Water cycle
advertisement

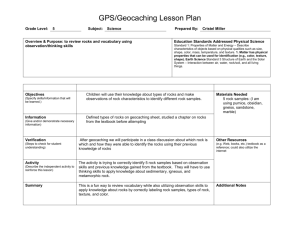
Bell work 10/28 Through which processes does water vapor enter the atmosphere? WATER CYCLE Interactions of Earth’s Systems Water Cycle ◦ The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth’s surface ◦ The sun provides the energy that drives the water cycle Evaporation ◦ Water absorbs thermal energy and becomes warmer ◦ Process by which a liquid turns into a gas Transpiration ◦ The process by which plants release water vapor through their leaves ◦ Respiration- organisms release water vapor when they breathe Condensation ◦ Temperatures in the troposphere decrease with altitude ◦ Process by which a gas changes to a liquid ◦ Releases thermal energy ◦ Clouds form when millions of water droplets come together Precipitation ◦ Moisture that falls from the clouds to Earth’s surface ◦ Snow, rain, sleet, or hail ◦ More than 75% falls into the ocean ◦ Water continuously moves between the hydrosphere, cryosphere, atmosphere, biosphere, and geosphere Water cycle contributes to the weather Weather- the state of the atmosphere at a certain time or place ◦ Temperature ◦ Air pressure ◦ Humidity- amount of water vapor ◦ Climate- The average weather pattern for a region over a long period of time Bell Work 10/29 How are transpiration and respiration similar? How are they different? Bell work 10/30 Give an example of how the water cycle impacts the rock cycle. ROCK CYCLE Interactions of Earth’s Systems Rock Cycle The series of processes that transport and change rocks into different forms Cooling and Crystallization ◦ When magma flows onto Earth’s surface it is called lava ◦ Mineral crystals form as magma cools changes the molten material into igneous rock Uplift ◦ The process that moves large bodies of Earth materials to higher elevations ◦ Ex: mountain building Weathering and Erosion ◦ Weathering- Things (Glaciers, wind, rain, organisms) break down rocks into sediment ◦ Rocks are exposed to the atmosphere, hydrosphere, the cryosphere, and the biosphere ◦ Erosion- Sediments are carried to new locations ◦ Deposition- Eroded elements are laid down (deposited) in new places ◦ Forms layers of sediment Compaction and Cementation ◦ As more layers are deposited, their weight pushes down on the bottom layers ◦ The deeper layers are compacted. ◦ Minerals dissolved in water crystallize between grains of sediments and cement them together produce sedimentary rocks High Temperature and Pressure ◦ Form Metamorphic rocks ◦ Happens deep within the Earth ◦ Then uplift brings the rocks to the surface ◦ Then rocks are broken down and continue moving through the rock cycle