Unit 4 Practice Problems Key Intermolecular Forces As volume
advertisement

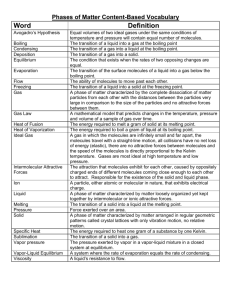
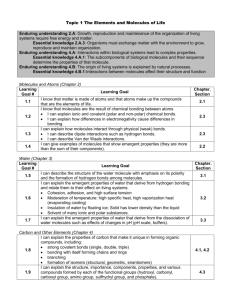
Unit 4 Practice Problems Key Intermolecular Forces 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. As volume decreases (pressure increase) and/or temperature decreases real gases act less ideally. CO2 is a nonpolar molecule with only weak LDF and therefore, would not experience as strong as IMF’s as SO2, which is a polar molecule with dipole-dipole interactions. In the decreasing volume of non-ideal conditions, the SO2 molecules would attract and their collisions with the container would be fewer and with 𝑃𝑉 less force causing the ratio to decrease. 𝑅𝑇 High pressure is generated by crowded molecules where the volume of empty space (Videal) is significantly less than 100 % of the total volume. The gas molecules themselves take up an increasing proportion of the 𝑃𝑉 volume. The ratio would increase. 𝑅𝑇 Close to boiling point (very cold temperatures << 0ºC), molecules slow down and clump and collide less often, which generates less pressure Preal < Pideal Dipole-Dipole d Pair H2O & H2S Dispersion b H-bond a ion-dipole c Justification H-bonding > dipole-dipole forces Ne & Kr 6. 7. 6. Both LDF, Greater atomic mass LDF for Cl2 weaker and dipole-dipole Cl2 & SO2 for SO2 Propanol molecules H-bond, which is a stronger attraction then ethyl methyl ether's dipole forces. H2= none, H2S= dipole-dipole, CHF3= dipole-dipole, NH3= H-bonding. 15. At constant pressure and increasing temperature; solid changing to liquid (melting) and liquid to gas (vaporization). 16. solid 17. 0.01ºC. 18. 0ºC 19. Above this temperature and pressure the gas and liquid phase are indistinguishable, called supercritical fluid. 20. a) b) 21. Can liquid CO2 exist at room pressure? no What happens to CO2(s) at -78.5oC? b) c) 8. a) b) c) d) e) 9. 10. 11. 12. 55 ºC 90ºC the phase changes 5.11 atm What is the critical temperature for CO2? 31.1 oC 22. Water boils when vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure. As air is pumped out of the bell jar, its pressure decreases until it reaches the vapor pressure. 23. Water boils at a lower temperature at high altitudes, which means that water based foods cook slower because they cook at the boiling point. 24. 𝑞 = 𝑚𝐶𝑝 ∆𝑇 10𝑔𝐻2 𝑂 × 10𝑔𝐻2 𝑂 × 18.02 𝑔 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. × 6.01𝑘𝐽 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 3.34𝑘𝐽 (10.0𝑔)(4.18 𝐽/𝑔𝐶)(100𝐶) = 4180𝐽 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 18.02 𝑔 𝑞 = 𝑚𝐶𝑝 ∆𝑇 25. . a) b) c) d) e) f) (10.0𝑔)(2.09)(5𝐶) = 104.5𝐽 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑞 = 𝑚𝐶𝑝 ∆𝑇 𝑞 = 𝑚𝐶𝑝 ∆𝑇 = (2.0 𝑔)(. 565 𝐽 ∙ 𝑔/𝐶)(25𝐶) = 𝟐𝟖. 𝟐𝟓 𝑱 𝑞 = 𝑚𝐶𝑝 ∆𝑇 = (2.0 𝑔)(. 565 𝐽 ∙ 𝑔/𝐶)(−20𝐶) = − 𝟐𝟐. 𝟔 𝑱 KE remains constant KE increasing Segment D-E is longer than segment B-C a) sublimation b) vaporization c) condensation d) solidification e) deposition f) melting (enthalpy of fusion) 13. gas 14. At constant temperature the pressure is increasing; gas changing to a solid (deposition), then solid changing to a liquid (melting). solid What is the triple point pressure for CO2? 7. Q-R is liquid only, R-S is phase change, S-T is gas only. As heat is absorbed the KE of the molecules in increasing. The molecules are undergoing a phase change, vaporization ∆𝐻𝑣𝑎𝑝 = 40.7 𝑘𝐽/𝑚𝑜𝑙 sublimates Which is the most dense phase for CO2? NaCl is ionic bonding, therefore; it would have the highest heat of vaporization. H2O and HF use Hbonding, HF is more polar because F is more electronegative than O. HF would have the higher heat of vaporization. a) The phase diagram for water shows that as the pressure increases the MP decreases, the slope of the line separating the solid and liquid phase is negative. Reason: water is unique in that the solid state is less dense than the liquid state. The solid/liquid line would have a positive slope. × 40.4𝑘𝐽 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 = 22.59𝑘𝐽 (10.0𝑔)(2.01 𝐽/𝑔𝐶)(5𝐶) = 100.5 𝐽 𝟑𝟎. 𝟑𝟐𝒌𝑱 𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 26.7 kPa 6.65 kPa 75ºC 26.7 kPa 118ºC temperature at which the vapor pressure is 1 atm or 101.2kPa g) approx. 72ºC h) approx. 116ºC i) 70ºC (remember boiling occurs when Pvap=Patm) j) approx. 20kPa water pentane First pentane would boil away, then tetrachloromethane and finally water. a) approx. 40kJ/mol, based on extrapolation of graph. b) All show dispersion forces c) As number of electrons increase “polarizability” of atom also increases, therefore the dispersion forces for I2 are stronger, more energy has to be absorbed to vaporize. a) H2O=H-bonding, all others dipole-dipole b) H2O has high Hvap, then drops down and climbs again for H2Te. c) The increase for the large molecules is a result of increasing LDF for the larger, more polarizable molecules. 32. 31. a) b) c) All have LDF present. ethanethiol is LDF only, ethane is LDF only, ethanol has H-bonding. False statement. Boiling is a phase change and doesn’t involve breaking the covalent intramolecular bonding. Only the IMF’s are broken during phase changes. The water molecules (H-bonding) are able to attract to the ethanol because it too has H-bonding, therefore “like dissolves like” is appropriate. The other nonpolar molecules (LDF) will dissolve in another nonpolar molecule. Molecular Crystal London forces Dipoledipole attractions NH3 Kr Hydrogen Bonds Metallic Bonds Ionic Crystal Ionic Bonds X X X KMnO4 X NaCl X SO2 X CO2 X C3H8 X CH4 X CH3Cl X HF C6H6 Network Solid Covalent Bonds X HCl F2 Metal X X NO X H2SO4 X WC X Si X SiO2 X C(graphite) X N2 X CH3OH X Ag X (C2H5)2NH X NaOH X Al X PCl3 X 33. Structural Unit Bond name Bond strength Melting point Solubility Conductivity Malleability Metallic ion metallic variable variable low high high Covalent Network atom covalent strong high low low low Molecular molecule molecular weak low variable low variable Ionic ion ionic strong high high low low 34. 35. a) SO2 forms dispersion and dipole forces between molecules whereas, SiO2, a covalent network solid, forms covalent bonds throughout. The stronger covalent bonds, which break during melting of SiO2, require more energy (higher temperature) to break. b) Liquid Cl2 is held together by dispersion forces, which although weak increase in strength as the number of electrons increases. Liquid HCl is held together by dipole forces in addition to dispersion forces, but the addition of dipole forces between HCl molecules must not make up for the fewer electrons around the HCl. c) The stronger ionic bond in NaCl is due to the smaller Na+ ion compared to K+, which allows the Cl- ion to get closer and strengthens the attraction between ions, making the NaCl bond stronger and the melting point higher than KCl. d) Si is a covalent network solid with strong covalent bonds between atoms. Cl2 has discrete molecules with weak London dispersion forces between molecules. Therefore, melting Si requires a higher temperature than Cl2.