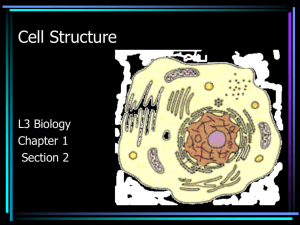
Cell structure and Fx pt 1
advertisement

Cell Presentations Part 1 Why does life require cells? How are cells organized? What is the advantage to having organelles? How do the interactions of cellular components allow for life processes? Cell Theory: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ What are the benefits & problems of the 2 different kinds of microscopy _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ How Big Are Cells? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ There are physical constraints on cell size: Too small: Can't fit all the stuff inside Too big: Can't exchange matter with the environment efficiently. Surface area increases ______________________________________________________________________________________ Two Major Cell Types: 1. Prokaryotic "simpler" (no membrane bound organelles) smaller (typically 10-100 um) Much more abundant Draw a typical Procaryotic Cell: 2. Eukaryotic: lots of membrane bound organelles. larger (100 um - 1mm) 2 major types Diagram “Plant-like” Cell Diagram “ Animal-Like” Cell. Why organelles? By enclosing parts of the cell in membrane, eukaryotic cells___________________________________! Membranes isolate different areas of the cell, which allows the cell to have varied conditions in different regions for example _____________________________________________________________________ Membranes also provide surface for various reactions _____________________________________________ The specialization of cellular regions is what makes eukaryotic cells so much more complex than prokaryotic cells. Specialization is also a prerequisite for multicellular life (why?)_________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Explain: “So Many Compartments = So many options” _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ The Life of the Cell All cells must do the following things to stay alive: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Many cells will also do the following: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ PROTEINS: Proteins are the molecules that a cell uses to do most of its work. Here is a brief list of things that proteins do: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Recieve and send messages to the environment/other cells Recieve and send messages to other cells The instructions to build proteins are stored in DNA (we can call them "genes") THE NUCLEUS The nucleolus is the region of the nucleus where ribosomal RNA genes are concentrated. It can be seen under magnification as a dark spot on the nucleus. RIBOSOMES: Structure: a complex of RNA and protein. 2 subunits ("large" & "small"). Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger than prokaryotic ribosomes. Endoplasmic Reticulum: Structure: a network of membrane channels attached to the nuclear membrane. 2 kinds: rough: closest to nucleus, covered in bound ribosomes free: farther from nucleus, no bound ribosomes Function: Rough ER compartmentalizes the cell, provides structural support, & targeted protein synthesis. Smooth ER synthesizes lipids for the cell (for things like membrane), detoxifies compounds, breaks down glycogen. Plasma Membrane: A phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Function: Controls transport of matter into and out of cell. Receives/Sends messages with environment. Make Sure You Can: Explain the cell theory Compare different types of microscopy. Explain why there are no giant cells around. Refine your contrast of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Relate the structure and function of the organelles in this presentation. Explain the interactions of the organelles in this presentation. Explain how the organelles in this presentation provide for essential life processes.