Earth Science Definitions Match Words Definitions 1. Mineral A. An
advertisement
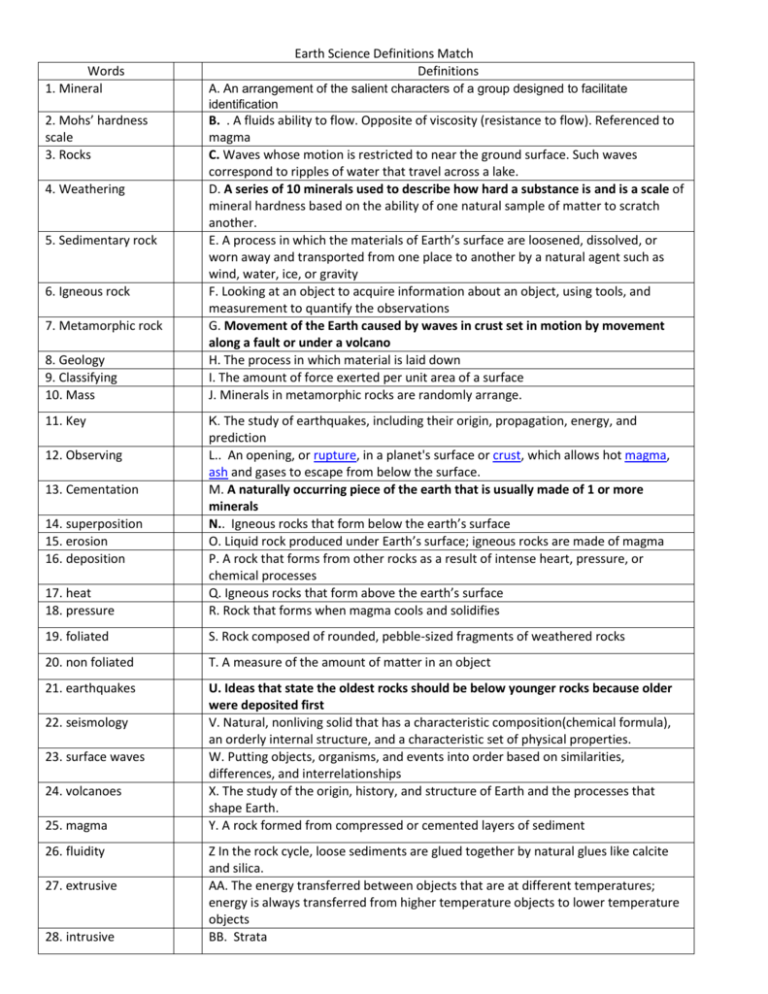
Words 1. Mineral Earth Science Definitions Match Definitions A. An arrangement of the salient characters of a group designed to facilitate identification 2. Mohs’ hardness scale 3. Rocks 8. Geology 9. Classifying 10. Mass B. . A fluids ability to flow. Opposite of viscosity (resistance to flow). Referenced to magma C. Waves whose motion is restricted to near the ground surface. Such waves correspond to ripples of water that travel across a lake. D. A series of 10 minerals used to describe how hard a substance is and is a scale of mineral hardness based on the ability of one natural sample of matter to scratch another. E. A process in which the materials of Earth’s surface are loosened, dissolved, or worn away and transported from one place to another by a natural agent such as wind, water, ice, or gravity F. Looking at an object to acquire information about an object, using tools, and measurement to quantify the observations G. Movement of the Earth caused by waves in crust set in motion by movement along a fault or under a volcano H. The process in which material is laid down I. The amount of force exerted per unit area of a surface J. Minerals in metamorphic rocks are randomly arrange. 11. Key K. The study of earthquakes, including their origin, propagation, energy, and 4. Weathering 5. Sedimentary rock 6. Igneous rock 7. Metamorphic rock 17. heat 18. pressure prediction L.. An opening, or rupture, in a planet's surface or crust, which allows hot magma, ash and gases to escape from below the surface. M. A naturally occurring piece of the earth that is usually made of 1 or more minerals N.. Igneous rocks that form below the earth’s surface O. Liquid rock produced under Earth’s surface; igneous rocks are made of magma P. A rock that forms from other rocks as a result of intense heart, pressure, or chemical processes Q. Igneous rocks that form above the earth’s surface R. Rock that forms when magma cools and solidifies 19. foliated S. Rock composed of rounded, pebble-sized fragments of weathered rocks 20. non foliated T. A measure of the amount of matter in an object 21. earthquakes U. Ideas that state the oldest rocks should be below younger rocks because older were deposited first V. Natural, nonliving solid that has a characteristic composition(chemical formula), an orderly internal structure, and a characteristic set of physical properties. W. Putting objects, organisms, and events into order based on similarities, differences, and interrelationships X. The study of the origin, history, and structure of Earth and the processes that shape Earth. Y. A rock formed from compressed or cemented layers of sediment 12. Observing 13. Cementation 14. superposition 15. erosion 16. deposition 22. seismology 23. surface waves 24. volcanoes 25. magma 26. fluidity 27. extrusive 28. intrusive Z In the rock cycle, loose sediments are glued together by natural glues like calcite and silica. AA. The energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures; energy is always transferred from higher temperature objects to lower temperature objects BB. Strata 29. conglomerate CC. Metamorphic rocks that are aligned or sorted into layers 30. rock layers DD. The natural process by which atmospheric and environmental agents, such as wind, rain, and temperature changes, integrates, and decompose rocks.











