each part of a prokaryotic cell listed below: a. Pilus Structure on the outside of a prokaryotic cell that anchors to surfaces and other cells. b. Flagellum Whip-like structure used in movement of a cell. c. Capsule Covering of a prokaryotic cell that protects the cell from threats in its environment. d. Cell wall Layer just under the capsule that also provides protection but gives the cell shape and support as well e. Ribosome Small structures in the cell that make all the proteins of the cell f. Nucleoid Region of the cell where the DNA is located g. Plasmid Small, circular pieces of the DNA that are picked up from other cells or the environment that contain genes to help a prokaryotic cell h. DNA Genetic material of the cell, NOT covered by a nucleus and contains all the instructions needed to run the cell 13. Identify the function of each part of an animal cell listed below: a. Nucleus 3 Region of the cell where the chromatin (DNA) is located. Carries instructions to run the cell. Membrane that surrounds it is called the nuclear envelope, also contains the nucleolus. b. Chromatin DNA of a eukaryotic cell. DNA contains instructions to build all proteins therefore running the cell. c. Cytoskeleton Proteins in the cell that give a eukaryotic cell both its shape and its structure. d. Cell membrane Barrier between the cell and its external environment. Exchanges materials with between the environment and the cell. e. Golgi body Flattened membrane sacs that are stacked on each other. Receives products (proteins, lipids) from rough ER and modifies, packages and ships them to their destination. f. Lysosome Membrane sacs in the cell filled with digestive enzymes in the cell that break down food and any unwanted objects. g. Centrosome with centrioles Structure in cells that makes and organizes the cytoskeleton. Animal cells only have centrioles h. Mitochondrion Membrane structure in the cell that carries out cellular respiration, which makes almost all the ATP (energy) for the cell. i. Smooth ER Folded membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus and has NO ribosomes. Responsible for making lipids (fats, steroids, phospholipids) that the cell needs. 4 14. Identify the function of each part of the plant cell listed below: a. Nucleolus Darker portion of the nucleus that makes ribosomes b. Ribosome Structures in the cell that are in the cytoplasm or bound to ER that build proteins. c. Rough ER Folded membrane structure just outside the nucleus that has ribosomes and makes proteins that will leave the cell. d. Cell wall Structure outside the cell wall that provides protection, support and shape for a PLANT cell e. Chloroplast Membrane bound structure found ONLY in PLANT cells that performs photosynthesis f. Central vacuole Large vacuole in PLANT cells that stores large amounts of water. Helps give the cell shape and structure. g. Cell membrane Barrier between the cell and its external environment. Exchanges materials with between the environment and the cell. h. Chromatin DNA of a eukaryotic cell. DNA contains instructions to build all proteins therefore running the cell. 15. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. 5 16. Complete the following table comparing a prokaryotic, animal and plant cells. Characteristic Nucleus and organelles Ribosomes Prokaryotic X Animal Plant X X X X Cell wall X Cell membrane X X X DNA X X X X X LARGER LARGER Cytoskeleton Size of cell Chloroplast SMALLER X X 6